TLDR;
This video provides a concise overview of hydroceles, focusing on their definition, clinical presentation, examination findings, potential causes, and management strategies. Key points include understanding the Tunica vaginalis's role, differentiating hydroceles from hernias, and recognising the importance of excluding serious underlying causes. Management options range from conservative approaches to surgical intervention, aspiration, and sclerotherapy.
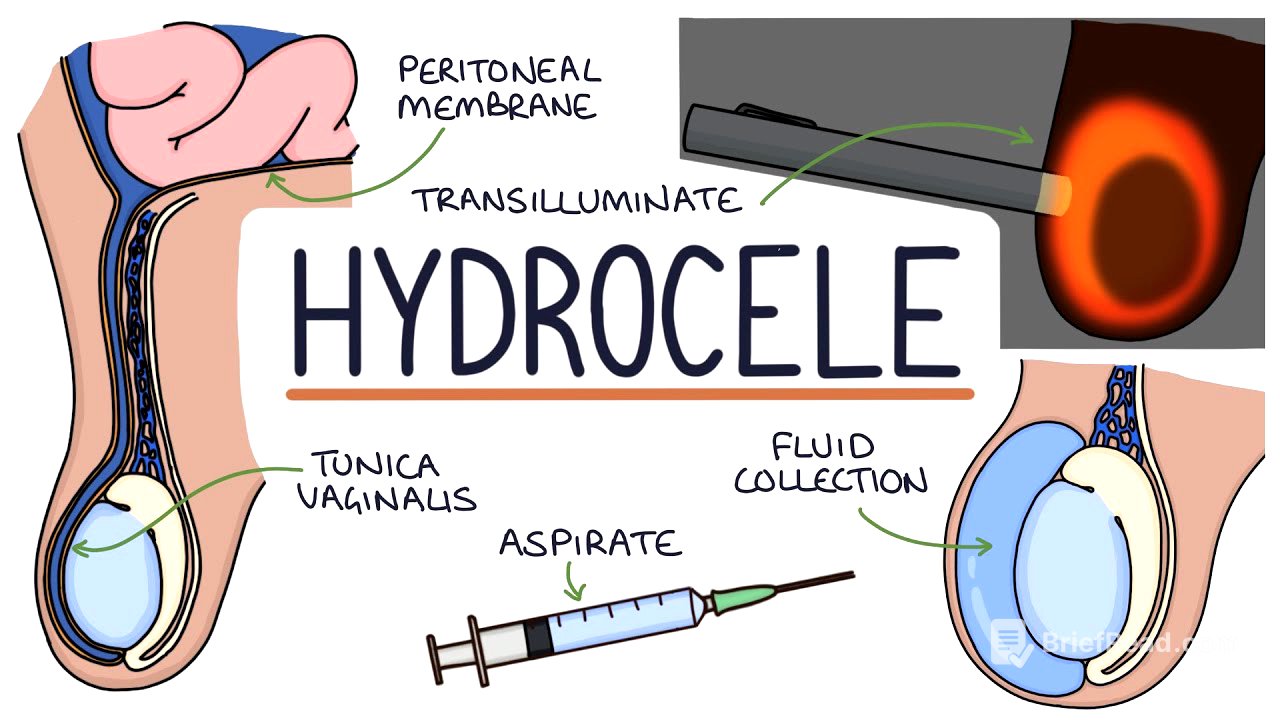
- Hydroceles are fluid collections within the Tunica vaginalis, typically presenting as painless scrotal swellings.
- Examination findings include a palpable testicle within a soft, fluctuant, irreducible lump that transilluminates.
- Management involves excluding serious causes like testicular cancer and considering conservative management, surgery, aspiration, or sclerotherapy based on the hydrocele's size and symptoms.
Introduction to Hydroceles [0:03]
A hydrocele is defined as a collection of fluid within the Tunica vaginalis, the membrane surrounding the testes. Hydroceles typically manifest as painless, soft swellings in the scrotum. The Tunica vaginalis is a sealed pouch that originates from the peritoneal membrane during fetal development, eventually separating and partially covering each testicle within the scrotum.
Examination Findings [1:06]
During examination, the testicle is palpable within the hydrocele, which feels soft and fluctuant and can vary in size. The lump is irreducible and lacks bowel sounds, distinguishing it from a hernia. Transillumination, achieved by shining a light through the skin into the hydrocele, causes the fluid to light up, potentially revealing the testicle floating within.
Causes and Management [1:46]
Hydroceles can be idiopathic, with no identifiable cause, or secondary to conditions such as testicular cancer, testicular torsion, epididymo-orchitis, infection, or testicular trauma. Management involves ruling out serious causes like testicular cancer. Idiopathic hydroceles may be managed conservatively, requiring no active treatment. For large or symptomatic hydroceles, options include surgery, aspiration, or sclerotherapy.