TLDR;
This session provides an overview of SuccessFactors Employee Central, covering key concepts such as foundation objects, employee data, and implementation methodologies. It also explains how Employee Central integrates with other SuccessFactors modules and how to use the SAP Launchpad for support.
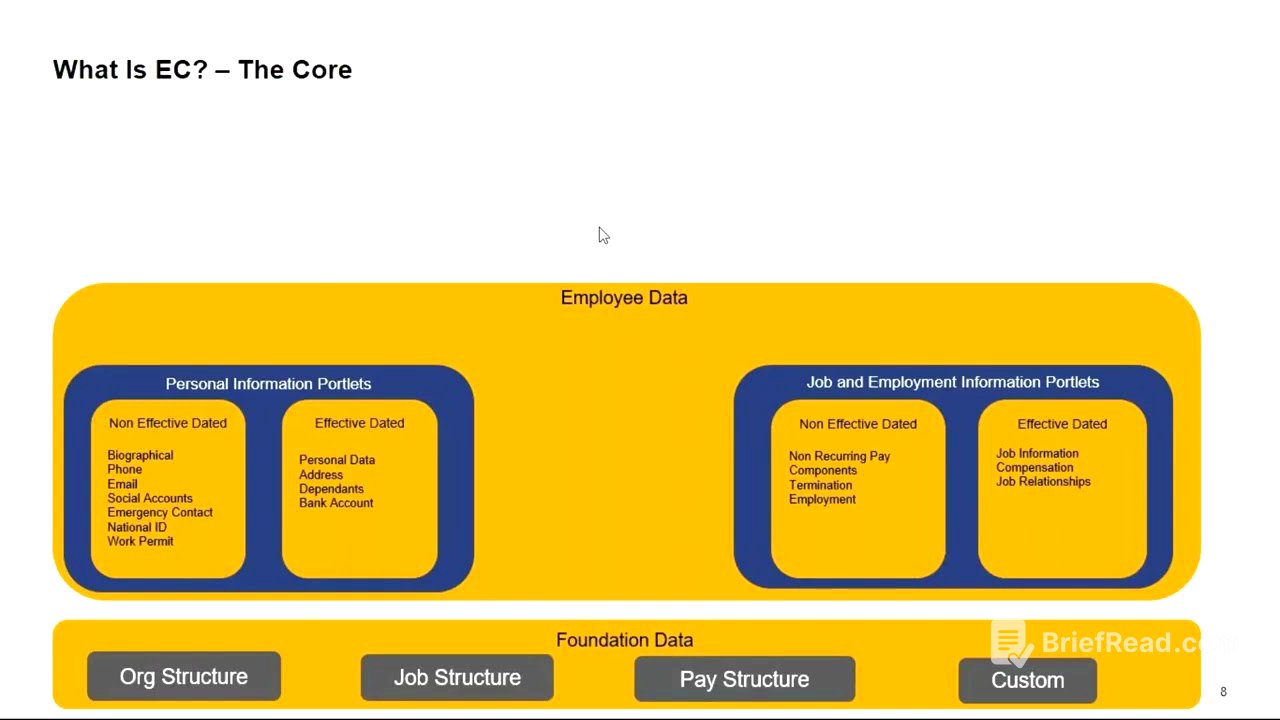
- Foundation objects are the building blocks of Employee Central, including organization, job, and pay structures.
- Employee data is divided into personal and job/employment information, with both effective-dated and non-effective-dated components.
- The Activate methodology is used for implementations, consisting of the prepare, explore, realize, and deploy phases.
- SAP Launchpad (now SAP for Me) is used to raise tickets for configuration issues or product defects.
Introduction to SuccessFactors Employee Central [0:38]
The session begins with a discussion of configuration workbooks, focusing on foundation objects, employee master data, and transaction data. Event reasons and workflows are configured under each event. People Central Hub combines foundation objects, employee master data, and transactions. Position management is discussed later, and the session transitions to the kickoff template.
Kickoff Template Overview [1:41]
The kickoff template, a PowerPoint presentation, explains SuccessFactors to the customer. It includes an agenda, an Employee Central demo, and an introduction to roles and project success. Employee Central is the core module, starting with foundation data, which includes organization, job, and pay structures. Standard and custom elements can be configured under these structures.
