TLDR;
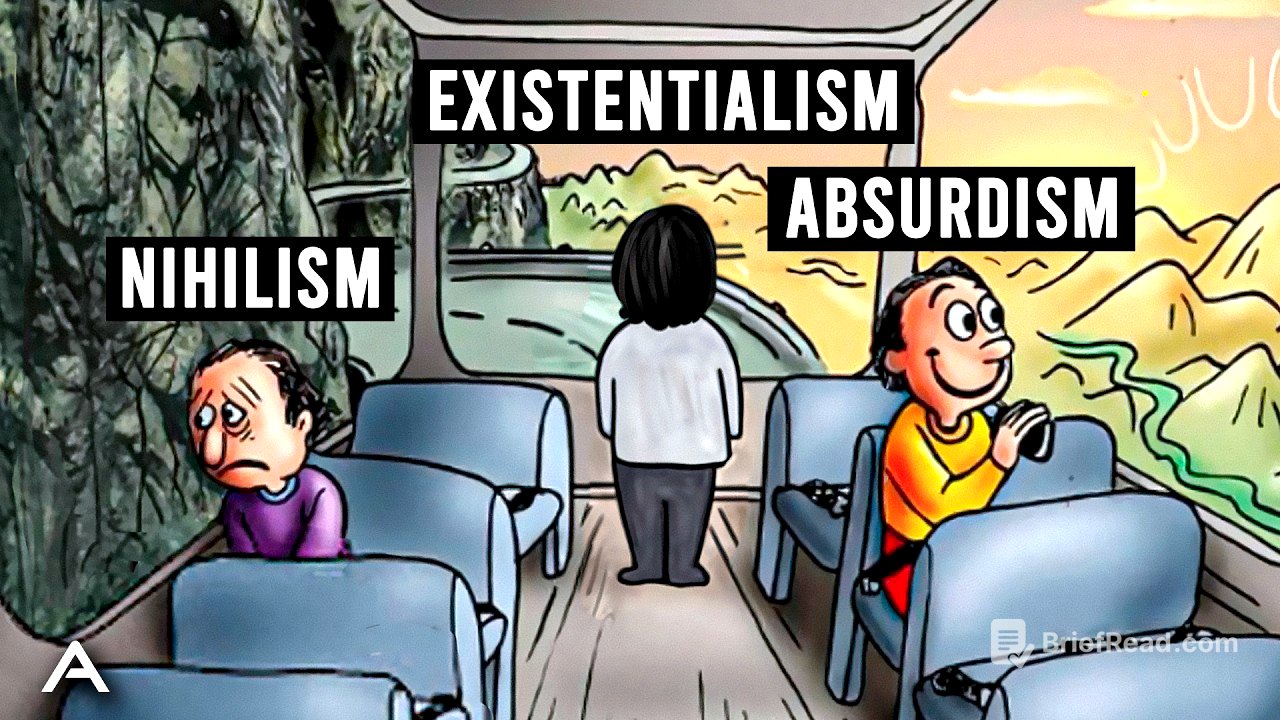
This video explores three philosophical concepts—existentialism, absurdism, and nihilism—as responses to the inherent meaninglessness of life. It explains how existentialism encourages individuals to create their own meaning, absurdism advocates for defiance against life's absurdity, and nihilism embraces the meaninglessness of existence. The video uses examples like Prince Harry, Albert Camus, Friedrich Nietzsche, and Nelson Mandela to illustrate these philosophies and their practical implications.
- Existentialism: Emphasizes personal freedom and responsibility in creating meaning.
- Absurdism: Acknowledges life's inherent contradictions and encourages defiance.
- Nihilism: Embraces the meaninglessness of life, sometimes leading to despair or optimistic re-evaluation.
Introduction: The Existential Crisis [0:12]
The video starts by describing a common scenario of feeling overwhelmed by life's problems, leading to an existential crisis where one questions the meaning of their existence. It introduces the idea that philosophies like existentialism can offer answers to these profound questions, challenging individuals to embrace their freedom and create meaning in the face of life's uncertainties. The introduction sets the stage for exploring how different philosophical perspectives address the fundamental human desire for purpose and understanding.
