TLDR;
This lecture provides an overview of the course "Power Electronics," covering the syllabus, grading, and the fundamental concepts of power conversion. It highlights the importance of power electronics in modern technology, from portable devices to large-scale power grids, and introduces the basic principles of switch-mode power converters as an efficient alternative to linear regulators. The course aims to equip students with the tools to design power electronics for various applications.
- Course mechanics and grading scheme.
- Importance of power electronics in modern technology.
- Introduction to switch-mode power converters.
Course Mechanics and Syllabus Overview [0:12]
The course will be managed through Canvas, where homework assignments can be downloaded, although submissions will be in paper format. Classes are scheduled for Mondays, Wednesdays, and Thursdays at 1 PM. While a textbook is recommended, additional resources are optional and available in the library. Homework, typically assigned on Mondays and due the following Monday, allows for collaboration, but individual solutions are required. Office hours are available on Thursdays and Fridays, with additional support from students in the Le laboratory. Assessments, replacing in-class exams, will be weekly take-home quizzes issued on Wednesdays and due on Thursdays, submitted via Canvas through GradeScope, and must be completed individually. Late homework submissions are accepted with prior arrangement, but assessments have a strict no-collaboration policy.
Grading and Final Project [4:31]
The final grade is composed of homework (40%), assessments (50%), and a final project (10%). The final project involves a paper design demonstrating the synthesis of knowledge acquired throughout the course, offering an opportunity to showcase the ability to design power electronics. Students requiring technical accommodations for GradeScope should inform the staff for assistance.
Introduction to Power Electronics [6:03]
Power Electronics is defined as the technology encompassing the use of electronic components, circuit theory, design techniques, and analytical tools for efficient electronic conversion, control, and conditioning of electric power. It involves converting electrical energy from one form to another, serving as a core technology in the electrical infrastructure. Modern applications require power conversion circuitry between the principal source and the final usage, impacting system efficiency and quality.
Applications of Power Electronics [10:16]
Power electronics are integral to numerous applications, including portable electronics, computers, communication systems, commercial devices, home appliances, medical equipment, scientific instruments, transportation (electric and hybrid vehicles, trains), power transmission and generation (renewable resources), and industrial processes. The field is continuously evolving to improve energy usage and enable new applications.
Components and Design of a Power Converter [16:19]
A power converter typically includes energy storage elements (inductors, capacitors) and semiconductor switches to manipulate energy flow. Energy is drawn from a source, stored, and then released to the output in a cyclic manner. Filters are used to reduce ripple and noise, and control circuitry manages the energy flow, especially in high-performance applications. The design leverages circuit design, semiconductor devices, passive components, materials, packaging, cooling, and controls. The goal is to make converters smaller, lighter, more efficient, and higher-performing.
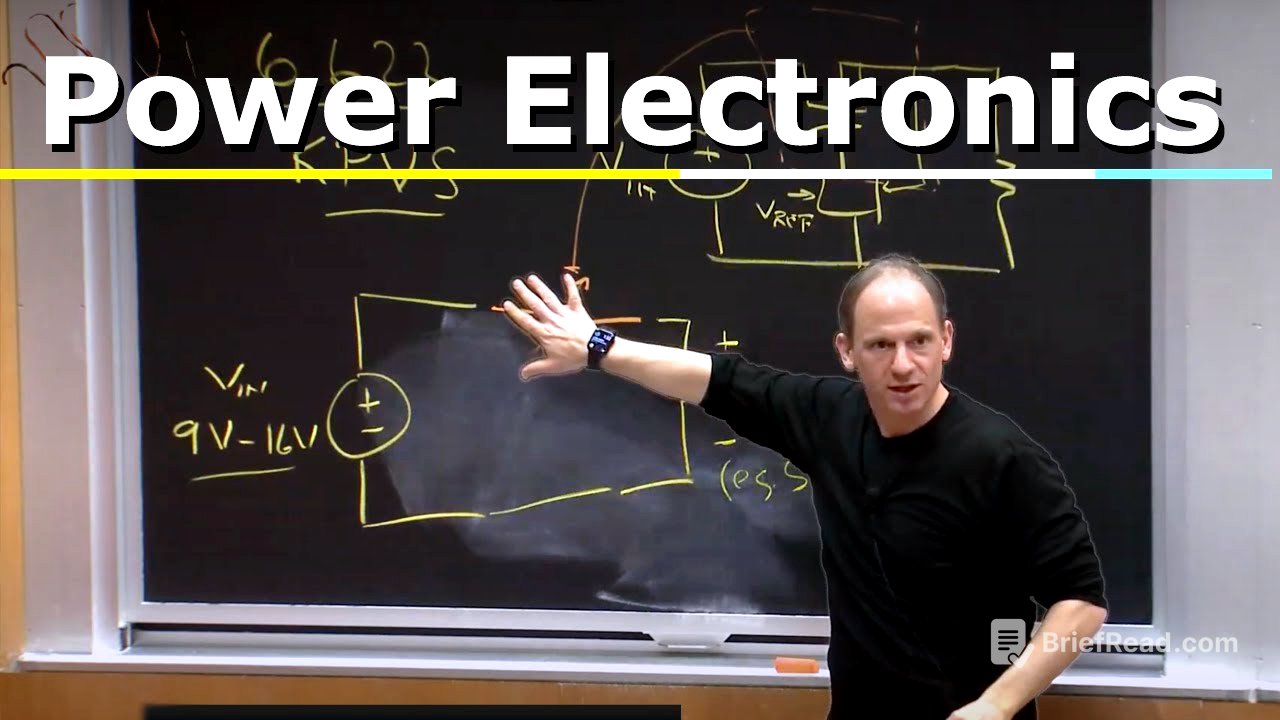
Linear vs. Switch-Mode Power Supplies [22:25]
A simple way to get 5 volts from a 9-16 volt input is to use a voltage divider with a variable resistor or a transistor acting as a variable resistor. However, this method, known as a linear power supply, has terrible efficiency because the input current equals the output current, wasting a large fraction of energy as heat. In contrast, switch-mode power converters use switches and energy storage elements to process energy efficiently.
Switch-Mode Power Conversion Principles [29:52]
Switch-mode power conversion involves using a switch to pulse the input voltage, creating a waveform with a controlled average voltage. By rapidly switching between connecting the output to the input voltage and ground, the average voltage can be controlled through pulse width modulation (PWM). A filter, typically an LC filter, is then used to extract the DC component of the pulsed voltage, providing a stable output voltage.
Efficiency and Components in Switch-Mode Converters [36:33]
Ideally, switch-mode converters can achieve close to 100% efficiency because they use lossless elements such as ideal switches and LC filters. Real-world components have losses, but efficiencies of 97% are achievable. The inductor in the filter also serves as an intermediate energy store, allowing energy to be transferred from the input to the output with voltage conversion and minimal energy loss. The course will cover the underlying principles, design, and control of these converters, aiming to equip students with the ability to design power electronics for various applications.