TLDR;
This lecture introduces the concept of public policy, highlighting its complex definition, importance, characteristics, and relevance to science. It covers the definition of policy, its nature as a process, product, and output, and explores what policies can and cannot do. The lecture also discusses the role of goals in policy-making, differentiating between short-term and long-term objectives, and provides examples to illustrate these concepts.
- Public policy is difficult to define due to varying opinions and perceptions.
- Policies guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes at individual, group, and organizational levels.
- Goals are essential in policy-making, serving as desired states that societies or organizations aim to achieve.
Introduction to Public Policy [0:07]
The lecture begins by acknowledging the difficulty in defining public policy due to diverse opinions and perceptions. The term is broadly applied to activities by politicians, bureaucrats, and government agencies related to policy matters. It is noted that not all government programs are public policies, and policies are not always formal laws. The lecture aims to define public policy, analyze its importance, describe its nature and characteristics, and discuss its relevance to science.
Defining Policy [1:44]
A policy is defined as a deliberate system of principles that guides decisions and achieves rational outcomes for individuals, social groups, or organizations. Policies are typically adopted by governing bodies within organizations, serving as rules for staff to follow in their responsibilities. Examples include return-to-work policies, which are developed through specific procedures and steps. Policy is also a process of decision-making, exemplified by the development and production of the COVID-19 vaccine. Additionally, policy can be an output, such as the delivery of goods and services or the enforcement of stay-at-home orders. Policies are implemented in various sectors, including education, health, and agriculture.
Characteristics and Levels of Policies [4:23]
Policies are predetermined decisions and rules applicable to everyone, especially those within organizations, based on their actions. Policies operate at political, management, financial, and administrative levels. Examples include equal opportunity policies, health and safety policies, codes of conduct, and policies related to attendance, vacation, and disciplinary actions.
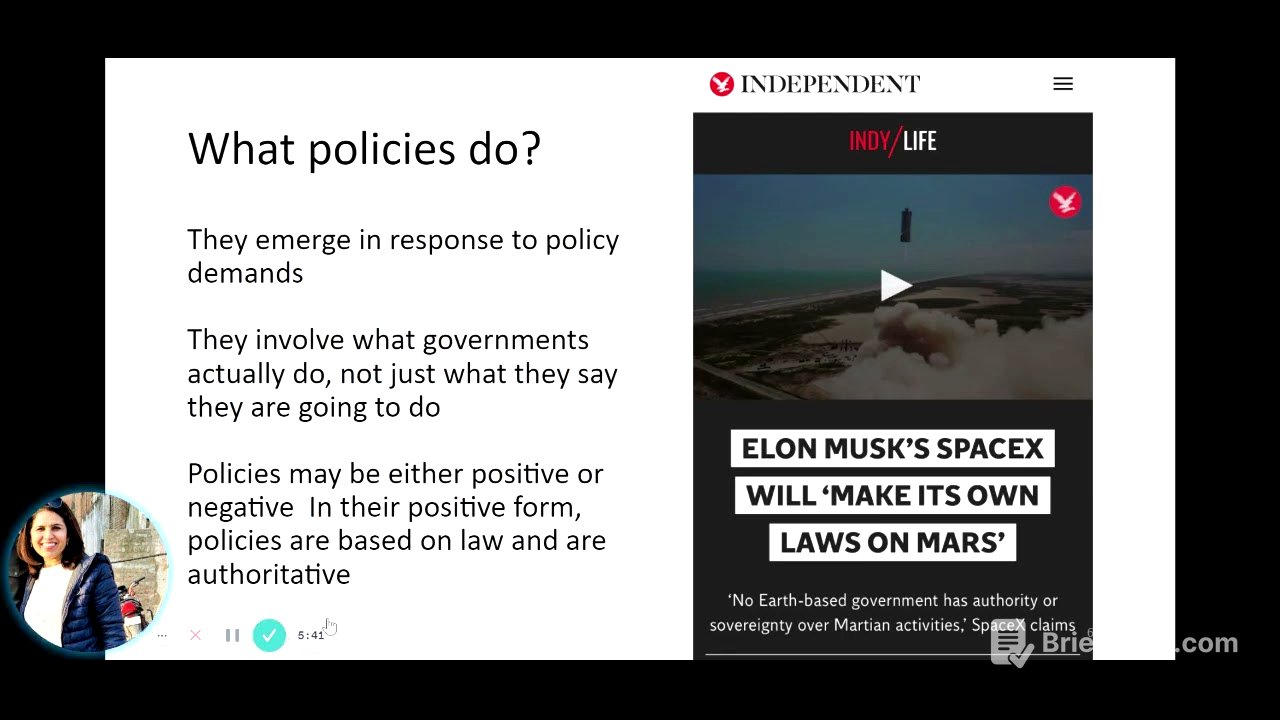
What Policies Can and Cannot Do [5:42]
Policies often emerge in response to policy demands, reflecting what governments can and should do. An example is given of Elon Musk's vision for SpaceX on Mars, where he suggests the company might create its own laws, potentially leading to both positive and negative impacts.
The Role of Goals in Policy [7:05]
Goals are essential in policy-making, representing the desired state of affairs that a society or organization aims to achieve. These goals can be short-term or long-term. Short-term goals must be accomplished to reach long-term objectives. Goals can be abstract values or specific and concrete targets. For example, a government's long-term goal might be the removal of poverty or addressing climate change, which requires setting short-term goals to achieve comprehensive change.




![The Epic Showdown with Milleniumon [Adventure 2020 Discussion] | Baby Flame Vol. 10](https://wm-img.halpindev.com/p-briefread_c-10_b-10/urlb/aHR0cDovL2ltZy55b3V0dWJlLmNvbS92aS9SXzE0THhNVVFHNC9ocWRlZmF1bHQuanBn.jpg)


