TLDR;
This YouTube video by PARMAR SSC is a recording of a live mock test session for the SSC CGL exam, focusing on statement-based questions. The instructor reviews questions from a mock test, providing detailed explanations, relevant facts, and tips on how to approach and solve these types of questions effectively. The session includes discussions on various topics such as geography, history, polity, economics, and general science, with an emphasis on revision and productive learning.
- The session emphasizes the importance of understanding concepts and facts.
- It provides strategies for tackling statement-based questions.
- It includes revision of key topics relevant to the SSC CGL exam.
Introduction and Mock Test Overview [0:27]
The instructor starts by welcoming everyone to the first mock test of level two for the upcoming SSC CGL exam. He confirms that the audio is clear and asks how many attendees attempted the mock test. The instructor mentions that there will be no class on July 31st due to a teachers' meeting, but the mock tests will otherwise be conducted daily. The PDF of the mock test will be shared in advance on the Parmar SSC Telegram channel at 12:00 PM daily. The instructor clarifies that the PDF is for reference during the class and for revision, and the actual test should be taken on the app or website.
Clarifications on PDF Answers and Exam Level [3:39]
The instructor addresses concerns about the answers being provided in the PDF, stating that from the next session, answers will not be included in the PDF. He explains that the answers are available after attempting the quiz on the app or website. The instructor emphasizes that these mock tests are designed for CGL aspirants and are at a graduation level, not for MTS or CHSL exams. He explains that the segregation of exam levels ensures that students preparing for CGL are challenged appropriately, while those preparing for lower-level exams will find the material easier.
Earth's Atmosphere and Climatic Conditions [7:44]
The session begins with the first question, which involves considering statements about the structure of the Earth's atmosphere and its role in climatic conditions. The instructor emphasizes the importance of identifying whether the question asks for correct or incorrect statements. He explains how to eliminate options to arrive at the correct answer. The instructor revises the layers of the atmosphere, including the troposphere (0-18 km, average 13 km), stratosphere (up to 50 km, contains the ozone layer), mesosphere (coldest layer, up to 85 km), and thermosphere (ionosphere, reflects radio waves). He also discusses the three stages of atmosphere evolution: loss of primordial atmosphere, degassing, and fixing. The instructor explains that the atmosphere is heated by terrestrial radiation, not incoming solar radiation, and discusses greenhouse gases, albedo, and the composition of the troposphere.
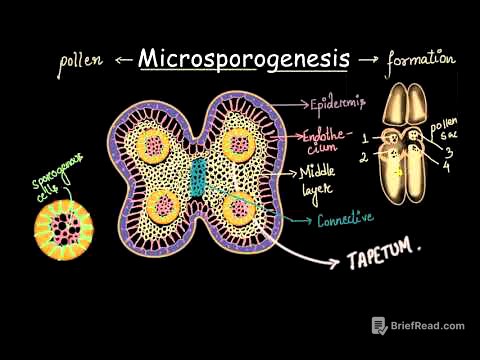
Urban Features and Cultural Aspects of the Indus Valley Civilization [15:43]
The second question focuses on the urban features and cultural aspects of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC). The instructor discusses the grid pattern layout of cities like Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, highlighting advanced urban planning. He mentions Dayaram Sahni's discovery of Harappa in 1921 and R.D. Banerjee's discovery of Mohenjo-daro in 1922. The instructor also touches on the drainage system, standardized brick ratio, and weights in multiples of 16. He explains that seals discovered from Harappan sites suggest animal domestication and early forms of writing, with most seals made of steatite. The instructor notes that the Mesopotamians called the Harappans "Melua." He emphasizes the importance of reading statements completely and carefully, as even one incorrect part can make the entire statement wrong.
Fundamental Rights Under the Indian Constitution [23:35]
The third question concerns the fundamental rights guaranteed under the Indian Constitution. The instructor recalls that fundamental rights are in Part III of the Constitution, taken from the USA (Bill of Rights), and span Articles 12 to 35. He notes that Article 15 prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, sex, and place of birth. The instructor explains that the right to property was removed from Article 31 and placed in Part 12 as Article 300A by the 44th Amendment in 1978. He discusses the five types of writs (Habeas Corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Certiorari, Quo Warranto) and the six fundamental rights: equality (14-18), freedom (19-22), right against exploitation (23-24), right to freedom of religion (25-28), cultural and educational rights (29-30), and right to constitutional remedies (Article 32). The instructor mentions the K.S. Putswamy judgment (Aadhar judgment) related to the right to privacy and the A.K. Gopalan case and Maneka Gandhi case regarding Article 21.
