TLDR;
This text explains ionic bonds, which are electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. Ionic compounds are rigid solids that can dissociate into ions in water, enabling them to conduct electricity as electrolytes. Electrolytes are crucial for biological functions like osmotic regulation, muscle contractions, and nerve impulses, and imbalances can have severe health consequences.
- Ionic bonds are electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions.
- Ionic compounds can dissociate into ions in water, acting as electrolytes.
- Electrolytes are essential for various biological processes, and imbalances can lead to severe health issues.
Ionic Bonds Overview
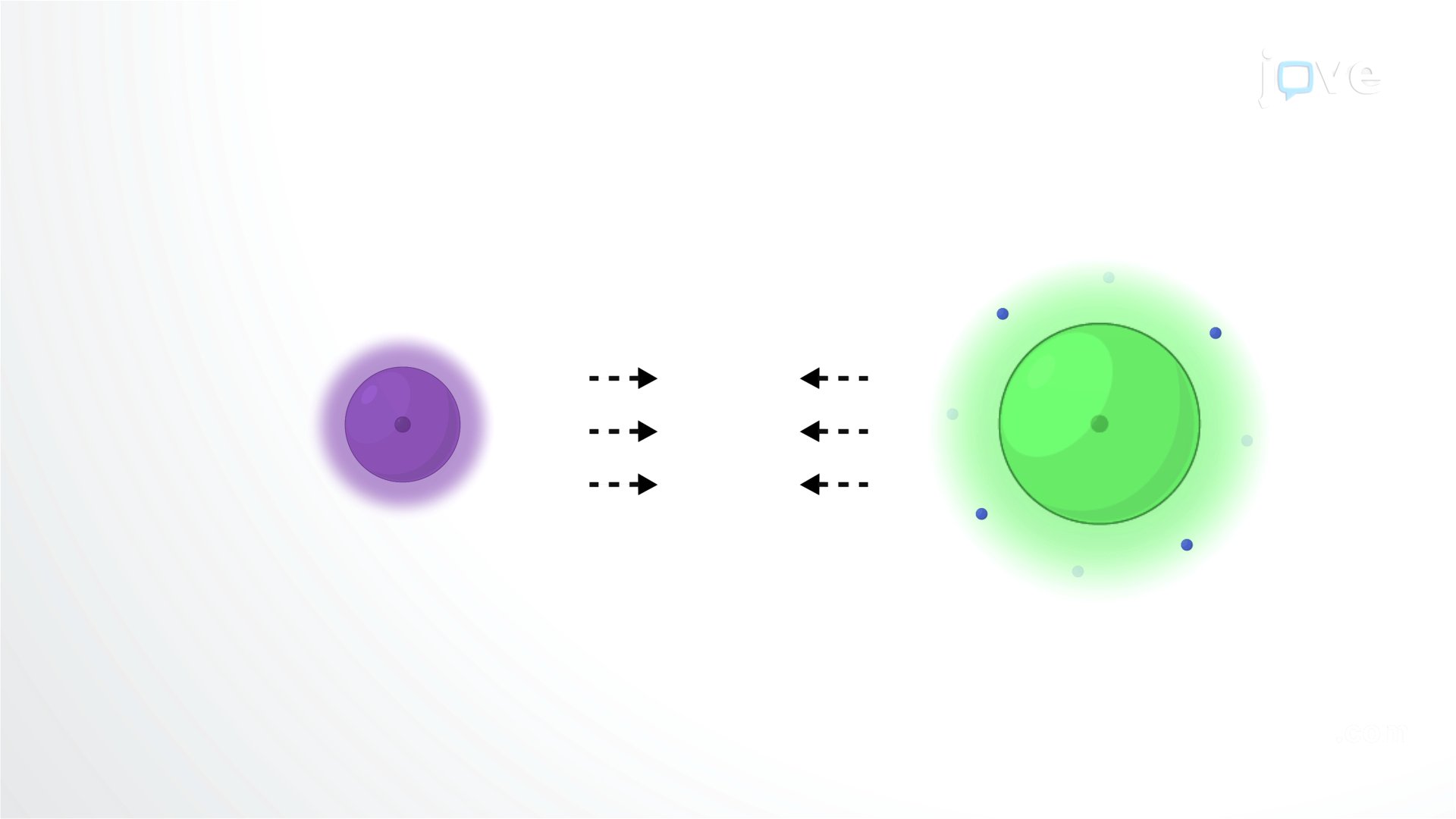
When atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration, they form ions. Ionic bonds are electrostatic attractions between ions with opposite charges. Ionic compounds are rigid and brittle when solid and may dissociate into their constituent ions in water, while covalent compounds remain intact unless a chemical reaction breaks them.
Opposing Charges Hold Ions Together in Ionic Compounds
Ionic bonds are reversible electrostatic interactions between ions with opposing charges. Elements with one valence electron or those needing one more valence electron are the most reactive. Ions that lose electrons have a positive charge and are called cations, while ions that gain electrons have a negative charge and are called anions. Cations and anions combine in ratios that result in a net charge of 0 for the compound they form. For example, potassium chloride contains one chloride ion for each potassium ion (charges of +1 and -1, respectively), and magnesium chloride contains two chloride ions for each magnesium ion (charges of +2 and -1, respectively).
Ions Can Dissociate from One Another in Water
The electrostatic forces holding ionic compounds together are strong in solid form, resulting in high melting points and their prevalence as solids on Earth's surface. However, ionic bonds are weaker than covalent bonds because ions can be pulled apart or dissolved in liquids like water. Ions dissolved in water are in a chemical reaction and can conduct electric currents.
Electrolytes Are Important for Biological Systems
Electrolytes are ions that conduct electricity when dissolved in water. In biological systems, they are essential for osmotic regulation, which is the balance of water across cellular membranes. Electrolytes also contribute to critical biological processes that rely upon electrical charges across the cell membrane, such as muscle contractions and nerve impulses. Common biological electrolytes include calcium , sodium , magnesium , potassium , phosphate and chloride ions . Electrolyte imbalances can cause severe physical symptoms and even death. Hyponatremia, or insufficient sodium levels in the blood, is a common electrolyte imbalance that can be a symptom of another medical condition or caused by ingesting too much water without adequately replacing sodium. Treatments for hyponatremia aim to restore the balance of sodium in the body so that the brain, heart, and other organs can function properly.