TLDR;
This video provides an overview of computer hardware, focusing on modular design, motherboard components, memory types (RAM, ROM, CMOS), and video cards. It explains the functions of various sockets, slots, and connectors, as well as the machine cycle within the CPU. The video also discusses the characteristics of RAM and ROM, the role of BIOS and firmware, and the importance of video cards for processing and displaying images.
- Modular design simplifies computer repair and upgrades.
- Motherboard facilitates connections and communication between components.
- RAM is fast, volatile memory used for active processes.
- ROM is non-volatile memory containing firmware like BIOS.
- Video cards with GPUs enhance graphics processing, especially in high-resolution displays.
Modular Design and Motherboard Components [0:08]
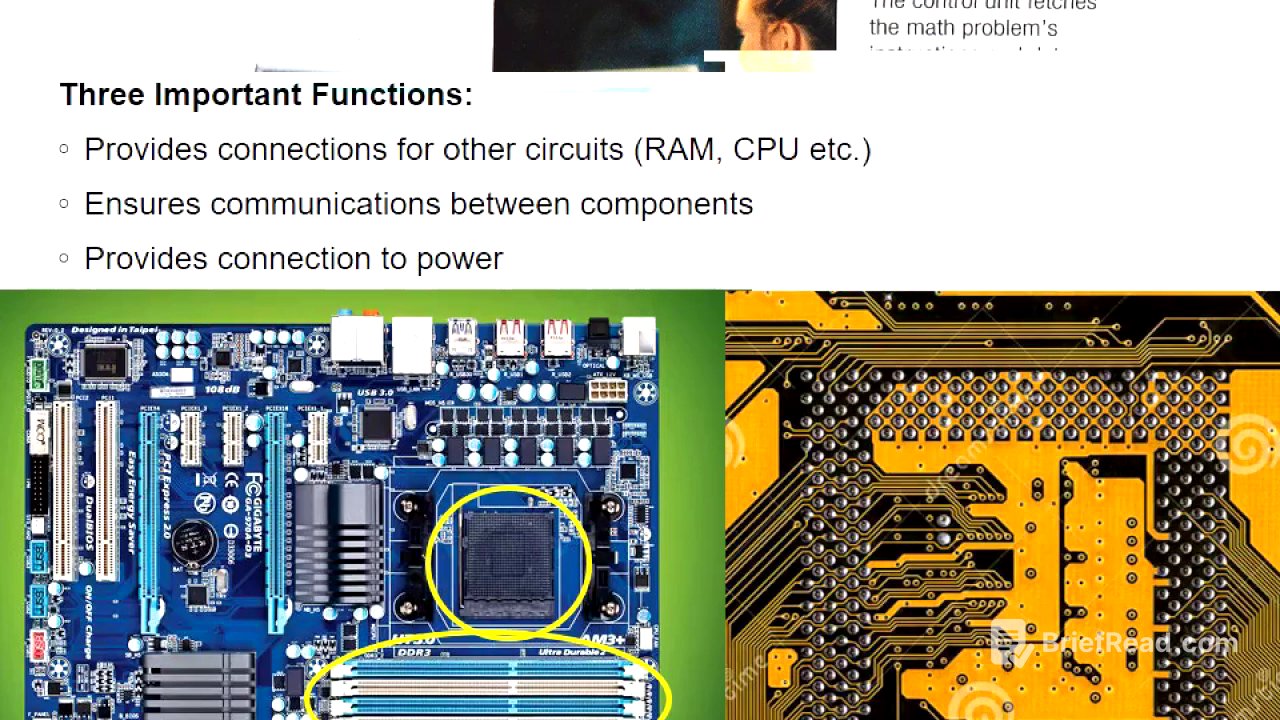
The video introduces the concept of modular design in computers, where separate components like the motherboard, peripherals, and other plug-in devices make up the system. This design facilitates easier repairs and upgrades. The motherboard is central, featuring sockets, slots, and connectors such as ZIF sockets for the CPU, DIMM slots for RAM, SATA connectors for hard drives, USB and VGA connectors, and expansion slots like PCI and PCIe for various cards including graphics cards.
Motherboard Functions and Machine Cycle [1:53]
The motherboard serves three primary functions: providing connections for circuits like RAM and video cards, ensuring communication between components via printed copper wires, and providing power to components through the power supply connection. The machine cycle within the CPU involves four steps: fetch (retrieving data and instructions from RAM), decode (separating the instruction into command and data), execute (the ALU performs the instruction), and store (sending the results back to memory).
RAM (Random Access Memory) Characteristics [3:49]
RAM consists of dual inline memory modules (DIMMs), which are green strips of PC boards with chips and gold pins on both sides. RAM is electronic with no moving parts, making it fast, and is volatile, losing its contents without power. It is more expensive per gigabyte than storage and is limited by the number of memory addresses accessible, which depends on the operating system (32-bit vs. 64-bit) and the number of RAM slots on the motherboard.
ROM (Read-Only Memory) and Firmware [5:55]
ROM differs from RAM as it retains its contents even without power and is not used as a scratch pad for constant reading and writing. ROM contains firmware, such as the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), which controls hardware at the lowest level and allows users to configure computer options. The BIOS runs a power-on self-test (POST) to check hardware and then loads the operating system into RAM.
CMOS and Firmware Upgrades [7:49]
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) stores BIOS settings and is powered by a battery to prevent data loss, including date and clock information. Users can access BIOS settings by pressing a specific key (like F10) during startup. Firmware, found in devices like printers, translates instructions for the hardware. Modern ROM is often EEPROM, which can be electronically erased and reprogrammed via flashing, a process that should not be interrupted.
Video/Graphics Card [11:02]
A video or graphics card plugs into the motherboard and connects the monitor to the computer. It contains a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) and RAM to create and send images to the monitor. The GPU offloads processing from the CPU, which is especially important for high-resolution displays. Laptops may have integrated video adapters and separate video cards, switching between them to save battery power. Connectors for graphics cards include DVI, VGA, HDMI, and Crossfire.