TLDR;
This YouTube video provides an introduction to React, a JavaScript library used for building front-end applications. It explains why React is beneficial, its key features such as single-page applications, component-based architecture, and declarative nature. The video also covers the history of React, the importance of NodeJS for running React applications, and how to set up a React app using Vite. Additionally, it touches on the concept of Virtual DOM and its role in making React faster compared to traditional JavaScript. The session includes practical demonstrations of creating a React app, understanding its file structure, and adding styling.
- React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
- Key features include single-page applications, component-based architecture, and a declarative approach.
- NodeJS is essential for running React applications.
- Vite is used as a build tool to create React apps.
- Virtual DOM enhances performance by efficiently updating the UI.
Introduction to React [36:50]
The session introduces React as a JavaScript library for building front-end applications, highlighting its advantages over traditional HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. React is described as a pre-built template that speeds up development. It's faster than JavaScript due to its pre-defined components and functions that can be easily imported and used.
Key Features of React [44:36]
React's top three features are single-page applications, component-based architecture, and its declarative nature. Single-page applications provide a smoother user experience by rendering only specific components instead of reloading the entire page, as demonstrated by comparing YouTube (single-page) and Flipkart (multi-page). Component-based architecture involves breaking down the UI into reusable components, making the code easier to understand and maintain. React's declarative nature allows developers to specify what they want to achieve without detailing how to achieve it.
Single and Multi-Page Applications [46:02]
Multi-page applications reload the entire page when a button is clicked, while single-page applications only render the specific component. Flipkart is used as an example of a multi-page application, where clicking on different categories reloads the entire page. YouTube serves as an example of a single-page application, where clicking on different sections only updates the relevant content without a full page reload.
Component-Based Architecture Explained [52:30]
Component-based architecture is likened to using functions in JavaScript, where each component is a reusable piece of code. In React, elements like "grocery", "mobiles", and "fashion" on a website can be treated as individual components. Dividing code into components makes it easier to understand and maintain.
Declarative Nature of React [54:38]
React's declarative nature is contrasted with an imperative approach. In an imperative approach, every detail must be specified, whereas in a declarative approach, the desired outcome is simply stated. For example, instead of specifying every detail of building a house (imperative), you simply request a 3BHK house (declarative). React allows developers to specify the desired functionality without needing to detail the implementation.
React History and NodeJS Installation [57:38]
React was created by a Facebook employee to simplify building applications. The current version is V21. To run React, NodeJS is required, which serves as an environment for running JavaScript applications. The video guides viewers through downloading and installing NodeJS, emphasising the need to verify the installation by running the command node -v in the command prompt.
React Documentation and NodeJS Verification [1:03:51]
The official React documentation at react.dev is highlighted as a resource for learning React concepts. The video revisits the NodeJS installation process, instructing viewers to verify the installation by running node -v in the command prompt. A successful installation will display the NodeJS version (V22).
Why React is Faster: Virtual DOM [1:08:34]
React's speed is attributed to its use of a Virtual DOM, which is a copy of the real DOM (Document Object Model). The DOM is an interface between HTML and JavaScript, representing the structure of a document as a tree of nodes. Unlike the real DOM, where any change causes the entire tree to update, the Virtual DOM updates only the specific component that has changed, leading to faster performance.
Real DOM vs Virtual DOM [1:15:57]
In a real DOM, any change requires the entire tree to be re-rendered, whereas the Virtual DOM only updates the specific component that has changed. The Virtual DOM compares the current state with the previous state and only updates the necessary parts of the real DOM. This process involves state change detection, difference computation, and re-rendering of only the changed component.
Creating a React App with Vite [1:34:00]
The video guides viewers through creating a React app using Vite, a build tool that enhances the development experience. The process involves creating a new folder, opening it in VS Code, and running the command npm create vite@latest . in the terminal. Viewers are prompted to select a framework (React) and a variant (JavaScript).
NPM and Node Modules [1:47:01]
NPM (Node Package Manager) is introduced as a tool that manages NodeJS packages. To start the React application, the command npm install is run to download the necessary node modules. The node modules folder contains pre-built functionalities and definitions required for the React app.
