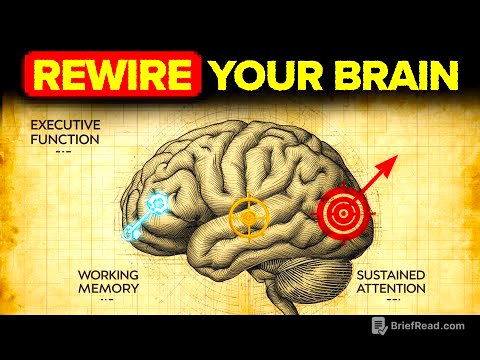
TLDR;
This video explores why intelligent people sometimes do unintelligent things, highlighting that intelligence isn't a straightforward gift but a double-edged sword. It discusses how evolution has shaped our brains with unique strengths and corresponding blind spots, leading to different cognitive specializations. The video introduces the concept of "cognitive trade-offs," where excelling in one area often means a compromise in another. It also touches upon neurodiversity, suggesting that conditions like dyslexia, autism, and ADHD aren't necessarily defects but variations that can be advantageous in the right environment. The video concludes by providing tools to help viewers decode their own cognitive wiring and make better life decisions.
- Intelligence is a double-edged sword with associated blind spots.
- Cognitive trade-offs lead to specialization in certain areas while compromising others.
- Neurodiversity can be an advantage in the right environment.
- Understanding your cognitive wiring can lead to better life decisions.
Intro [0:00]
The video starts by questioning why highly intelligent individuals sometimes make seemingly stupid decisions, using examples like Vitalik Buterin, Elon Musk, and Mark Zuckerberg. It points out that there's a secret code of nature that dictates the wiring of our brains and personalities. Intelligence is portrayed not just as a gift, but as a double-edged sword, or a loaded gun that can backfire. The video references the case of Steve Jobs, whose artistic genius was undermined by his rejection of conventional cancer treatment. It also mentions Jack Parsons, a NASA engineer who was deeply involved in occult practices, questioning whether a high IQ and pattern-obsessed mind can sometimes see connections that aren't really there. The speaker emphasizes that our understanding of intelligence is dangerously incomplete, and that everyone has a unique strength coupled with a significant blind spot. The goal is to understand reality, identify these blind spots, and reverse the glitch in our brains.
The Four Categories of Brains [4:36]
The video discusses how the human brain evolved in response to fear and the need for survival. In ancient times, humans lived in constant fear, which drove the development of different cognitive strategies. This led to the emergence of four categories of brains: Technical Brains, Social Brains, Explorers, and Stabilizers. Technical brains are good at logic, pattern recognition, and technical details. Social brains excel at reading emotions, forming alliances, and gaining power. Explorers are those who overcome fear to discover new paths. Stabilizers focus on maintaining existing responsibilities and ensuring the well-being of the community.
Cognitive Trade-Off [7:24]
The video introduces the concept of "cognitive trade-offs," explaining that these traits didn't develop as a package deal but rather in trade-offs. This means that excelling in one area often comes at the expense of another. Nature favored specialization over generalization. This principle is referred to as the cognitive trade-off, which is the first blind spot of the brain. The video also includes a promotional segment for CoinDCX, highlighting its features for crypto trading, such as a user-friendly interface, SIP options, and transparent fee structure.
The Spectrum of Brains [10:54]
The cognitive trade-off has led to the creation of different spectrums of human brains. On one end, there's the technical brain, and on the other, the social brain. The more a brain excels at logical reasoning and technical patterns, the weaker it is in social smartness, and vice versa. These are referred to as the "systemizing brain" versus the "mentalizing brain." Similarly, there's the explorer brain, driven by dopamine, and the stabilizer brain, driven by serotonin. The more someone is inclined towards exploration, the less they prefer stability. These four traits form a cognitive gradient, and most brains today stretch across these evolutionary dimensions.
Neurodiversity [13:18]
The video introduces the concept of neurodiversity, which is the idea that variations in brain function and behavioral traits are normal and valuable. Neurodiversity is a design for survival, not a defect. However, society often views neurodivergence as a defect rather than a design. People whose brains don't fit into the current system are often labeled as stupid. Conditions like dyslexia, autism, and ADHD are often seen as disabilities, but many successful individuals have these conditions. The video emphasizes that these individuals simply need the right environment to thrive.
Why Specialization? [15:01]
The video explains why nature didn't create polymathic geniuses but instead opted for neurodiversity and specialization. The first reason is energy conservation. The brain consumes a significant amount of energy, so it can only master a few skills. The second reason is the law of evolution. Survival requires variety. A tribe of only explorers would get lost and die, while a tribe of only stabilizers would freeze in the winter. Neurodiversity makes cooperation possible.
Finding Yourself [16:25]
The video emphasizes the importance of understanding your brain's base code. The speaker shares his personal experience of discovering that his cognitive wiring aligns with Asperger's syndrome. This understanding helped him make sense of his life and career choices. The video then discusses where personalities like Vitalik Buterin and Elon Musk fall on the spectrum, noting their strengths in technical fields and potential compromises in social skills. It also mentions Shah Rukh Khan as an example of someone with high social intelligence.
Explorers vs Stabilizers [19:56]
The video discusses the spectrum of explorers versus stabilizers. Explorers, like Neil Armstrong and Charles Darwin, are willing to take risks for the sake of discovery. On the opposite end are stabilizers, like government employees, who prioritize stability and routine. Explorers change the world, while stabilizers run it. The video poses the question of whether you are a technical brain or a social brain, an explorer or a stabilizer, or a rare hybrid that can make history.
Decoding Your Brain [22:17]
The video provides a tool to decode your base wiring in two simple steps. Step one involves answering questions in a basic screening tool to understand your thinking style alignment. It's important to answer honestly and select options that reflect your natural behavior. Step two depends on the results of the first test. If the results indicate high neurodivergence, a proper scientific-grade test is recommended. Links to these tests are provided in the description. The video concludes by emphasizing that intelligence is environmental, and the next video will discuss the control button that governs how your intelligence is used.