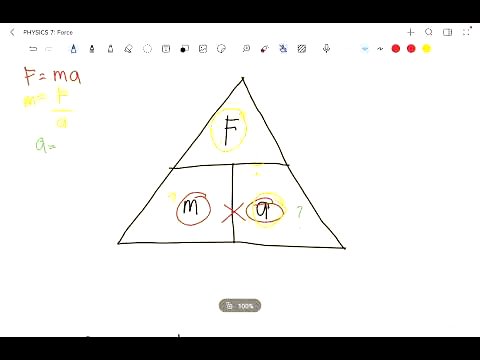
TLDR;
This video provides a comprehensive review of key environmental science topics for BA Programme B Honours Semester One students. It covers essential definitions, concepts, and issues, including land degradation, atmospheric layers, wetlands, nuclear energy, ozone depletion, tundra ecosystems, energy flow, and sustainable development goals. The lecture emphasizes practical understanding and application of these concepts, using real-world examples and addressing potential exam questions.
- Key environmental science topics explained with real-world examples.
- Focus on definitions, causes, impacts, and solutions for various environmental issues.
- Discussion of sustainable development goals and India's efforts towards achieving them.
Introduction [0:32]
The host, Sumit Kashyap, welcomes viewers to a class focused on important questions for the Environmental Science paper in the BA Programme B Honours Semester One. He emphasizes that the content is derived from various sources to provide a holistic view. The video aims to help students with last-minute preparations by covering key topics through important questions.
Holistic Notes and Graphical Design [4:33]
The instructor explains that the notes provided are designed to be helpful for both last-minute studying and throughout the semester. The content is graphically designed to enhance memory and interest, distinguishing it from typical textbooks. These notes are available for purchase in both English and Hindi mediums via a link in the description.
Defining Key Environmental Terms [6:08]
The lecture begins by defining several key environmental terms: land degradation, atmosphere, wetland, nuclear energy, ozone hole, and tundra ecosystem. Each term is explained in detail to ensure a clear understanding of its meaning and significance.
Land Degradation [6:50]
Land degradation is defined as the deterioration or reduction of soil quality due to factors like excessive farming, deforestation, overgrazing, pollution, water and wind erosion, chemical use, and urbanization. The causes and consequences of each of these factors are discussed, emphasizing the importance of soil testing and conservation.
Atmosphere and Its Layers [17:16]
The atmosphere is defined as the layer of air surrounding the Earth, essential for life and filled with gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. The lecture explains the different layers of the atmosphere: troposphere (Shobh Mandal), stratosphere (isotherm), mesosphere, thermosphere, and ionosphere. The characteristics and importance of each layer are detailed, including the role of the ozone layer in the stratosphere.
Wetland [25:19]
A wetland is defined as an area where the land is mostly moist or marshy, serving as a transitional zone between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Wetlands are crucial for climate change mitigation, flood control, water recharge, and environmental balance. Various types of wetlands, such as swamps, lakes, and ponds, are discussed, along with their ecological importance in supporting diverse species.
Nuclear Energy [33:03]
Nuclear energy is explained as the energy present within an atom's nucleus, obtainable through nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. Nuclear fission involves breaking a heavy element's nucleus, like Uranium-235, into smaller nuclei by hitting it with neutrons, releasing energy. This process is used in controlled nuclear reactors to produce electricity. Nuclear fusion involves combining lighter elements, like hydrogen, to form a larger nucleus, requiring extremely high temperatures.
Ozone Hole [46:52]
The ozone hole is described as an area in the Earth's atmosphere where the ozone layer is thin, particularly above Antarctica. This thinning allows harmful UV rays to penetrate, leading to skin cancer, eye diseases, and environmental imbalances. The lecture identifies CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) from refrigerators and ACs as major contributors to ozone depletion.
Tundra Ecosystem [53:07]
The tundra ecosystem is found in cold regions like the Arctic and alpine tundra, characterized by long winters, low rainfall, and permafrost. The flora includes moss, lichen, grass, and dwarf trees, while the fauna includes polar bears, arctic foxes, lemmings, and snowy owls. Climate change and human activities, such as oil and gas exploration, are damaging the permafrost, threatening the ecosystem.
