TLDR;
This video discusses the multifaceted responsibilities, characteristics, and qualities of teachers, emphasizing their role in shaping students and contributing to society. It covers essential aspects such as subject matter knowledge, patience, intellectual curiosity, and community involvement. The video also addresses the importance of professional development, ethical conduct, and the various roles teachers play within the educational system.
- Teachers' responsibilities and roles
- Characteristics and qualities of teachers
- Professional development and ethical conduct
Introduction: Teachers and Their Responsibilities [0:00]
The speaker, Sir Arnold Ryan New Mercado, begins by highlighting the familiarity of teachers with their responsibilities, emphasizing their professional role in caring for students. He poses the question of whether teachers are still familiar with their duties and if they need to be reminded, reskilled, and re-equipped. The objectives of the session include identifying teacher responsibilities, presenting teacher characteristics and qualities, and providing knowledge and skills related to the position and competency profile of a teacher.
Defining Students and Teachers [1:52]
The discussion starts by defining a student as someone devoted to learning, seeking knowledge from teachers and books, and willing to pay the price for education. A teacher is defined as someone involved in the distinctively human activity of imparting knowledge and facilitating the learning process. Teachers are concerned with the growth and development of a student's whole personality, including mind, spirit, character, and behaviors. They select and organize teaching methods, consciously planning and controlling situations to achieve optimum student learning, with the goal of preparing learners for the future of society.
TEACHING Acronym [4:23]
The speaker introduces an acronym for the word "TEACHING" to encapsulate the essence of the profession:
- T stands for Transfer of knowledge.
- E stands for Enlightenment, giving students a better understanding and practicality of life.
- A stands for Aligning with portion and real life, providing direction to students.
- C stands for Character building, molding learners with the right attitude and behavior.
- H stands for Healing touch, helping students with their knowledge needs and providing solutions to societal problems.
- I stands for Involvement with the Student is in studies, helping students evolve and improve in their learning.
- N stands for Nurturing the thoughts into reality, delivering the curriculum and experiences effectively.
- G stands for Giving a final shape, helping students become solid graduates and future teachers.
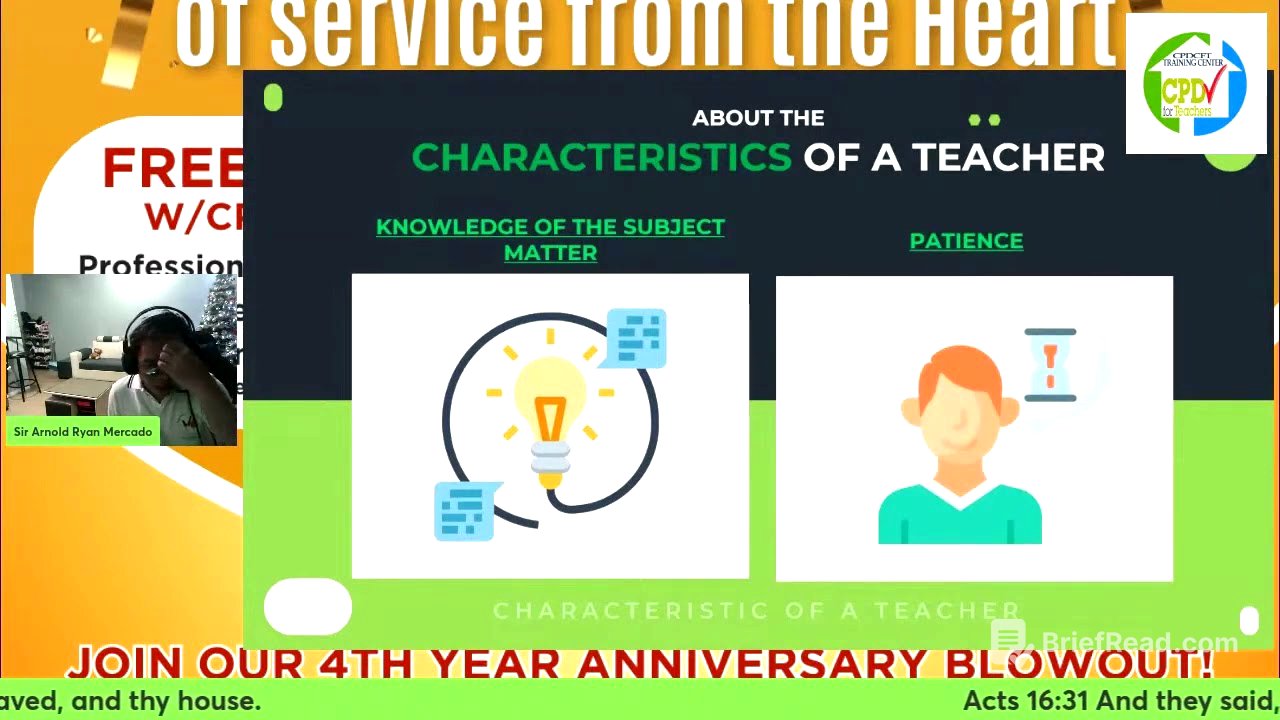
Characteristics of a Teacher: Knowledge and Patience [7:42]
The first characteristic discussed is the knowledge of the subject matter. Teachers must master their subject to maintain prestige and effectively teach students, even if it requires learning new subjects outside their major. The speaker shares personal experiences of teaching subjects outside his major, emphasizing the importance of passion and continuous learning. The second characteristic is patience, which is essential for dealing with students who may lack discipline or have difficulties learning. Impatience with sincere students is seen as a teacher's own shortcoming.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Intellectual Curiosity and Achievement [14:22]
Intellectual curiosity is highlighted as a key trait, with good teachers staying abreast of changes in their fields and being flexible and adaptable. The speaker discusses the challenges of adapting to new implementations like the ipcrf and rpms, emphasizing the need for continuous learning and sharing best practices. Achievement as a teacher is not only about personal accomplishments but also about the success of students, such as guiding them to graduation or molding them into champions.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Awareness and Maturity [20:27]
Awareness is crucial for teachers to stay informed about their environment and current events, enabling them to answer student questions effectively. This includes understanding the culture and language of the current generation, especially post-pandemic. Maturity is also essential, as teachers need to handle their own emotions and provide solutions for students' problems, separating personal issues from their professional role.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Community Involvement and Organization [24:20]
