TLDR;
This documentary explores the world of insects, highlighting their diversity, anatomy, survival strategies, behaviors, and their impact on the environment and human culture. It also addresses the threats they face and what can be done to help them.
- Insects comprise 80% of known animal species.
- They play crucial roles in pollination, decomposition, and pest control.
- Human activities threaten insect populations, but conservation efforts can make a difference.
Introduction [0:04]
The video introduces the animal kingdom, focusing on insects and their significance. It emphasizes their impressive, tenacious, innovative, and genuine nature, highlighting their past, present, and future. The video promises to reveal the breathtaking, intriguing, and tremendous aspects of insects.
Insects: A Planet of Bugs [1:02]
Insects are incredibly numerous, with an estimated 1.4 billion insects for every human. They make up at least 80% of all known animal species and have existed for hundreds of millions of years, even outliving the dinosaurs. Insects have conquered almost every environment on Earth, except for active volcanoes and frozen extremes. They provide essential services such as pollination, decomposition, pest control, and food.
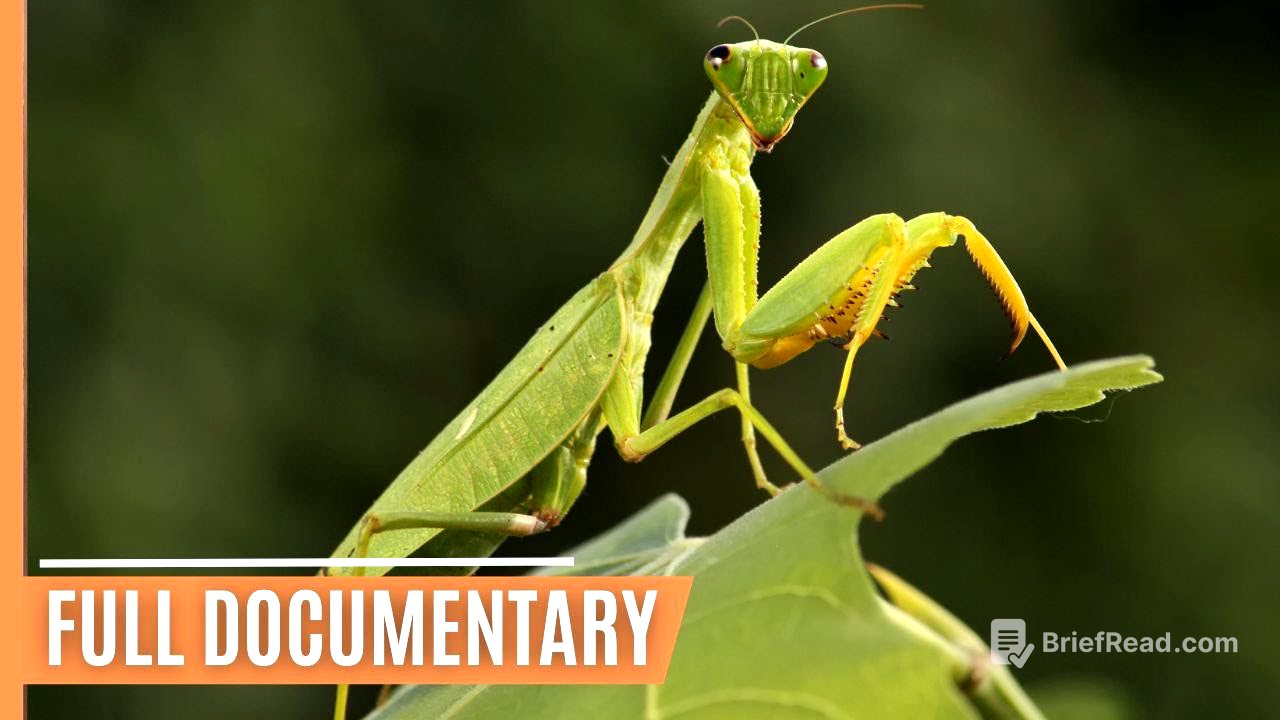
Anatomy of an Insect [4:14]
Insects are invertebrates with bodies divided into three parts: head, thorax, and abdomen. They have an exoskeleton, segmented bodies, and three pairs of jointed legs. The head contains compound eyes, ocelli (simple eyes), and antennae. The thorax is responsible for transport and has three segments, each with a pair of legs, and wings on the last two segments. The abdomen houses organs for digestion, reproduction, and respiration through spiracles.
