TLDR;
This lecture introduces the role of physical therapy in sports injury rehabilitation. It emphasizes aligning physical therapy principles with tissue healing, adapting strategies for sports, and understanding practical aspects with case examples. Key points include the importance of physical therapists as a link between athletes and coaches, the shift from focusing on impairment to function and performance, and the concept of exercise as medicine. The lecture also covers the scope of physical therapy in sports medicine, including injury prevention, acute injury care, prehabilitation, post-operative rehabilitation, and return-to-play planning, highlighting the importance of a structured, objective, and multi-disciplinary approach.
- Physical therapy is a crucial link between athletes, coaches, and trainers.
- Exercise should be prescribed therapeutically, like medicine.
- Psychological aspects significantly impact sports rehabilitation.
Introduction to Physical Therapy in Sports Injury Rehabilitation [0:15]
The lecture begins by addressing the role of physical therapy in sports rehabilitation, particularly in achieving better outcomes for athletes recovering from injuries. It outlines the learning objectives, which include understanding the role of physical therapy, aligning its principles with tissue healing, adapting these principles for sports rehabilitation, and discussing practical strategies with a case example. The speaker, Wing Commander Chandra Shaka Guru, a sports medicine physician, emphasizes the importance of physical therapy in the context of sports injuries.
Tissue Healing and Rehabilitation Phases [1:25]
The discussion covers the tissue healing process following an injury, which includes the inflammation phase (up to a week), the proliferation phase (where cells lay down collagen), and the remodeling phase (maturation of collagen). These phases are aligned with the rehabilitation phases: acute (preventing further damage), subacute (restoring function for daily activities), return to sport (advancing strengthening and sport-specific drills), and reinjury prevention. Understanding this alignment is crucial for effective rehabilitation.
Role of Physical Therapy in Sports [3:00]
Physical therapists serve as a vital link between athletes, coaches, and trainers, communicating the nature of the injury and the timeline for recovery. The focus in sports physical therapy has shifted from merely addressing physical impairment and disability to enhancing function, performance, and preventing reinjury. Therapeutic exercise is the backbone of this approach, with exercise prescribed as medicine, following the "FIT" protocol (frequency, intensity, type, and timing/duration) to optimize rehabilitation.
Scope of Physical Therapy in Sports Medicine [6:10]
The scope of physical therapy in sports medicine includes injury prevention programs, acute injury care, prehabilitation (therapeutic exercise before surgery to improve post-operative recovery), post-operative rehabilitation, and return-to-play planning. Physical therapy concepts are essential for a smooth transition from therapeutic exercises to sport-specific training, aligning with athletic trainers and coaches.
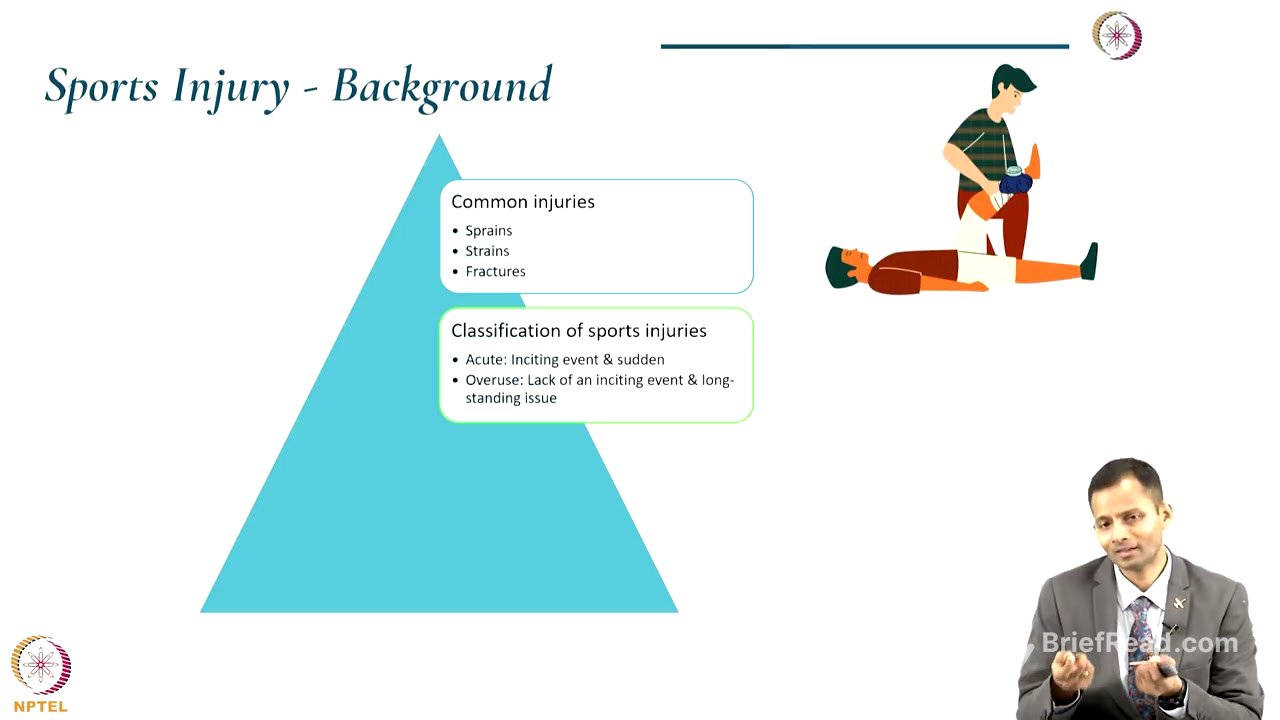
Sports Injuries: Types and Management [7:40]
Sports injuries are classified into acute (sudden onset with a specific event) and overuse (cumulative effect of micro-injuries over time). Management involves injury prevention programs, acute management (phase one), and structured rehabilitation (phases two and three). The rehabilitation phases target pain control and inflammation reduction (phase one), restoring function and addressing impairments (phase two), and returning to sports with advanced strengthening and sport-specific drills (phase three), with a final phase focused on long-term reinjury prevention.
Goals of Physical Therapy Across Rehabilitation Phases [10:43]