Community involvement is emphasized as maintaining good relationships with parents, administrators, and leaders, enhancing community effectiveness in the classroom. Teachers should be active in community organizations and leverage opportunities for personal and professional growth. Organization is also vital, as teachers must manage multiple personalities and organize subject matter to benefit the maximum number of students.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Mission, Enthusiasm, and Ideal Character [27:30]
A teacher must have a clear sense of mission to provide quality education and satisfaction with their choice of teaching as a life mission. Enthusiasm is crucial, as it is contagious and helps students feel engaged. Teachers should maintain their passion and enthusiasm, even when facing administrative hassles. An ideal character is also important, with teachers serving as models of praiseworthy attitudes and good habits, practicing impartiality, and adhering to ethical standards.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Balanced Personality and Literary Interest [30:58]
A balanced personality is essential for teachers to control their emotions and foster cooperation. Literary interest helps teachers harmonize their knowledge with current demands through various sources like newspapers, magazines, radio, and TV, enabling them to answer student questions effectively.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Love for Teaching and Professional Skills [32:33]
Teachers should be in love with teaching, continuously learning and giving their best, viewing it as a noble profession and lifetime passion. Professional skills are also vital, with teachers staying updated on the latest teaching methods through training and research, adapting them to their students' needs.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Awareness of Children's Growth and Teaching Methods [36:17]
Awareness of children's psychology and different growth stages is crucial for effective teaching, addressing their physical, emotional, mental, and social problems. Teachers should use teaching methods that align with their students' abilities, adapting to their needs.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Polite Attitude and Love for Profession [38:09]
A polite attitude is another key characteristic, as it helps teachers win the hearts of others and create a pleasant school atmosphere. Teachers should always practice respect and good behavior, reflecting their culture and influencing learners positively. They should also maintain a love for their profession, giving exclusive attention to the growth and development of their students while also pursuing their own growth.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Daily Preparation and Questioning Skills [39:53]
Daily preparation is essential for effective teaching, with careful and systematic arrangements of subject matter and classroom activities. Teachers should be well-prepared with their dll, dlp, and instructional materials. Skilling questioning is also vital, with teachers using higher-order thinking skills (hots) to lead students from the unknown to the known.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Use of Material Aids and Leadership [41:26]
The use of material aids brings clarity to teaching, with teachers using stories and illustrations to make abstract concepts clear. While modules are helpful, teachers should also use other sources to avoid student dependency. Good leadership is essential, with teachers being disciplinarians in a nice way and acting as allies to their students.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Communication and Voice [43:03]
Good communication skills are crucial, enabling teachers to explain things comfortably and become resource speakers. A good voice is also important, with teachers using a clear and modulated voice to capture student interest.
Characteristics of a Teacher: Memory, Vitality, and Democratic Attitude [45:40]
Good memory helps teachers correlate many things, differentiating them from others. Good vitality is essential for maintaining continuity of work and influencing children positively. A democratic attitude is also important, with teachers acting as friends, philosophers, and guides, inspiring collaboration and trust rather than competition.
