TLDR;
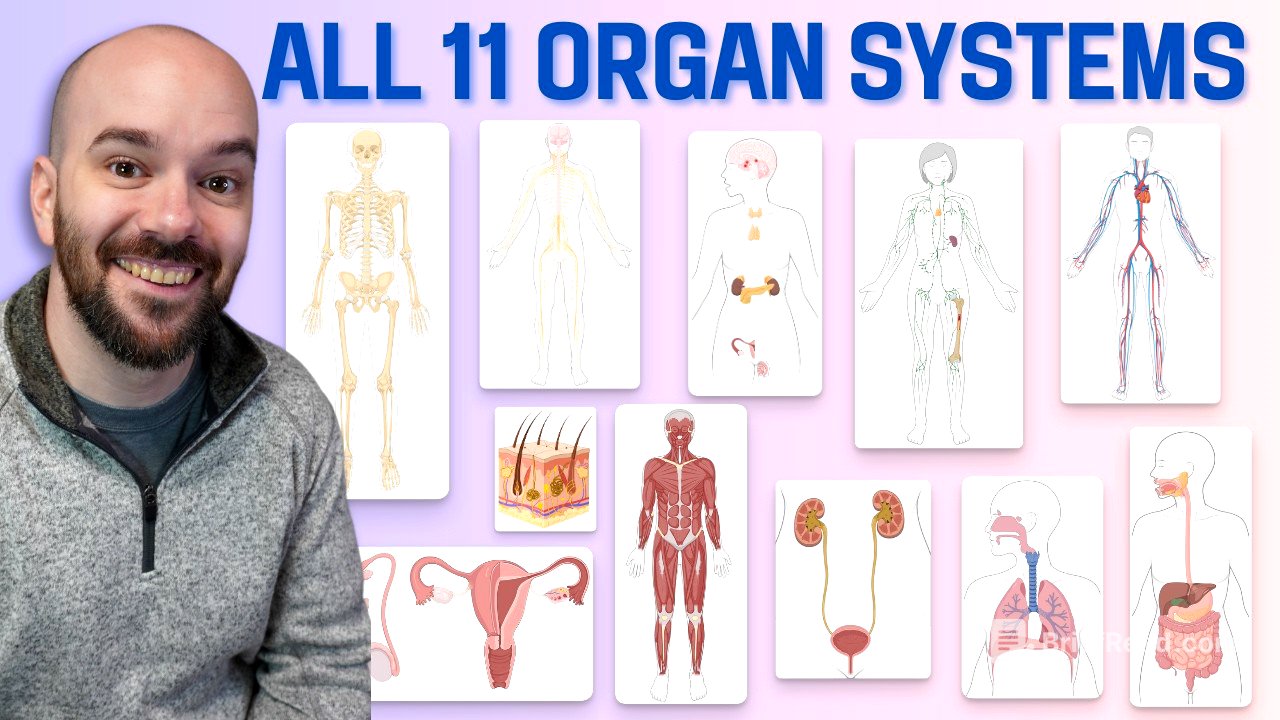
This video provides an overview of the 11 organ systems in the human body, categorized by function: support and movement, integration and coordination, transport, absorption and excretion, and reproduction. It details the organs within each system and their primary functions, offering a foundational understanding for anatomy and physiology students.
- Support and Movement: Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscular
- Integration and Coordination: Nervous, Endocrine
- Transport: Cardiovascular, Lymphatic & Immune
- Absorption and Excretion: Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary
- Reproduction: Reproductive
Systems Overview & Study Guide [0:00]
The video introduces the 11 organ systems to be studied, emphasizing the complexity and volume of information involved. A free downloadable study guide is mentioned, designed to aid learning through practice activities and exercises. The organ systems are categorized into five groups based on their primary functions: support and movement, integration and coordination, transport, absorption and excretion, and reproduction.
