TLDR;
This session focuses on research methods in sociology, emphasizing their importance in analyzing social phenomena. It covers the historical, comparative, experimental, and statistical methods, detailing how each is used to study society. The session also introduces methods of analysis and interpretation, specifically social surveys, and prepares students for practical application through online questionnaires.
- Discusses the birth of sociology and its connection to the industrial and French revolutions.
- Explains four key research methods: historical, comparative, experimental, and statistical.
- Introduces social surveys as a method of analysis and interpretation, distinguishing between descriptive and interpretive surveys.
Introduction to Sociology and the Importance of Research Methods [0:00]
The session begins by highlighting the significance of sociology as an integrated science, tracing its origins to the industrial and French revolutions. These revolutions brought about transformations that led to the development of sociology. The discussion touches on the positive and negative repercussions of the industrial revolution and the philosophical trends—individual and public—that emerged from the French Revolution. The upcoming exam structure is also addressed, emphasizing the goal of identifying students' weak points for targeted improvement.
Methods Used in Sociological Research [2:51]
The lecture transitions to the core topic: methods used in sociological research. The method is defined as the approach used in research, crucial for determining its success or failure. The primary aim of employing methods in sociology is to analyze phenomena and identify their constituent elements. Examples of social phenomena in Lebanese society, such as poverty, unemployment, and the impact of Corona, are discussed to illustrate the application of these methods.
The Historical Method [6:04]
The historical method is detailed, focusing on analyzing the emergence and development of a phenomenon. It involves understanding how a phenomenon originated, its elements (e.g., physical, moral, and verbal violence), and its progression over time. The importance of tracing the history of a phenomenon, including its emergence, location, and evolution, is emphasized. Additionally, the relationship between the phenomenon and related social issues, along with their mutual effects, is explored.
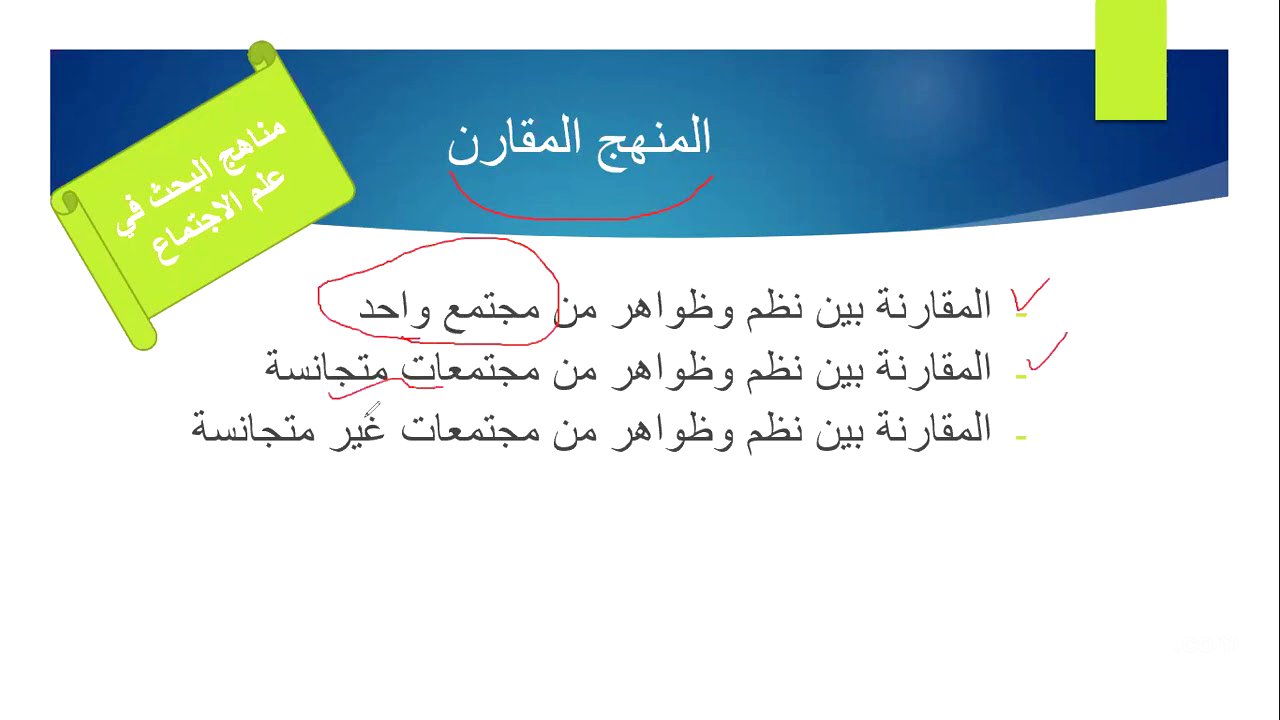
The Comparative Method [9:30]
The comparative method involves comparing phenomena within one society, between homogeneous societies, and between heterogeneous societies. Examples include comparing openness and freedom of expression between Lebanon and Iraq, and customs and traditions between Qatar and Lebanon. The discussion emphasizes the importance of specifying social phenomena when making comparisons, such as differences in social interaction and marriage customs.
The Experimental Method [14:08]
The experimental method is based on conducting a social experiment in the field to reveal facts. This involves selecting a sample that represents the community where the experiment is conducted, ensuring it includes diverse demographics. If the experiment is successful, the results are generalized and published. Examples include experiments in educational systems and distance learning, with the aim of social reform. The importance of conducting social experiments to address problems and adopt successful solutions is highlighted.
The Statistical Method [20:39]
The statistical method involves using numerical results to understand societal trends and conditions. It is a scientific method for studying social problems by analyzing trends in relation to these problems. The importance of this method lies in its ability to provide objective judgment on phenomena, reveal scientific facts, and help uncover relationships between different phenomena. The statistical method also aids in establishing laws based on objective and scientific findings. It’s noted that the statistical method can be a tool within the experimental method, highlighting the overlap between different research approaches.
Methods of Analysis and Interpretation: Social Survey [25:58]
The session introduces methods of analysis and interpretation in sociology, starting with the social survey. A social survey is defined as a scientific study of a region or problem aimed at obtaining data and information. It is likened to a scanner that collects information. Social surveys are divided into descriptive surveys, which collect information, and interpretive surveys, which interpret the collected information. The steps involved in conducting a social survey include choosing a representative sample, collecting information, processing the information, and interpreting it to reach a conclusion.