Diversity of Insects [8:19]
Insects are classified into at least 29 orders. The largest insect can be the Titan beetle (almost 17 cm) or the Atlas moth (wings wider than a human handspan), while the smallest are fairy wasps (about 3 mm). The largest order is the Coleoptera (beetles), characterized by their sheath wings or elytra. Other diverse orders include Diptera (true flies), Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths), Hymenoptera (bees, wasps, and ants), and Hemiptera (true bugs).
Insect Skills and Adaptations [16:37]
Insects have various survival skills and adaptations. They produce many offspring to ensure the survival of their species. Some insects, like ants and termites, exhibit eusocial behavior, living in organized colonies with defined roles. Insects use camouflage, mimicry, repellent sprays, and bright colors as defense mechanisms. They also have well-developed senses, including photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and chemoreceptors, to interpret their surroundings.
Insect History [25:10]
Insects have a long history, with ancestors dating back 500 million years. Dragonflies are the closest modern relatives to the first winged insects. Prehistoric insects were larger due to higher oxygen levels. Grasshoppers and crickets appeared around 100 million years later, followed by cockroaches, flies, ants, bees, and wasps. Insects and crustaceans diverged between 500 and 450 million years ago.
Insect Behavior [27:35]
Insects exhibit a range of behaviors, including instinctive actions like grooming and spinning cocoons, and learned behaviors like memorizing landmarks. They communicate through sound and pheromones. Migration is another notable behavior, with monarch butterflies migrating thousands of kilometers. Colonial insects display cooperative behaviors such as foraging and hunting in groups.
Insect Construction Skills [32:46]
Weaver ants are known for their construction skills, building nests by linking their bodies together to bend leaves into a tent shape. They use their larvae to secrete silk, binding the leafy walls together. These nests can be half a meter long and are often completed in less than 24 hours.
Insect Reproduction and Development [34:33]
Insects use visual signals, sounds, and pheromones to find partners. They undergo metamorphosis, either complete (four stages: egg, larva, pupa, adult) or incomplete (three stages: egg, nymph, adult). Complete metamorphosis involves a pupation stage where the body transforms, while incomplete metamorphosis involves nymphs shedding their exoskeletons. Metamorphosis reduces competition for resources between juveniles and adults.
Insect Feeding Habits [39:41]
Insects have various mouth types, including chewing, sponging, lapping, and sucking mouthparts, depending on their diet. About 50% of insects are herbivorous, feeding on plant material. Locusts can form large swarms and become cannibalistic when food is scarce. Carnivorous plants, like the Venus flytrap, trap insects for food. Many insects are predators, and they are also prey for other animals.
Insects' Role in the Environment [43:51]
Insects play crucial roles in the environment, including pollination, soil aeration, nutrient recycling, and pest control. They are also a vital food source for many animals. Their actions aid the soil, allowing water, oxygen, and nutrients to reach plant roots.
Insects and Human Culture [45:31]
Insects have influenced human culture for millennia. Ancient Egyptians revered the scarab beetle as a symbol of renewal and resurrection. In ancient Greece, the goddess Psyche was depicted with butterfly wings. The Chinese art of silk production, using silkworms, was a closely guarded secret for thousands of years. Bees have been cherished throughout the ages, symbolizing fertility and nature.
Threats to Insects and Conservation Efforts [47:44]
Insect populations are declining due to habitat loss, pollution, overuse of agricultural chemicals, extreme weather conditions, and climate change. Humans can help by raising awareness, using organic fertilizers, planting native flowers, placing out feeding stations, and setting up insect hotels. These actions can lead to positive outcomes for insects and the entire animal kingdom.