Integumentary System [1:35]
The integumentary system includes the skin, hair, and fingernails, with the skin being the primary organ. The functions of the skin can be remembered using the acronym PTSD: Protection against pathogens and UV radiation, Temperature regulation through sweat glands and blood flow, Sensation via nerve endings and sensory receptors, and Vitamin D synthesis using sunlight.
A&P Memory Lab Course [3:32]
The A&P Memory Lab is introduced as a five-week program designed to improve learning and retention of anatomy and physiology content. It focuses on teaching effective learning strategies to help students retain information and reduce study time. Participants also gain access to a full A&P curriculum with exclusive videos and practice resources.
Skeletal System [4:40]
The skeletal system includes bones and joints, with three types of joints: fibrous (immovable), cartilaginous (slightly movable), and synovial (highly movable). Ligaments connect bone to bone, providing joint stability. Functions of the skeletal system include structural support, acting as levers for muscles, protecting vital organs (e.g., skull protecting the brain, ribs protecting heart and lungs), producing blood cells in the bone marrow, and storing minerals like calcium and phosphate.
Muscular System [7:38]
The muscular system primarily consists of skeletal muscles and tendons, which connect muscles to bones. The main functions of the muscular system are movement, maintaining posture, and producing heat. Skeletal muscles contract to cause movement, maintain body posture, and generate heat to keep the body warm.
Nervous System [9:27]
The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors. Its functions include fast communication and control via nerve impulses, sensory processing, and coordination of body functions like breathing and heart rate. The brain serves as the main control center, processing sensory information and controlling both conscious and unconscious functions.
Endocrine System [11:43]
The endocrine system uses hormones for long-term communication and regulation. Organs include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control other endocrine organs. The thyroid gland regulates metabolism, while the parathyroid glands regulate calcium levels. The pancreas regulates blood sugar through insulin and glucagon. The ovaries and testes produce hormones that control reproductive functions and secondary sex characteristics.
Cardiovascular System [16:50]
The cardiovascular system transports substances throughout the body, including blood, water, nutrients, red and white blood cells, gases, and hormones. Organs include the heart, blood vessels (arteries and veins), and blood. The heart pumps blood, while blood vessels transport it. Blood consists of red blood cells (oxygen transport), white blood cells (immune response), and platelets (clotting). Oxygen exchange occurs in capillary beds within the tissues.
Lymphatic & Immune System [19:51]
The lymphatic system reduces swelling by draining excess fluid from tissues, absorbs lipids, and facilitates the immune response. Organs include lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, the spleen, thymus, and bone marrow. Lymph nodes act as scanning centers for pathogens, while the thymus develops T-cells and bone marrow develops B-cells, both crucial for the immune response.
Respiratory System [23:36]
The respiratory system facilitates gas exchange, bringing oxygen into the bloodstream and removing carbon dioxide. Organs include the lungs and diaphragm. Air enters through the nasal cavity, passes through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, and reaches the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs with blood capillaries.
Digestive System [26:40]
The digestive system digests food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste. Organs include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Food is mechanically and chemically broken down in the mouth and stomach. The small intestine absorbs nutrients, while the large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes. The liver produces bile, stored in the gallbladder, and the pancreas produces digestive enzymes.
Urinary System [30:42]
The urinary system removes waste from the blood and regulates water, electrolyte, and pH balance. Organs include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood, producing urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder for storage and is then excreted through the urethra.
Reproductive System [32:42]
The reproductive system produces and transports gametes (sperm and egg cells) and, in females, nurtures a developing fetus. The male reproductive system includes the testes (where sperm is produced), epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral gland, and penis. The female reproductive system includes the ovaries (where eggs are produced), oviducts (fallopian tubes), uterus, and vagina.
Practicing the 11 Organ Systems! [35:20]
The video concludes by emphasizing the importance of practicing active recall and reasoning to strengthen understanding and memory of the 11 organ systems. Viewers are encouraged to download the free study guide for practice exercises and to consider joining the A&P Memory Lab for further learning resources.