TLDR;
This YouTube video by PythonLife provides a comprehensive introduction to the NumPy library in Python. It covers fundamental concepts such as array creation, dimensions, shapes, data types, and various operations like slicing, copying, and views. The video also touches on statistical functions, trigonometry, stacking, inserting, deleting, and the 'where' function. The session aims to equip viewers with a solid foundation in NumPy for data manipulation and analysis.
- Introduction to NumPy library in Python
- Covers array creation, dimensions, shapes, and data types
- Explains slicing, copying, views, and various array operations
- Touches on statistical functions, trigonometry, and the 'where' function
Introduction to NumPy [0:06]
The video starts by outlining the topics covered, including different types of inheritance, polymorphism (method overloading and overriding), access modifiers (public, private, protected), and data abstraction. It also mentions the steps in a machine learning lifecycle: data gathering, preprocessing, visualization, modeling, and deployment. The discussion emphasizes the use of libraries like NumPy and Pandas in these processes.
MPC Students and Matrix Forms [2:51]
The discussion addresses the audience, particularly MPC (Maths, Physics, Chemistry) students, and their familiarity with matrix forms. It acknowledges that the mathematical nature of NumPy might be challenging for non-math students but encourages them to try. The video prompts viewers to install Anaconda and Jupyter Notebook, referencing previous videos for guidance.
NumPy as a Python Library [4:25]
NumPy is introduced as a Python library for numerical computing, consisting of multi-dimensional array objects. It's used in various applications, including computer vision, where image data is converted into matrix form for analysis. Real-world applications in NASA and Tesla are mentioned to highlight NumPy's utility in science-oriented research.
Array Fundamentals [11:29]
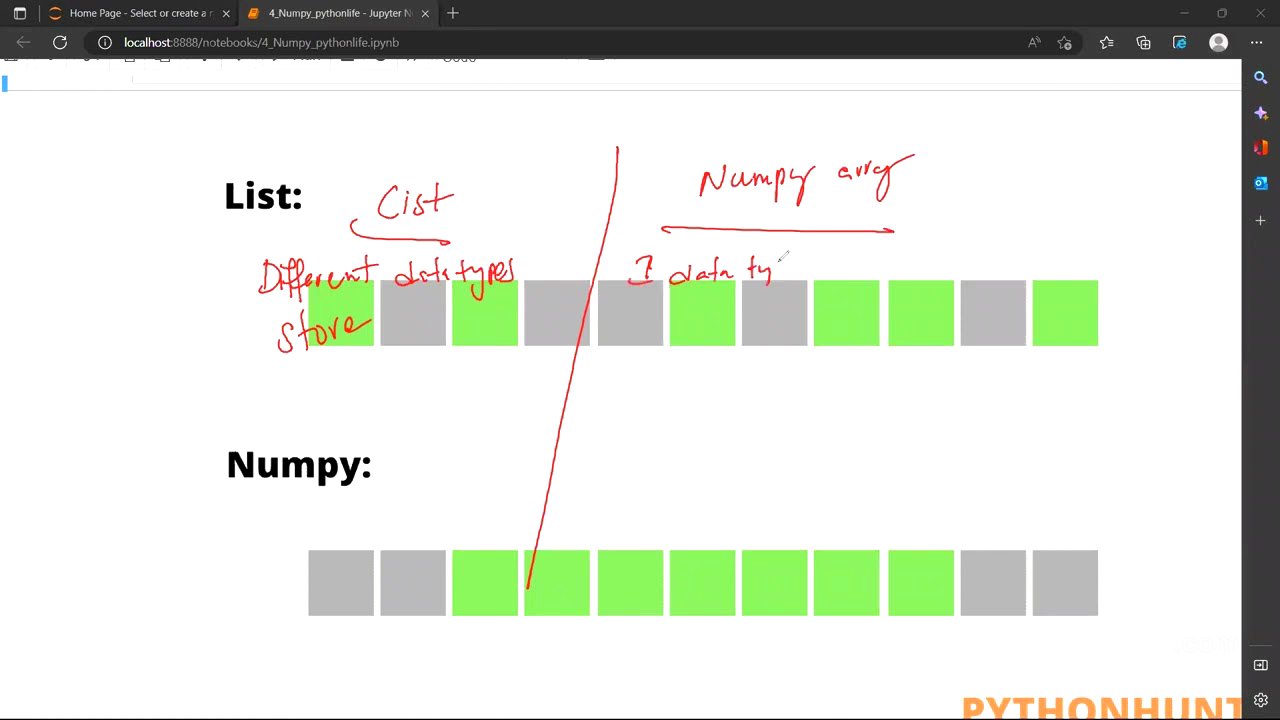
The video explains the characteristics of arrays, noting that they store the same data type and offer fast, sequenced storage. It distinguishes arrays from lists, which can store different data types. The discussion covers 2D and 3D arrays, explaining axes (Axis Zero, Axis One, Axis Two) and layers in 3D arrays.
