TLDR;
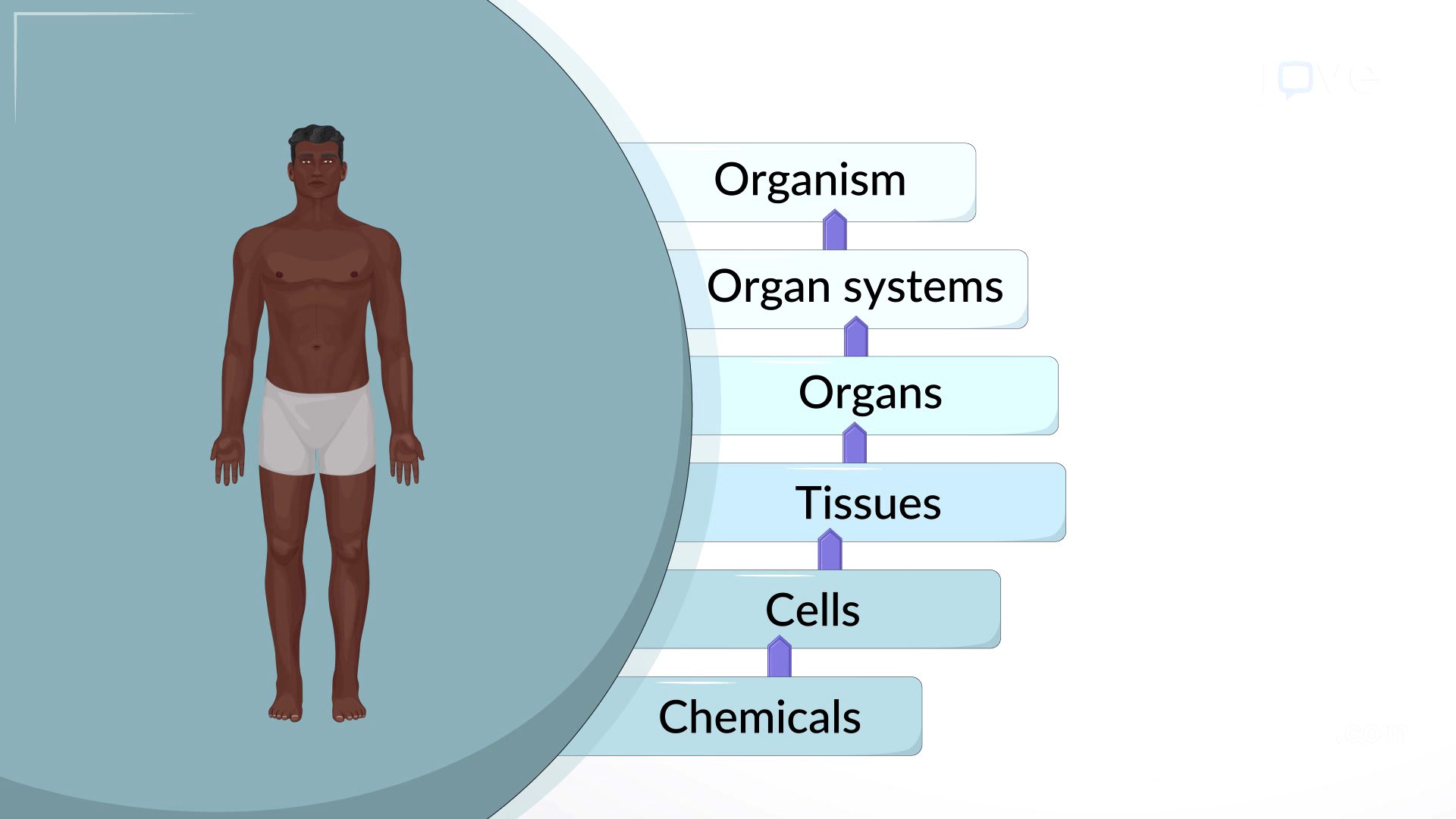
The human body is organized in a hierarchical manner, starting from the simplest building blocks to the complex organism level. This organization includes chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, and organ system levels, all working together to maintain life and health.
- Chemical level includes subatomic particles, atoms, and molecules.
- Cellular level consists of cells, the smallest independently functioning units.
- Tissues are groups of similar cells performing specific functions.
- Organs are composed of two or more tissue types performing specific physiological functions.
- Organ systems are groups of organs working together to perform major functions.
- The organism level is the highest, where all components work together to maintain life.
Structural Organization of the Human Body: An Overview
The structural organization of the human body can be broken down into several levels of increasing complexity: subatomic particles, atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and ultimately, the organism. The chemical level involves the study of matter's basic building blocks: subatomic particles, atoms, and molecules. Elements are pure substances, such as hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, calcium, and iron, and their smallest unit is an atom, which consists of subatomic particles like protons, electrons, and neutrons. Atoms combine to form molecules, including water, proteins, and sugars, which are essential for body structures.
A cell is the smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism, exemplified by bacteria, which are single-celled organisms. Human anatomy comprises cells, and human physiology relies on cells to perform or initiate functions. A typical human cell includes flexible membranes enclosing cytoplasm, a water-based fluid, and organelles, which are tiny functioning units. Cells in all organisms perform life functions.
A tissue is a group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function. An organ is a distinct body structure composed of two or more tissue types, each performing specific physiological functions. An organ system is a group of organs that collaborate to perform major functions or meet the body's physiological needs. Organs can belong to multiple systems and contribute to various functions.
The organism level represents the highest level of organization. An organism is a living being with a cellular structure capable of independently performing all physiological functions necessary for life. In multicellular organisms like humans, all cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems work in coordination to maintain the organism's life and health.