Additional Characteristics and Qualities [48:29]
Additional characteristics include thorough knowledge of the subject matter, excellent speech, neatness, poise, broad interests, a well-balanced personality, and a sense of humor. Teachers should be well-groomed, tolerant, fair, kind, patient, good communicators, and keen observers, with leadership ability and deeper knowledge.
Qualities of a Teacher: Learning Styles [50:32]
The qualities of a teacher include facilitating learning through various styles:
- Learning by seeing, using visual aids like maps, charts, and multimedia.
- Learning by saying, encouraging students to participate in discussions and express themselves.
- Learning by doing, involving students in laboratories, projects, and simulations.
- Learning by listening, enhancing active listening and note-taking skills.
Worst Qualities of a Teacher [53:28]
The worst qualities of a teacher include:
- Believing teaching is just a job.
- Arriving late to school and class regularly.
- Having parents complain about classroom issues.
- Using inappropriate language and demeaning students.
- Having classroom discipline problems.
- Being insensitive to students' culture.
- Expressing bias.
- Lacking conflict resolution skills.
- Not accepting responsibility for classroom events.
Roles of a Teacher: Instructional, Faculty, and Individual [57:00]
The roles of a teacher are multifaceted:
- Instructional: Providing clear instructions, facilitating learning, and motivating students.
- Faculty: Contributing to school plans and policies, collaborating with colleagues, and serving on committees.
- Individual: Maintaining personal development, acting as a community member and citizen.
Professional Responsibilities of a Teacher [1:01:09]
Professional responsibilities include:
- Being conscious of their duty of care to students.
- Demonstrating high standards of professional behavior.
- Collaborating in school development plans and policies.
- Devising and documenting teaching and learning programs.
- Treating students equally, including those with disabilities.
- Meeting individual learning needs and assisting students to maximize their learning outcome.
- Effectively managing programs for child protection and student welfare.
- Undertaking ongoing professional development.
- Complying with legislative and industrial requirements.
- Being familiar with relevant legislation.
- Complying with directions from supervisors and principals.
- Implementing departmental priorities and ensuring professional actions reflect government policy.
Functions of a Teacher: Explaining, Initiating, and Unifying [1:14:01]
The functions of a teacher include:
- Explaining and informing, providing accurate and legitimate information.
- Initiating, directing, and administering, organizing and making decisions.
- Unifying the group, developing a group spirit within the classroom.
- Giving security, providing warm recognition and a friendly atmosphere.
- Clarifying attitudes, beliefs, and problems.
- Diagnosing learning problems and providing support.
- Making curriculum materials and resources.
- Evaluating, recording, and reporting student progress.
- Arranging and organizing the classroom.
- Participating in school activities.
- Participating in professional life.
IPCRF and Key Result Areas (KRA) [1:27:06]
The discussion touches on the ipcrf, highlighting the duties and responsibilities of teachers, such as facilitating learning, monitoring student progress, and counseling students. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining updated records, supporting governmental and non-governmental organizations, and maintaining harmonious relationships with colleagues and parents. The key result areas (kra) include teaching-learning process, community involvement, and professional growth and development.
Career Stages for Teachers [1:36:30]
The video outlines the different career stages for teachers:
- Beginning teachers: Possessing requisite knowledge and skills, seeking advice from experienced colleagues.
- Proficient teachers: Professionally independent, providing focused teaching programs.
- Highly proficient teachers: Working collaboratively with colleagues, providing support and mentoring.
- Distinguished teachers: Exhibiting commitment to inspire the education community, contributing to the profession.
Domains and Strands in IPCRF [1:43:38]
The speaker briefly mentions the various domains and strands in the ipcrf, including content knowledge, research-based knowledge, positive use of ict, strategies for literacy and numeracy, developing critical and creative thinking, and classroom communication strategies.
Conclusion: Be Good in the Face of Failure [1:47:46]
The presentation concludes with a quote emphasizing the importance of being good in the face of failure, choosing kindness, and maintaining a focus on being better every day. The speaker encourages teachers to believe in goodness and to always strive to be good, even when facing challenges and competition.




![15 Kdramas SO AMAZING They Make Everything Else Seem Like Trash! [Ft HappySqueak]](https://wm-img.halpindev.com/p-briefread_c-10_b-10/urlb/aHR0cDovL2ltZy55b3V0dWJlLmNvbS92aS9KVE1Cem9SRzdEMC9ocWRlZmF1bHQuanBn.jpg)