TLDR;
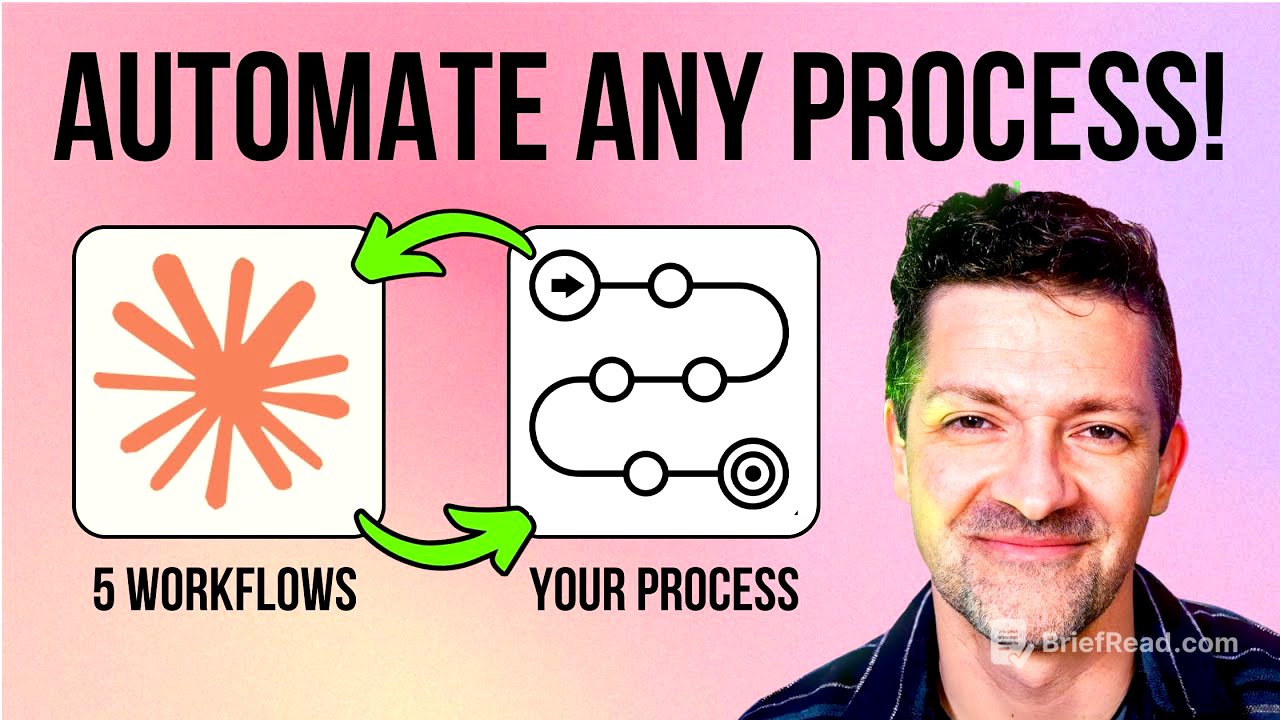
This video outlines a five-level framework for AI automation, starting from simple prompts and advancing to AI-integrated coding. It emphasizes the importance of simplicity, strategic prompt engineering, and the potential of AI-driven coding to transform ideas into reality. It also touches on the limitations of current AI agent technology and offers resources for further learning and coaching.
- Simple prompts can be surprisingly effective.
- Strategic prompt engineering, including the use of "big ass prompts" (BAPs), allows for greater control and specificity.
- Multi-step prompt sequences are useful for automating complex processes.
- AI agents and tool use are still in early stages of development and may not be as reliable as other methods.
- AI-integrated coding offers transformative potential for those willing to learn.
Simple Prompts and GPT for Sheets [0:00]
The video starts by highlighting the power of simple prompts in AI automation, using the example of GPT for Sheets. The author shares a personal experience where simple prompts outperformed complex ones, emphasizing that even basic instructions can yield significant results when used effectively. GPT for Sheets is introduced as a tool that allows users to leverage large language models for various tasks within spreadsheets, such as keyword analysis and chord extraction for songs. The author uses GPT for Sheets weekly for Patreon resource management, including generating descriptions and tags.
Big Ass Prompts (BAP) [2:55]
The video introduces the concept of "big ass prompts" (BAPs) for situations requiring more control and specificity. BAPs involve providing multiple examples to guide the AI, a technique known as few-shot training. The author uses BAPs to create newsletters by including examples of previous emails and the content of the guide. By separating the prompt from the context using quotation marks and utilizing the 01 pro mode, the author achieves high-quality results with minimal editing. BAPs are also valuable for maintaining consistent formats in legal documentation, market analysis, and other professional contexts.
Sequence of Prompts [4:34]
The video transitions to level three, focusing on sequences of prompts for automating processes that require multiple deliverables. The process involves documenting the process, converting it into a series of prompts, and then transforming those prompts into instructions for custom GPTs or cloud projects. The author demonstrates this by planning a professional meetup, using GPT-4o to create a step-by-step process, and then converting it into a prompt sequence. A custom GPT is used to generate instructions, which are then loaded into a new custom GPT to guide users through the steps of planning the event.
Tool Use and Agents [7:04]
The video addresses level four, which involves tool use and agents, but expresses reservations about their current reliability. While these tools can be useful for simple tasks like scraping websites or transferring data between applications, the author finds that agent swarms and autonomous agents often fall short of practical, consistent performance. The author notes that even major AI labs are still developing truly functional agents, citing examples like Chat GPT's research and operator tool. The author suggests caution when automating systems that require significant independent thinking, but mentions Anthropic's MCPS as a promising development for uniform tool control by large language models.
Code with AI Integration [9:30]
The video explores level five, which involves coding with AI integration, highlighting its transformative potential. The author references Peter Levels' work on projects like an advanced flight simulator and an AI photographer app, built using vibe coding. The author encourages viewers to reconsider coding, emphasizing that new tools have made it more accessible. The basic process involves using a large language model to determine software features and technologies, building core functionality, and adding features. The author recommends tools like Cursor, Replit, and Windsurf for building custom code to automate processes. The author emphasizes that these advanced techniques build upon the simple principles of prompt engineering covered earlier in the video.