TLDR;
Okay, so basically, this whole thing is about a talk on biodiversity, conservation, and sustainable human life, especially in the context of environmental science. The speaker, Professor Sandhu, emphasizes the importance of balancing economic benefits with the needs of future generations, touching upon the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and how India can improve its standing in achieving them. He stresses the need for collective action, highlighting how individual efforts can contribute to larger environmental goals and even boost a college's ranking.
- Importance of balancing economic benefits with environmental conservation.
- Overview of the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and their relevance to environmental science.
- Practical steps individuals and institutions can take to contribute to sustainable development.
Introduction and Speaker Intro [0:02]
So, the session starts with an introduction by Dr. Gajendra Namdev, who welcomes everyone and introduces Professor Sharad Singh Sandhu. Dr. Namdev mentions that Professor Sandhu is the Director of the MM-TTC and the Director of the Design Innovation Center, also heading the Department of Biological Sciences at Rani Durgavati University, Jabalpur. He lists Professor Sandhu's many achievements, like his numerous publications, awards, and international fellowships, highlighting his extensive experience and contributions to science and education.
Welcome Address and Context Setting [5:00]
Professor Sandhu starts by thanking the Vice-Chancellor and Registrar for allowing the program to be conducted at MM-TTC. He acknowledges UGC for providing the slot and mentions the successful completion of several courses. He welcomes participants from all over India, assuring them of an engaging online experience with eminent speakers. Professor Sandhu then shares that he was the President of the Environment Science section at the Indian Science Congress for three years and invites everyone to participate in the upcoming Science Congress session, encouraging them to submit abstracts and presentations. Instead of a typical introductory lecture, he plans to discuss the sustainable development of the environment, aligning with his Indian Science Congress lecture, so that participants can incorporate it into their education and curriculum.
Understanding Environment Science and Sustainable Development [9:58]
Professor Sandhu explains that environment science involves studying the environment, integrating social and economic aspects to achieve livable, viable, and equitable conditions, which is what sustainability is all about. Sustainable development means using economic benefits to improve living standards for the present generation without compromising the needs of future generations. It involves conserving resources in both quantity and quality. The main aim is to balance population, resources, environmental aspects, and development. He mentions the UN's quantitative time-bound goals from 1960 to 2000, highlighting achievements like the eradication of smallpox and increased life expectancy.
UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [18:26]
Professor Sandhu talks about the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), or SDG's for short, created to ensure prosperity, peace and partnership for people and the planet. These goals address poverty, food, health, education, water, sanitation, energy, and women's empowerment. He emphasizes that governments focus on these issues because they align with achieving sustainable development and improving India's global standing. Sustainable economic growth, full employment, and reduced inequality are crucial. No country should be left behind, promoting a global family concept. The goals also cover climate action, marine and terrestrial ecosystems, peace, social justice, and global partnerships.
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals [20:54]
Professor Sandhu lists the 17 Sustainable Development Goals set by the UN. These include no poverty, zero hunger, good health and well-being, quality education, gender equality, clean water and sanitation, affordable and clean energy, decent work and economic growth, industrial innovation and infrastructure, reduced inequalities, sustainable cities and communities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, life below water, life on land, peace, justice and strong institutions, and partnership for the goals. He suggests that incorporating these goals into teaching and college activities can lead to green environment certifications and better grades.
Necessity to Sustain Environment for Better World Development [21:26]
Professor Sandhu raises the question of whether the world will become a better place in the coming years. He notes that while the UN believes it's possible, there are challenges like global power struggles. The 17 SDGs aim to address these issues, but achieving them by 2030 seems nearly impossible given current global crises. He reiterates the importance of each goal, from poverty reduction and quality education to gender equality and clean water.
Achieving SDGs Through Biodiversity [27:32]
Professor Sandhu explains how biodiversity can help achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. To end poverty, he suggests saying no to deforestation and plastic use, as biodiversity loss leads to disasters that harm communities. To end hunger, he promotes crop rotation and the use of biopesticides instead of chemical ones, mentioning specific bacteria and fungi that can control pests. For good health, he emphasizes planting trees and incorporating biodiversity into urban planning, referencing the green Mumbai Airport.
Quality Education, Gender Equality and Clean Water [30:56]
Professor Sandhu stresses the importance of stopping child labor and ensuring quality education by removing unqualified educators. He addresses gender inequality, particularly the wage gap, advocating for equal pay for equal work. For clean water and sanitation, he suggests planting trees, implementing water treatment methods, and applying the "Five R" principles: reduce, reuse, recover, recycle, and replenish.
Affordable Energy, Economic Growth and Sustainable Infrastructure [33:28]
Professor Sandhu promotes the use of solar and wind energy, encouraging the adoption of these sources for heating and power. He highlights the importance of planting trees to reduce energy use for cooling. For economic growth, he emphasizes fair wages and decent work conditions. He also discusses building resilient infrastructure and promoting sustainable industrialization through innovations like green roofs and solar systems.
