TLDR;
This video provides an overview of the major classes of psychiatric medications (psychotropics), which affect a person's mental state. It covers antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, sedative hypnotics, stimulants for ADHD, medication-assisted treatment for substance use disorders, and anti-dementia medications. The video also discusses subtypes within each class and examples of specific medications. Additionally, it addresses secondary medications used to manage the side effects of primary psychiatric drugs.
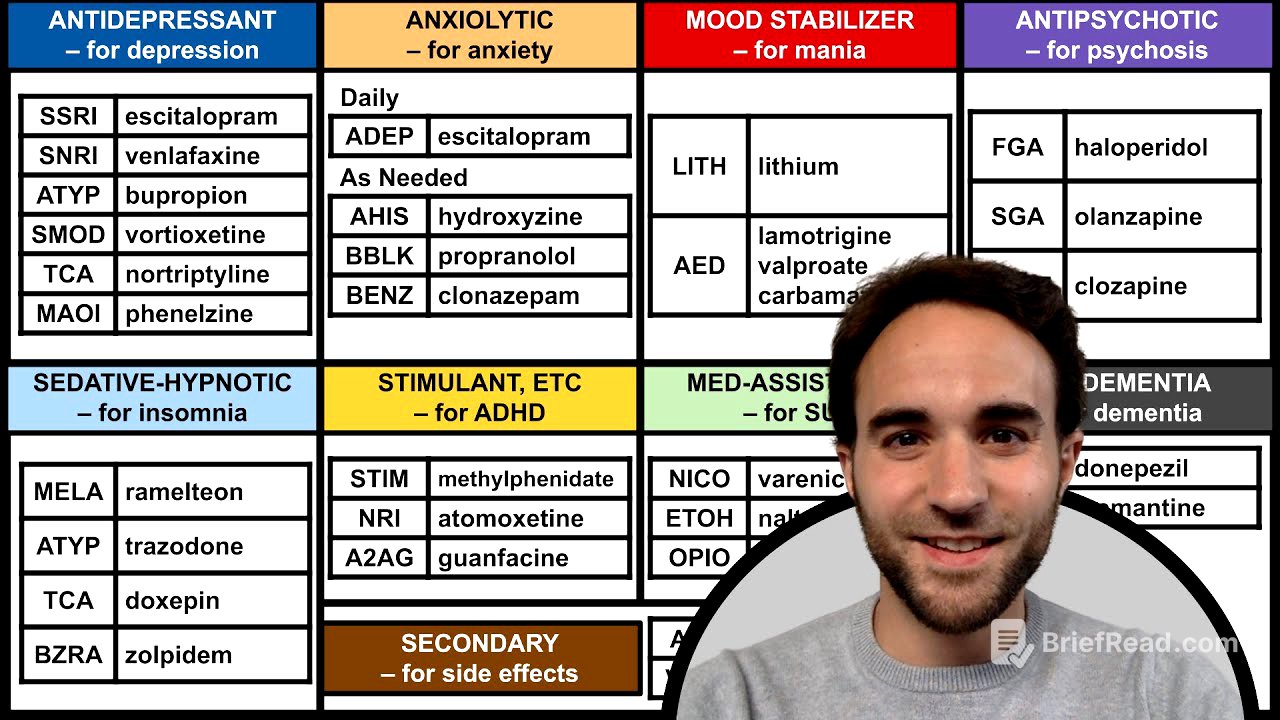
- Antidepressants: SSRIs, SNRIs, atypical antidepressants, serotonin modulators, TCAs, and MAOIs.
- Anxiolytics: Antidepressants (daily use), antihistamines, beta blockers, and benzodiazepines (as needed).
- Mood Stabilizers: Lithium, lamotrigine, valproate, and carbamazepine.
- Antipsychotics: First and second-generation antipsychotics, with clozapine as a distinct category.
- Sedative Hypnotics: Melatonin agonists, trazodone, doxepin, and benzo receptor agonists.
- ADHD Medications: Stimulants, norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and alpha-2 agonists.
- Substance Use Disorder Medications: Medications that agonize or antagonize receptors of abused substances.
- Anti-Dementia Medications: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA antagonists.
- Secondary Medications: Used to treat side effects of primary psychiatric medications.
Introduction to Psychiatric Medications [0:00]
The lecture introduces the major classes of psychiatric medications, also known as psychotropics, which are defined as medications that affect a person's mental state. The main categories to be discussed include antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, sedative hypnotics, stimulants and related medications for ADHD, medication-assisted treatment for substance use disorders, and anti-dementia medications. The presentation will further outline subtypes within each class and provide specific examples.
Antidepressants [0:45]
The different types of antidepressants are outlined. These include Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs), atypical antidepressants, and serotonin modulators. Additionally, the older classes of antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), are mentioned.
Anxiolytics [1:07]
Anxiolytics are discussed, noting that anxiety disorders are often treated with the same medications used for depressive disorders, namely antidepressants, on a daily basis. For acute anxiety or panic attacks, as-needed medications like antihistamines, beta blockers, and benzodiazepines may be required to provide immediate relief.
Mood Stabilizers [1:30]
The class of mood stabilizers includes lithium and anti-epileptic drugs such as lamotrigine, valproate, and carbamazepine. These medications are primarily used to manage mania and stabilize mood fluctuations.
Antipsychotics [1:37]
Antipsychotics are categorized into first and second-generation antipsychotics. Clozapine, while technically a second-generation antipsychotic, is placed in a separate category due to its unique characteristics, including higher efficacy and the need for intensive side effect monitoring.
Sedative Hypnotics [1:54]
Sedative hypnotics are a diverse group of medications used to promote sleep, with various mechanisms of action. Examples include the melatonin agonist ramelteon, trazodone, the tricyclic antidepressant doxepin, and zolpidem, which is a benzo receptor agonist.
Stimulants and ADHD Medications [2:12]
Stimulants and related non-stimulant medications are used to treat ADHD symptoms. These include norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors and alpha-2 agonists, which help manage attention and hyperactivity.
Medication-Assisted Treatment for Substance Use Disorders [2:21]
Medications used to treat substance use disorders, often referred to as medication-assisted treatment, exert their therapeutic effects by agonizing or antagonizing receptors that substances of abuse typically bind to. Examples include medications targeting nicotine and opioid receptors.
Anti-Dementia Medications [2:39]
Anti-dementia medications include acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA antagonists. These medications aim to manage cognitive symptoms associated with dementia.
Secondary Medications [2:46]
Secondary medications are used to treat the side effects of primary psychiatric medications. Examples include antihistamines and VMAT inhibitors for the extrapyramidal side effects of antipsychotics, metformin for antipsychotic-induced weight gain, levothyroxine for lithium-induced thyroid toxicity, and levocarnitine for valproate-induced hyperammonemia.