Sponsor Message: BetterHelp [1:14]
The video includes a brief message from the sponsor, BetterHelp, an online therapy service. BetterHelp aims to make therapy more accessible and affordable by connecting users with professional therapists through an online platform. They emphasize the importance of human empathy in therapy, contrasting it with AI solutions, and offer a discount for the first month of service to viewers who sign up through the provided link.
Existentialism: Defining Your Own Essence [2:17]
Existentialism is presented as a philosophy that gained prominence through thinkers like Jean-Paul Sartre, emphasizing individual freedom and the rejection of predetermined essences. It contrasts with essentialism, the belief that individuals are born with intrinsic attributes defining their identity. Existentialism posits that existence precedes essence, meaning people define their own purpose through their choices and actions, exemplified by Prince Harry's decision to leave the royal family.
Freedom and Responsibility in Existentialism [4:30]
The summary explains that existentialism asserts individuals are not bound by societal or religious norms, highlighting the responsibility that comes with freedom. Choosing to live authentically means accepting the consequences of rebelling against conventional authority, while living according to a predetermined rule book is considered "bad faith." The core of existentialism is that individuals must determine their own meaning in life, aligning their actions with their genuine desires rather than succumbing to external pressures or fears.
Absurdism: Embracing the Meaningless [6:28]
Absurdism is introduced as a philosophy that goes further than existentialism by suggesting that life is inherently meaningless, and any attempt to find purpose is futile. It encourages individuals to confront their existence with defiance, embracing the contradictions of life without succumbing to nihilism or despair. Albert Camus is highlighted as a key figure who viewed absurdism as a rebellion against humanity's search for meaning, urging people to acknowledge the absurd as the first step to living in reality.
Existentialism vs. Absurdism: Responding to Meaninglessness [7:56]
The summary contrasts existentialism and absurdism, noting that while absurdism sees meaning as a futile endeavor, existentialism encourages active engagement with life. Existentialism emphasizes authenticity, self-awareness, and the pursuit of meaning, even when faced with life's indifference. It challenges individuals to take ownership of their lives and find significance in their attachments, using the example of losing a home to illustrate how existentialism encourages finding meaning in response to adversity.
Nihilism: Embracing Hopelessness [9:12]
Nihilism is presented as a philosophy that embraces the meaninglessness of life, often associated with despair. It contrasts with both absurdism and existentialism, with nihilists doubling down on life's meaninglessness rather than defying it or seeking personal meaning. The summary mentions Friedrich Nietzsche's concept of the "death of God" as a precursor to nihilistic thoughts, leading to a state where traditional values are questioned and found empty.
Optimistic Nihilism: Finding Opportunity in Meaninglessness [10:17]
The video introduces optimistic nihilism as a variation that challenges conventional values and sees the removal of traditional meanings as an opportunity to create new moral and cultural horizons. It suggests that this perspective can be liberating, opening doors to values based on collective and personal will. Elon Musk is presented as an example of someone who embodies optimistic nihilism through his boundary-pushing approach to technology and space exploration.
Existentialism vs. Nihilism: Shaping a Meaningful Existence [11:35]
The summary contrasts existentialism and nihilism, highlighting that while nihilism sees no inherent meaning in the universe, existentialism believes in the capacity to live a defined and fulfilling life through choices and actions. Existentialism emphasizes personal growth, ethical engagement, and the freedom to shape one's life and identity, even in a universe lacking objective meaning. It advocates for confronting modern existential dilemmas with a focus on creating personal meaning.
Comparing Philosophies: Solitary Confinement Analogy [12:00]
The video uses the analogy of being trapped in solitary confinement to illustrate the differences between absurdism, nihilism, and existentialism. Absurdism teaches one to laugh in the face of suffering, nihilism suggests doing nothing because nothing matters, and existentialism encourages using the experience for self-reflection and personal evolution. Nelson Mandela's commitment to human dignity during his imprisonment is given as an example of finding meaning through personal struggles, reflecting the existentialist theme.
Conclusion: Creating Meaning in an Absurd World [13:43]
The video concludes by emphasizing that existentialism allows individuals to embrace individuality and create meaning, even in a world that may seem absurd. It encourages viewers to see life as an art form, transforming uncertainties into opportunities for personal growth. The final message is a call to reflect on what truly matters, prioritize a meaningful life, and live authentically, even when facing challenges or working in unfulfilling fields, to avoid succumbing to "bad faith."