The goals of physical therapy across all phases include protecting the injured site, controlling pain and inflammation, restoring range of motion, and restoring function from basic activities to sport-specific movements. Improving strength, endurance, and cardiorespiratory fitness is also crucial, along with incorporating functional training that includes attention training for sports like boxing or post-concussion recovery. Return-to-play planning involves collaboration with coaches and athletic trainers for a smooth transition to sports-specific activities.
Key Physical Therapy Principles in Sports Injury Rehabilitation [12:34]
Key principles include individualizing the rehab program based on the athlete's level, sport demands, and available facilities. Progressive overload is essential for sustained improvement, aligned with rehabilitation phases and used to assess patient outcomes. Functional progression moves from daily activities to sport-specific tasks. Regular assessment and evaluation, both subjective and objective, are necessary to monitor progress and adjust the program accordingly.
Assessment and Evaluation in Physical Therapy [14:19]
Assessment involves subjective feedback from the patient and objective measures like range of motion and strength testing. Strength can be assessed through manual muscle testing or dynamometers. Functional tests, such as squats, help identify deficits and inform corrective strategies. Outcome measures, including patient-reported objective measures, provide a multi-dimensional view of improvement in the rehab program.
Modalities in Sports Rehabilitation [18:36]
Various modalities assist in sports rehabilitation, including cryotherapy (ice packs, cryosprays for acute injury management), manual therapy (joint and soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release for chronic conditions), taping (rigid for preventing movement, kinesio for aiding movement and proprioception), and electrotherapy (for pain modulation and inflammation control). Therapeutic exercise is the backbone of physical therapy, with modalities used to facilitate exercise performance and promote behavioral changes for long-term adherence.
Role of Physical Therapy in Pre- and Post-Surgical Cases [23:39]
Prehabilitation involves therapeutic exercises before surgery to activate muscles and improve strength, leading to faster post-surgical recovery. Post-surgical rehabilitation is staged and structured, focusing initially on the stages of healing, avoiding full weight-bearing, and gradually increasing weight-bearing as appropriate. It also includes range of motion exercises, muscle activation, and advanced strengthening programs.
Psychological Aspects of Sports Rehabilitation [25:34]
Psychological factors play a significant role in sports rehabilitation, addressing emotional responses, reduced confidence, and identity crises resulting from the inability to play. Neuromuscular activation and mental training sessions can boost confidence. Educating the athlete and providing social support from coaches and administrators are crucial. A multi-disciplinary team approach, including the athlete, coach, sports physician, and family, is essential for successful rehabilitation.
Conclusion and Self-Study Exercise [27:52]
Physical therapy in sports medicine is multi-dimensional and requires a collaborative team effort. The lecture concludes with a self-study exercise, prompting viewers to consider modalities and strategies used by physical therapists during various phases of injury management. Examples for the acute phase include cryotherapy, compression, taping, joint mobilization, pain-free range of motion, stretching, and electrotherapy for pain control. The summary emphasizes that physical therapy is a key part of sports rehabilitation, exercise is medicine, psychological aspects are important, and a structured, objective, multi-disciplinary approach is necessary.