Major Civilian Awards in India [28:30]
The fourth question addresses the major civilian awards in India. The instructor states that Bharat Ratna is awarded for exceptional service in art, literature, science, and public service. He clarifies that Padma Vibhushan is a higher honor than Padma Bhushan. The instructor lists the five recipients of the Bharat Ratna in 2024: Karpoori Thakur, L.K. Advani, P.V. Narasimha Rao, Chaudhary Charan Singh, and M.S. Swaminathan. He also names the seven recipients of the Padma Vibhushan in 2024, including Kumudini Lakhia, L. Subramaniam, and Sharda Sinha.
Principles of Electric Current and Circuit Behavior [31:04]
The fifth question covers the principles of electric current and circuit behavior. The instructor explains that in a series circuit, the total resistance increases as more resistors are added, while in a parallel circuit, the voltage across each resistor remains equal to the total applied voltage. He reviews Ohm's law (V = IR) and the relationship between resistance, length, and area of cross-section (R = ρL/A). The instructor notes that Ohm's law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance but does not directly explain how resistance varies with a conductor's dimensions.
Vibrant Villages Programme [34:01]
The sixth question discusses the Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP). The instructor clarifies that VVP Two was launched to cover villages not included in VVP One. He mentions that the total budget outlay is approximately ₹6829 crores and covers villages on international borders, not just northern borders. The instructor emphasizes the importance of being aware of extreme keywords in statements.
Computer Terms and Quantum Supremacy [36:40]
The seventh question asks which computer term is associated with the concept of quantum supremacy. The instructor notes that this type of question, which is not statement-based and lacks scope for elimination, is difficult to answer without prior knowledge. The correct answer is quantum computing.
International Environmental Treaties and Conventions [37:57]
The eighth question concerns international environmental treaties and conventions. The instructor explains that the Montreal Protocol addresses the phasing out of substances that cause ozone layer degradation and was signed in 1987. He mentions the Kigali Amendment, which focuses on phasing out hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). The instructor clarifies that the Kyoto Protocol mandates emission reduction targets for developed countries, not all countries equally. He notes that the Paris Agreement allows countries to voluntarily set their own climate goals and submit nationally determined contributions.
Characteristics of Peninsular Rivers in India [40:46]
The ninth question focuses on the characteristics of peninsular rivers in India. The instructor explains that peninsular rivers are mostly rainfed and exhibit a seasonal flow pattern. He notes that these rivers generally do not form extensive deltas. The instructor clarifies that most rivers in the region originate from the Western Ghats and flow from the west to the east. He discusses various rivers, including Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Narmada, and Tapi, and their origins and drainage patterns.
Evolution and Spread of Buddhism [44:30]
The tenth question addresses the evolution and spread of Buddhism. The instructor explains that Buddhism was divided into Hinayana and Mahayana during the Fourth Buddhist Council. He describes the differences between Hinayana (Theravada), which is more conservative and relies on written scriptures like the Pali Canon, and Mahayana, which introduces the concept of Buddhist entities (Bodhisattvas). The instructor notes that Ashoka's missionary efforts played a significant role in spreading Buddhism beyond India.
Emergency Provisions in the Indian Constitution [48:49]
The eleventh question concerns the emergency provisions in the Indian Constitution. The instructor explains that during a financial emergency, the President can reduce the salaries of all government employees, including judges. He clarifies that financial emergency is under Article 360, not 356. The instructor recalls the three types of emergencies: national emergency (Article 352), state emergency or President's rule (Articles 356 and 365), and financial emergency (Article 360).
International Institutions and Headquarters [53:32]
The twelfth question asks about international institutions and their headquarters. The instructor states that the International Court of Justice (ICJ) is located in The Hague, Netherlands, not Geneva, Switzerland. He notes that the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is in Washington D.C. The instructor briefly discusses the Bretton Woods Conference, the General Agreement on Trade and Tariff (GATT), and the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Monetary Policy and CRR [54:28]
The thirteenth question is about monetary policy and the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR). The instructor explains that higher CRR reduces liquidity in the economy. He discusses the roles of CRR and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) and the effects of increasing or decreasing various rates (CRR, SLR, bank rate, repo rate, reverse repo rate) on liquidity. The instructor defines tight/hawkish/contractionary and expansionary/dovish monetary policies.