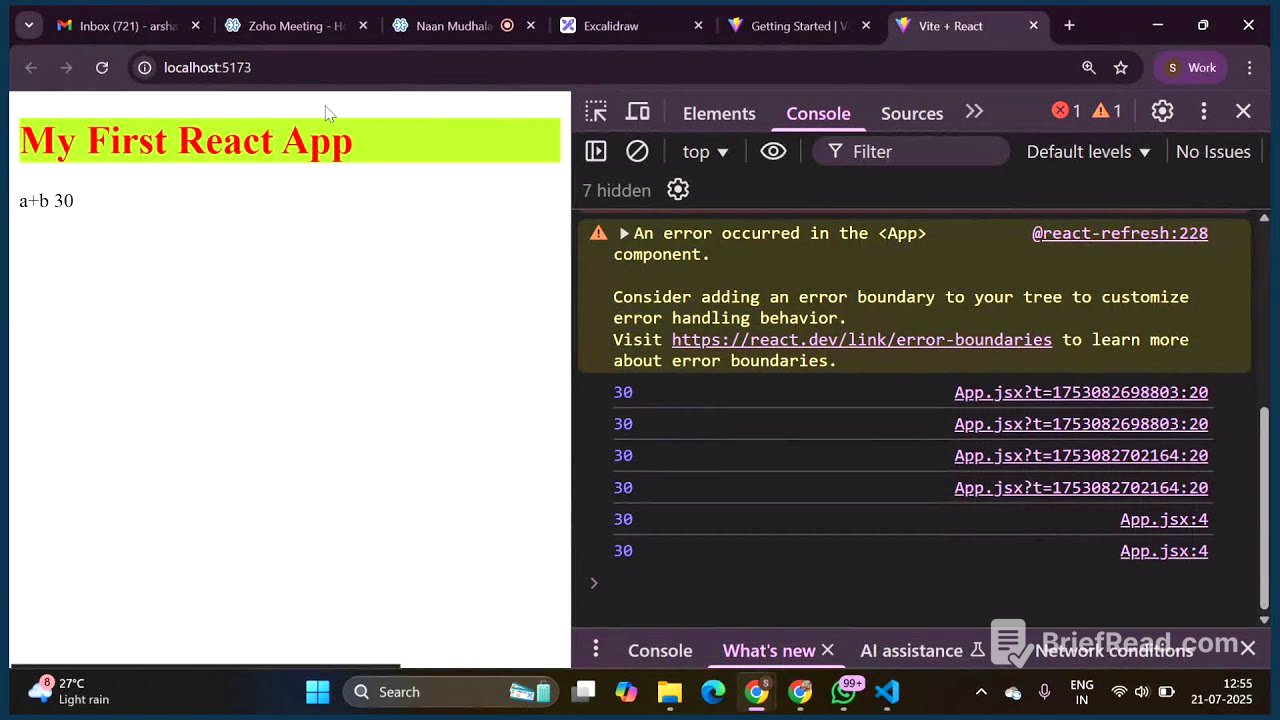
Running the React App and File Structure [1:50:33]
The command npm run dev is used to start the React application. The application runs on a local host with a default port number of 5173. The video explains the significance of the HTTP protocol, local host, and the port number. The file structure of the React app is explored, including the node modules, public folder (for static files), and the src folder (for React code).
Understanding Key Files: index.html and main.jsx [1:58:24]
The index.html file is the root file for the React application, containing a div with the id "root" that establishes a connection to the src folder. The main.jsx file uses the DOM to create an element and render the app component. Commenting out the render function in main.jsx results in an empty screen, demonstrating its role in displaying content.
Package.json: The Heart of the NodeJS Application [2:01:45]
The package.json file is described as the heart of the NodeJS application, containing essential information about the project, including dependencies. Dependencies are the packages that the project relies on to function correctly. The file includes scripts for development, building, and previewing the application.
App.jsx: Components and JSX [2:04:52]
The app.jsx file contains the actual code displayed on the web page. React uses a component-based architecture, where a component is a function with a file name that starts with a capital letter. JSX (JavaScript XML) allows developers to write HTML and JavaScript code together. The video demonstrates how to write JavaScript code within HTML using curly braces {}.
Writing HTML and JavaScript in React [2:08:42]
Code above the return statement is considered JavaScript, while code inside the return statement is considered HTML. React enforces a rule that components must have a single parent tag. JavaScript code can be embedded within HTML by wrapping it in curly braces {}.
Adding Styling: Inline and Global CSS [2:22:51]
Styling can be added to React components using inline styles or global CSS. Inline styling involves using the style attribute with double curly braces to define CSS properties. Global CSS involves creating a CSS file (e.g., index.css) and importing it into the main.jsx file. The video demonstrates how to add both inline and global styles to a React component.