Employee Data Setup [5:35]
Employee data is divided into personal information and job/employment information, each with effective-dated and non-effective-dated components. Effective-dated records require a date and maintain history, while non-effective-dated records show only one current record. Job information includes organizational details, and compensation information tracks salary history. Events and event reasons are mandatory for job information changes, and transactions may require approvals configured in workflows.
People Profile and Optional Additions [14:14]
The people profile contains sections and subsections with standard or custom portlets. Optional additions include time off, time sheets, global assignments, concurrent employment, and contingent workers. Global assignments are for employees working in multiple countries, while country transfers involve terminating services in one country and moving to another. Concurrent employment allows multiple jobs within one organization, and contingent workers are contractors with minimal data maintained.
Summary of Key Concepts [18:20]
Foundation objects are the building blocks of the EC system, containing organization, job, and pay structures. Employee data includes standard and customized portlets with configurable attributes. Events and event reasons are required for job information transactions, and workflows can be configured for these transactions. Role-based permissions (RBP) are crucial for data sensitivity, controlling access for different roles. Administrative functions include data imports, mass changes, and theme configurations.
Role-Based Permissions (RBP) [19:29]
Permissions in SuccessFactors are controlled through role-based permissions (RBP). Employees can view and update their own information to some extent, while managers can see their direct reports' data. HR managers have access to all employee data but may be restricted from updating their own details. RBP controls who can see and edit specific data, ensuring data privacy and accuracy.
Data Imports and Mass Changes [22:17]
Robust administrative functions, such as data imports and mass changes, are performed to add employees, process transfers, and promote employees in bulk. Foundation data, like locations, can be uploaded through imports. Workflows can be configured, and teams can be set up with different themes and logos for different customers.
Questions and Answers on RBP and Data Imports [23:42]
The number of records that can be edited cannot be controlled, but access to specific employee data can be restricted based on location or role. Data input can be performed for specific events like salary changes, and multiple events can be included in a single file. Imports do not trigger approvals; only manual events in the system do.
Integration with Other SuccessFactors Modules [27:48]
Employee Central integrates with other SuccessFactors modules, such as succession, goals, and performance. Data can be sent from Employee Central to other modules and retrieved from them. For example, positions created in Employee Central can be converted into requisitions in recruiting, and candidate data from recruiting can be pulled into Employee Central upon hiring. Performance appraisal data can be sent to compensation for salary revisions, and updated salaries are pushed back to Employee Central.
People Profile vs. User Data File (UDF) [30:33]
The people profile contains multiple portlets with effective-dated and non-effective-dated fields, storing all information about an employee and allowing historical data tracking. The user data file (UDF) contains only active data from selected fields in the people profile. The UDF is used to send data to other modules like recruiting, compensation, and performance management. The people profile is at the user level, while the UDF provides a snapshot of current data.
Implementation Methodology: Activate [34:07]
The Activate methodology, recommended by SAP, consists of four phases: prepare, explore, realize, and deploy. The prepare phase involves project initiation and resource allocation. The explore phase includes analyzing customer requirements and identifying gaps. The realize phase involves configuration, unit testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT). The deploy phase includes cutover activities and data migration to the production system.
Testing Methodology and Iterations [39:22]
Testing follows a three-iteration methodology: define, refine, and finalize. In the first iteration, customers provide requirements in workbooks, and the implementation partner configures the system. The second iteration refines the data and focuses on workflows and RBP. The final iteration completes all data configurations and customizations. The customer is responsible for loading data into the system after go-live.
SAP Launchpad (SAP for Me) for Support [48:02]
SAP Launchpad (now SAP for Me) is used to raise tickets for configuration issues or product defects. Tickets are created using a customer-specific S user ID. Knowledge-based articles (KBAs) are available to resolve common issues. Tickets can be prioritized as low, medium, high, or very high, depending on the severity of the issue.
Ticket Priorities and Consultant Responsibilities [52:29]
Very high priority tickets are for system-down situations, while high priority tickets are for major issues during go-live. Medium and low priority tickets are for development or quality system issues. Consultants should first go through KBAs to resolve issues before raising tickets. Raising tickets for simple issues can lead to escalation to the implementation partner.