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem [1:01:53]
Energy flow in an ecosystem is explained, starting with producers (plants) that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. The 10% rule is highlighted, where only about 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
Multiple Choice Questions [1:06:57]
Several multiple-choice questions are addressed, including whether mangrove forests can be found in Madhya Pradesh (false), whether biomedical waste is hazardous (true), and whether rubber resin is an example of non-timber forest products (true). The removal of the top layer of soil by wind and water is identified as soil erosion, not land degradation.
Ganga Action Plan and National Solar Mission [1:11:18]
Short notes are provided on the Ganga Action Plan (GAP), an initiative to clean the Ganga River, and the National Solar Mission, a part of India's action plan on climate change. The GAP, initiated in 1985, aims to reduce pollution in the Ganga, Yamuna and Gomti rivers. The National Solar Mission promotes solar energy technologies to ensure energy security and sustainable development, targeting 1 lakh MW by 2022.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [1:26:32]
A cheat code is introduced to remember the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), using the mnemonic "Useless Home on our Earth, there is a Earth far away More resourceful clean clear and Lalan is the top planet". Each letter corresponds to a specific goal, such as no poverty, no hunger, good health, quality education, gender equality, clean water, clean energy, decent work, infrastructure and industry, reduced inequalities, sustainable cities, responsible consumption, climate action, life below water, life on land, peace and justice, and partnership for the goals.
Sustainable Development Goal Number Seven [1:36:30]
Sustainable Development Goal Number Seven focuses on ensuring affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all. The main objectives include cheap and accessible energy, promotion of clean energy sources, energy efficiency, and reducing the impact on climate change.
Biogas vs. Petroleum [1:42:55]
The differences between biogas and petroleum are discussed. Biogas is a renewable energy source produced from organic matter, while petroleum is a non-renewable fossil fuel. Biogas has lower greenhouse gas emissions but also a lower calorific value compared to petroleum.
Landfill vs. Composting [1:54:46]
Landfill and composting are compared as waste disposal methods. Landfill involves burying waste, while composting is a natural process that uses microorganisms and earthworms to decompose biodegradable waste into nutrient-rich compost. Composting is more environmentally friendly and yields a useful product (fertilizer).
Industrial Waste vs. Agricultural Waste [2:01:07]
Industrial waste and agricultural waste are differentiated. Industrial waste includes unwanted substances from manufacturing and mining, often toxic and non-biodegradable. Agricultural waste consists of non-edible materials from farming, mainly organic and biodegradable.
Ecological Succession: Primary vs. Secondary [2:08:50]
Ecological succession is defined as the gradual change of an ecosystem over time. Primary succession begins in barren areas, like those created by lava flows, while secondary succession occurs in habitats where life previously existed but was recently destroyed.
Services Provided by Forest Ecosystems [2:18:53]
The various services provided by forest ecosystems are discussed, including biodiversity conservation, carbon storage, water filtration, soil regeneration, recreation, timber and non-timber products, and air filtration.
Environmental Studies as a Multi-Discipline Subject [2:25:49]
Environmental studies is presented as a multi-discipline subject, requiring expertise from various fields to tackle complex issues like water pollution. The contributions of chemical science, biology and botany, geology and hydrology, social science and economics, and legal and law aspects are highlighted.
Sustainable Water Management in Colleges [2:35:00]
A plan for sustainable water management in colleges is outlined, including rainwater harvesting, survey and identification of leakages, reuse of RO waste water, regular testing of waste water samples, and community participation.
Noise Pollution [2:47:35]
Noise pollution is discussed as a global public health threat, with long-term effects on human health. Sources of noise pollution in Indian cities include transportation, industrial activities, construction work, religious and social programs, and airplanes and trains.
Sustainable Development in India [2:52:58]
The lecture concludes by discussing sustainable development in India, highlighting the roles of NITI Aayog and the Ministry of Statistics in setting targets and collecting data. Various initiatives, such as broadband connectivity, new manufacturing policies, and the National Solar Mission, are mentioned as steps towards achieving sustainable development goals. The importance of environmental awareness and community participation is emphasized.