TLDR;
This video introduces the concept of chemical bonding, explaining why atoms form bonds and the different types of bonds that exist. It covers primary and secondary bonds, detailing their characteristics and the forces involved. The video also touches on specific types of bonds like ionic, covalent, coordinate, metallic, hydrogen bonds, and Van der Waals forces.
- Atoms form bonds to achieve stability by attaining a stable electronic configuration and reducing energy.
- Chemical bonds are primarily of two types: primary and secondary.
- Primary bonds involve the participation of electrons, while secondary bonds involve electrostatic forces.
Introduction to Chemical Bonding [0:25]
The presenter welcomes viewers to the inorganic chemistry web series, emphasising understanding over rote memorisation. The series aims to build from basic principles to advanced concepts. The initial episode, titled "Bonds ki Baraat" (loosely translated as "The Wedding of Bonds"), promises to explain chemical bonding in a simple, accessible manner. The presenter encourages viewers to take notes and follow the series diligently.
Why Atoms Form Bonds [2:53]
Atoms, like humans, seek stability. They are inherently unstable due to their unstable electronic configurations and high energy states. To achieve stability, atoms form bonds, which leads to the creation of chemicals. This process of atoms combining to form bonds is always exothermic, meaning it releases energy.
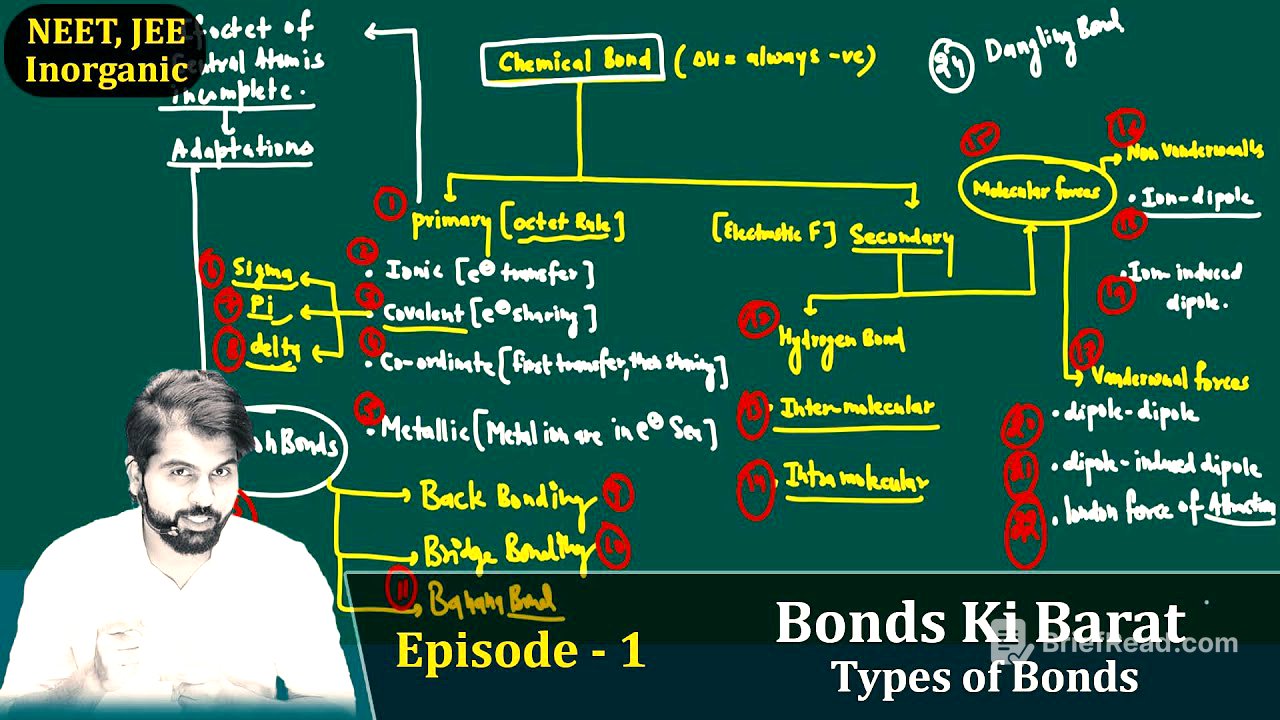
Primary vs. Secondary Bonds [6:56]
Chemical bonds are mainly of two types: primary and secondary. Primary bonds involve the participation of electrons, while secondary bonds do not. Molecules and compounds are formed via primary bonds; secondary bonds play no role in their formation. Primary bond formation releases a significant amount of energy (200 to 400 kJ/mol), whereas secondary bond formation releases less energy (2 to 40 kJ/mol). Secondary bonds form after primary bonds and determine the state (solid, liquid, gas) in which a molecule exists. Primary bonds determine whether a molecule or compound will exist at all. Secondary bonds are based on electrostatic forces.
Types of Primary Bonds [15:18]
Primary bonds are based on the octet rule and are of four types: ionic, covalent, coordinate, and metallic. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons. Coordinate bonds involve one atom donating both electrons for the bond. Metallic bonds consist of metal ions immersed in a sea of electrons. Covalent bonds can be further classified into sigma, pi, and delta bonds.
Types of Secondary Bonds [18:33]
Secondary bonds are mainly of two types: hydrogen bonds and molecular forces. Hydrogen bonds can be intermolecular (between molecules) or intramolecular (within a molecule). Molecular forces can be classified into Van der Waals forces and non-Van der Waals forces. Non-Van der Waals forces include ion-dipole interactions. Van der Waals forces include dipole-dipole interactions, dipole-induced dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces.
Deviation Bonds [23:23]
If the octet state of the central atom is incomplete, it leads to tension or deviation, resulting in deviation bonds. These include back bonding, bridge bonding, and banana bonding. The presenter concludes by summarising the different types of bonds discussed and promising a deeper dive in the next episode.





![[Part-1] Complete CGGS | Rapid Revision Series (Marathon) || CGPSC Prelims | 2025](https://wm-img.halpindev.com/p-briefread_c-10_b-10/urlb/aHR0cDovL2ltZy55b3V0dWJlLmNvbS92aS91WGxJUFJIaHhRdy9ocWRlZmF1bHQuanBn.jpg)