Acids, Bases, and Neutralization Reactions [56:31]
The fourteenth question covers acids, bases, and neutralization reactions. The instructor explains that acids release H+ ions in aqueous solutions and have a pH less than 7. He notes that bases are bitter in taste, slippery, and have hydroxide ions present. The instructor clarifies that neutralization reactions always form salt and water, not hydrogen gas. He discusses the pH scale, alkalis, and the nature of metal oxides.
Inheritance and Gene Expression [59:06]
The fifteenth question addresses inheritance and gene expression. The instructor explains that dominant traits are always expressed in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions. He discusses Mendel's laws: the law of dominance, the law of segregation, and the law of independent assortment. The instructor notes that the phenotype is the observable expression of the genotype and is not always identical to the genotype.
Books and Authors [1:03:35]
The instructor presents a matching question involving books and authors. The books mentioned include "Why I am a Hindu," "Paradoxical Prime Minister," "Ambedkar Life," "God of Small Things," "Ministry of Utmost Happiness," "Ordinary Man's Guide to Empire," "India's Struggle for Freedom," and "Philosophy of the Nation." The authors include Shashi Tharoor, Arundhati Roy, Bipin Chandra, and S. Radhakrishnan.
Delhi Sultanate Rulers and Administrative Contributions [1:04:29]
The instructor presents a matching question involving Delhi Sultanate rulers and their administrative contributions. The rulers mentioned include Iltutmish, Alauddin Khilji, Mohammad Bin Tughlaq, and Firoz Shah Tughlaq. The administrative contributions include the introduction of silver tanka and copper jethal, market control measures, shifting the capital from Delhi to Daulatabad, and establishing Diwan Bandgan and Diwan Khairat departments.
Geological Events in Chronological Order [1:09:02]
The instructor presents a question requiring the arrangement of geological events in chronological order. The events include the breakup of Pangea, the formation of the Himalayas, the opening of the Atlantic Ocean, and the formation of the Western Ghats. The instructor explains the Continental Drift Theory by Alfred Wegener and the formation of the Himalayas due to the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates.
Revolt of 1857 [1:13:07]
The instructor discusses the Revolt of 1857. He clarifies that the revolt began with the mutiny of sepoys in Meerut, not Barrackpore. The instructor mentions Mangal Pandey from the 34th Bengal Native Infantry and the Enfield rifle with greased cartridges as immediate causes. He notes that the revolt was not completely spontaneous and lacked planning. The instructor recalls leaders from various regions, including Maulvi Ahmadullah from Faizabad, Rani Lakshmibai from Jhansi, General Bhakt Khan from Delhi, Begum Hazrat Mahal from Lucknow, and Nana Saheb and Tatiya Tope from Kanpur.
Early Sessions of the Indian National Congress (INC) [1:16:27]
The instructor discusses the early sessions of the Indian National Congress (INC). He states that the first session of the INC was presided over by Vomesh Chandra Banerjee and held in Bombay. The instructor notes that moderates believed in constitutional agitation and prayer petitions. He clarifies that the INC did not demand complete independence from the first day; Purna Swaraj was discussed in the Lahore session of 1929.
Federal Constitution with Unitary Bias [1:20:34]
The instructor discusses the federal constitution with a unitary bias. He explains that the Indian Constitution is federal with a unitary bias, with the division of powers between the center and the state. The instructor notes that the Concurrent List was taken from the Constitution of Australia, while the concept of a federation with a strong center was taken from Canada.
Five Year Plans [1:25:09]
The instructor discusses the Five Year Plans. He states that the First Five Year Plan (1951-1956) focused on agriculture, while the Second Five Year Plan was based on the PC Mahalnobis model and prioritized heavy industries. The instructor notes that the 12th Five Year Plan was the final plan before the Planning Commission was dissolved.
Tripartite Struggle for Kannauj [1:27:23]
The instructor discusses the Tripartite Struggle for Kannauj. He clarifies that the struggle was mainly among the Palas, Gurjar Pratiharas, and Rashtrakutas, not the Cholas. The instructor notes that all three wanted to control Kannauj due to its symbolic prestige and economic importance.
Carbon Credit Concept [1:28:48]
The instructor explains the concept of carbon credit in environmental economics. He states that carbon credit is a certificate permitting a country or organization to emit a certain amount of CO2, with one credit equaling one ton of CO2.
Important Dates and Homework [1:30:07]
The instructor mentions important dates, including Environment Day (June 5) and International Women's Day (March 8). He provides homework questions about World Population Day and what is celebrated on March 22, April 22, and May 22. The instructor concludes by providing contact numbers for technical queries and important messages.