Reducing Inequalities and Sustainable Cities [35:26]
Professor Sandhu advocates for educating and investing in biodiversity conservation, especially in rural areas. He gives the example of Cordyceps militaris, a valuable fungus that grows on insects, emphasizing the economic benefits of preserving insect populations. He also stresses the importance of creating safe, resilient, and sustainable cities with ample green spaces, contrasting the temperature differences between areas with and without trees.
Responsible Consumption, Climate Action and Life Below Water [37:24]
Professor Sandhu urges responsible consumption and production patterns, advising against overproduction that leads to waste. He highlights the importance of climate action, referencing the protective effect of trees during tsunamis. He also discusses the need to protect marine ecosystems by reducing plastic pollution and promoting sustainable fishing practices.
Life on Land, Peace, Justice and Partnership for the Goals [39:25]
Professor Sandhu emphasizes protecting terrestrial ecosystems and promoting biodiversity by preventing hunting. He advocates for peaceful societies and strong institutions to combat misinformation and ensure justice. He concludes by stressing the importance of global partnerships to achieve all the Sustainable Development Goals, encouraging actions like cycling, reducing waste, and planting trees.
Why SDGs are Needed and India's Current Status [41:26]
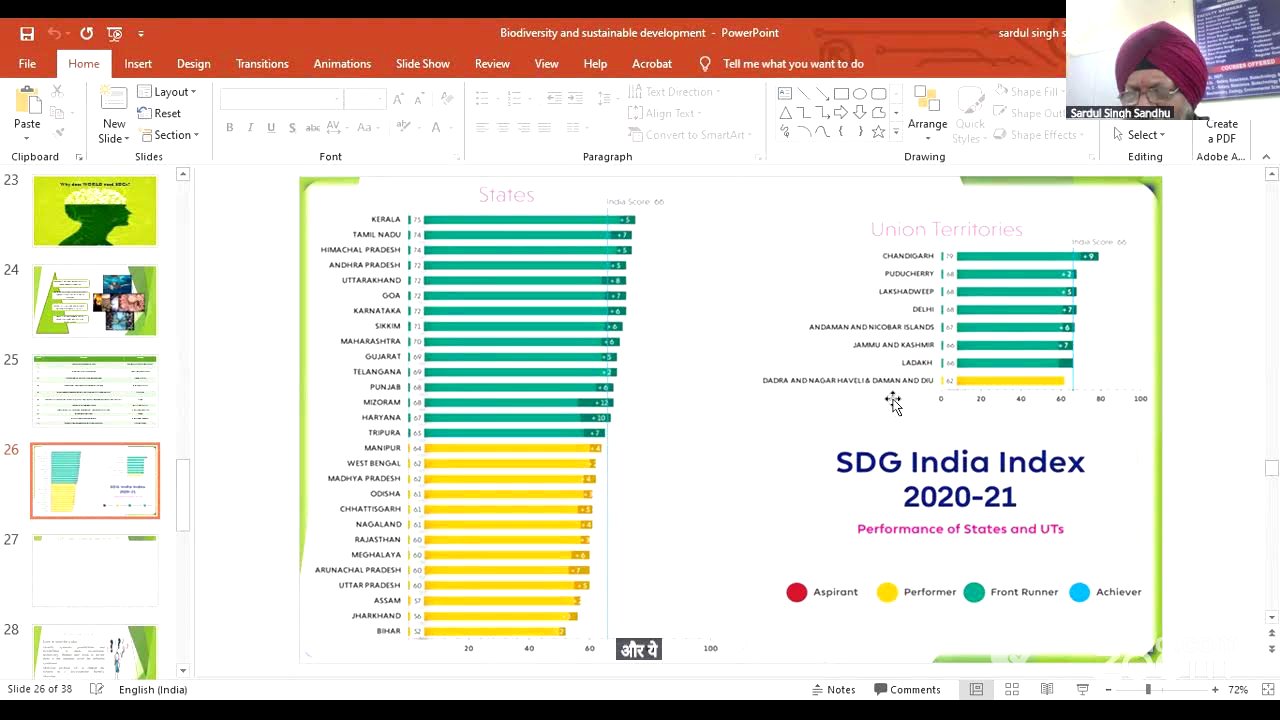
Professor Sandhu explains why the SDGs are crucial, citing alarming statistics such as the 8 million tons of plastic entering the ocean annually and the millions of people living in water-stressed countries. He presents data on India's SDG index, noting that some states are performing better than others and that India ranks 121st globally. He urges everyone to work towards achieving these goals to improve the country's standing and ensure a sustainable future.
Conclusion and Call to Action [44:21]
Professor Sandhu summarizes the key points, emphasizing the need to keep the SDGs in mind, identify possibilities for change, and mobilize potential to create a development-friendly environment. He encourages civil society to link these goals at every level. Despite the simplicity of environmental science, achieving these goals requires significant effort. He concludes by thanking everyone for their attention and offering to discuss the lecture further via email.