Installing and Using NumPy in Jupyter Notebook [21:43]
The presenter guides viewers on how to install NumPy and use it within a Jupyter Notebook. The file extension for Jupyter Notebooks, IPYNB (Interactive Python Notebook), is highlighted as important for interviews. The use of VS Code and Google Colab for machine learning tasks is also mentioned. The process of importing NumPy with an alias (e.g., import numpy as np) is explained.
Understanding Dimensions in NumPy Arrays [26:19]
The video explains how to determine the dimensions of a NumPy array by counting the number of square brackets. It introduces the ndim attribute to check the dimension of an array. Multi-dimensionality is discussed, noting that beyond three dimensions, arrays are generally referred to as multi-dimensional.
Shape of NumPy Arrays [29:30]
The 'shape' attribute is introduced to determine the dimensions of an array, indicating the number of rows, columns, and layers. The video explains how to use the .shape attribute to find the shape of arrays and clarifies how the shape is represented for zero-dimensional arrays.
Data Types in NumPy [36:13]
The video discusses data types (D types) in NumPy, such as integers (int32, int16, int64), and how they relate to system bits. It explains how to check the data type of an array using the dtype attribute.
Range Function in NumPy [37:02]
The range function is discussed in the context of NumPy, relating it to the familiar range function used in for loops (start, stop, skip). The video explains how to generate data within a specified range inside an array.
Notebook Structure and Functions [37:56]
The structure of Jupyter Notebook is explained, emphasizing that each cell has a connection and functions only if the cell is loaded. The presenter highlights the notebook's utility for learning, research, and documentation, containing information from basic Python to NumPy.
Array Creation Functions: I, Zeros, and Ones [41:09]
The video introduces functions for creating specific arrays: I (identity matrix), zeros (array of zeros), and ones (array of ones). It explains how to use these functions with different parameters to create matrices of various sizes and data types (e.g., float).
Reshape Function [55:15]
The reshape function is explained, emphasizing that the original value should match the multiplied values after reshaping. The video demonstrates how to change the dimensions of an array using reshape, providing examples of converting a 1D array into 2D and 3D arrays.
Ravel and Flatten Functions [56:13]
The video differentiates between the ravel and flatten functions. Ravel is described as an "undo" function, reverting an array to its previous dimension, while flatten always converts an array to one dimension.
Slicing in NumPy Arrays [1:00:14]
Slicing is explained as a way to extract specific parts of an array, using start, stop, and skip parameters. The video uses an image analogy to explain how slicing works in multi-dimensional arrays, demonstrating how to select elements based on row and column indices.
Copy vs. View in NumPy [1:11:44]
The critical difference between copying and viewing arrays is discussed. Copying creates a new array, so changes to the copy do not affect the original. Viewing, however, does not own the data, and changes to the view will affect the original array, and vice versa.
Array Operations: Boolean Indexing and Transpose [1:12:58]
The video covers boolean indexing, where conditions (e.g., a > 3) return True or False, and how to use these conditions to extract data. The transpose operation is explained, where rows become columns and vice versa, using the transpose function.
Stacking Arrays: Hstack and Vstack [1:16:20]
The concepts of horizontal stacking (hstack) and vertical stacking (vstack) are introduced. Hstack stacks arrays along columns, while vstack stacks along rows. The video clarifies how these operations affect the dimensions of the resulting arrays.
Insert and Delete Operations [1:20:13]
The video demonstrates how to insert and delete elements in NumPy arrays. The insert function adds elements at a specified location, while the delete function removes elements based on their index.
Trigonometry in NumPy [1:21:54]
The video briefly mentions the availability of trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) in NumPy. It notes that while some functions like cotangent are not directly available, they can be computed using other trigonometric functions.
Exponential and Sum Operations [1:23:52]
Exponential and summation operations are discussed, including the use of the sum function with the axis parameter to sum along rows or columns.
Statistical Functions: Mean, Median, Mode, and Range [1:25:06]
The video explains basic statistical functions: mean (average), median (middle value), mode (most frequent value), and range (difference between smallest and largest values). It provides examples of how to calculate these statistics.
Standard Deviation and Other Statistical Measures [1:30:32]
The video briefly mentions standard deviation and other statistical measures available in NumPy. It suggests that a deeper dive into statistics will be covered in future sessions.
The 'Where' Function [1:32:21]
The 'where' function is explained, which is used to find the indices of elements that satisfy a given condition. The video provides examples of using 'where' to find elements that meet specific criteria, such as even numbers.
Default Functions and Syntax [1:35:33]
The video notes that many functions in NumPy have default behaviors. It encourages viewers to explore the documentation for lists and sets to understand available functions and syntax.
Additional Resources and Conclusion [1:37:11]
The presenter recommends referring to the NumPy documentation for more in-depth content. The session concludes by stating that the material covered is sufficient for machine learning engineers and data scientists, and the IPNB file will be shared on Telegram.




![Benarkah Tasawuf Itu Sesat dan Bid'ah [BEDAH MASALAH]](https://wm-img.halpindev.com/p-briefread_c-10_b-10/urlb/aHR0cDovL2ltZy55b3V0dWJlLmNvbS92aS84d3pTZklmRlhXMC9ocWRlZmF1bHQuanBn.jpg)



