TLDR;
This video introduces OData services in SAP, explaining their purpose, technical design, and how data flows from the database to UI applications. It draws parallels between OData and older technologies like IDoc to aid understanding. The video also covers the steps to create and activate an OData service, including generating runtime objects and testing the service through the SAP Gateway Client.
- OData services facilitate communication between SAP and non-SAP systems, especially UI applications, using XML format.
- Creating an OData service involves defining a project, model, and runtime artifacts, then activating the service to generate a URL for UI access.
- The video demonstrates how to create entity types and sets within an OData service to structure and manage data.
Introduction to OData Services [0:00]
The video introduces OData services as a means of transferring data between a database and a UI application. The presenter outlines the plan to cover the basics of OData, its necessity, and its technical design. The focus will be on the OData service itself, without delving into UI applications. The goal is to explain how data is populated from the database to the UI based on input and output requirements.
OData Service vs. IDoc [1:39]
The presenter draws a comparison between OData services and IDocs to explain the concept. IDocs are structures used for two-way communication, allowing data transfer in and out of SAP with a predefined structure that can be customized. Similarly, OData services provide a format for communication between SAP and non-SAP systems, particularly UI applications, using XML. The process involves defining the structure, filling it with data using function modules or CDS views, and then communicating it to the UI.
Key Terminology and Steps to Create OData Service [7:18]
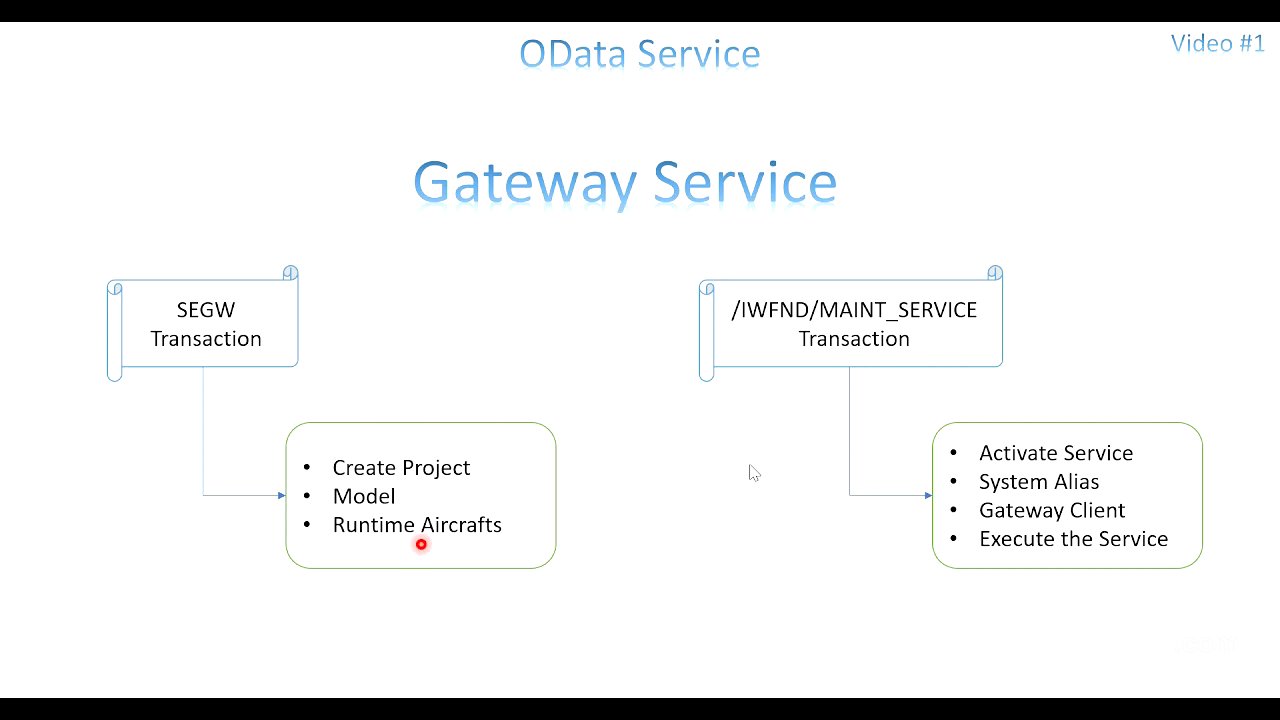
The presenter introduces key terms like "gateway service," which is an add-on in ECC systems, and the transaction codes SEGW and /IWFND/MAINTENANCE_SERVICE for managing OData services. The steps to create an OData service include creating a project, defining a model (data structure), and generating runtime artifacts (extension classes). The service then needs to be activated using the /IWFND/MAINTENANCE_SERVICE transaction, which generates a URL that can be shared with the UI application team.
Creating a Project in SEGW [11:49]
The presenter demonstrates creating an OData service project using the SEGW transaction in a newer version (7.6) of SAP. The process involves creating a new project, assigning it to a local object, and noting the automatically generated folders for data model, service implementation, and service maintenance. The presenter then generates runtime objects, which creates model provider and data provider classes. The service name is also noted for activation in the next transaction.
Activating the OData Service [15:51]
The presenter navigates to the /IWFND/MAINTENANCE_SERVICE transaction to activate the created OData service. The service is added by searching for the project name with a wildcard, selecting the service, and adding it. The presenter emphasizes the importance of ensuring that the metadata loads successfully. After activation, the service status should be green, and the SAP Gateway Client can be used to execute the service and view the XML output.
Testing the OData Service [17:38]
The presenter demonstrates how to test the activated OData service using the SAP Gateway Client. Executing the service should return a 200 status code, indicating success. The presenter explains that different status codes indicate different types of errors, which can be investigated in the error log. The URL generated can then be shared with the UI application team.
Creating an Entity Type and Entity Set [19:36]
The presenter creates an entity type (structure) with fields like material and material type within the OData project. The presenter then creates an entity set, which is like an internal table, to hold data for the structure. The presenter regenerates the project after making these changes.
Reflecting Changes in Gateway Client [23:36]
The presenter returns to the SAP Gateway Client to demonstrate how the newly created entity type and entity set are reflected in the XML output. The presenter explains that selecting the entity set and executing it results in a "Not Implemented" error (501) because the corresponding method in the data provider class has not been implemented yet. The presenter concludes by encouraging viewers to experiment with creating OData services and offers assistance with any doubts.