TLDR;
The video provides an overview of the digestive system and the process of nutrition in higher organisms, particularly mammals. It outlines the five key steps of nutrition: ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. The video also describes the structure of the elementary canal, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), and large intestine (cecum, colon, rectum), as well as the three main digestive glands: salivary glands, pancreas, and liver.
- Five steps of nutrition: ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.
- Elementary canal: mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus.
- Three digestive glands: salivary glands, pancreas, and liver.
Digestion and Absorption Nutrition [0:06]
Nutrition involves five key steps: ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. Ingestion is the process of taking in food. Digestion is the conversion of complex food substances into simple, absorbable forms. Absorption is when these simplified substances are absorbed through living membranes. Assimilation incorporates the absorbed food into cell components. Egestion is the removal of undigested residual food.
Digestive System [0:27]
Higher organisms have specialized organs for each step of nutrition. Mammals exhibit holozoic nutrition, consuming whole animals or plants or their parts. The digestive system includes the elementary canal and associated digestive glands, which produce enzymes necessary for the chemical breakdown of food into simpler substances.
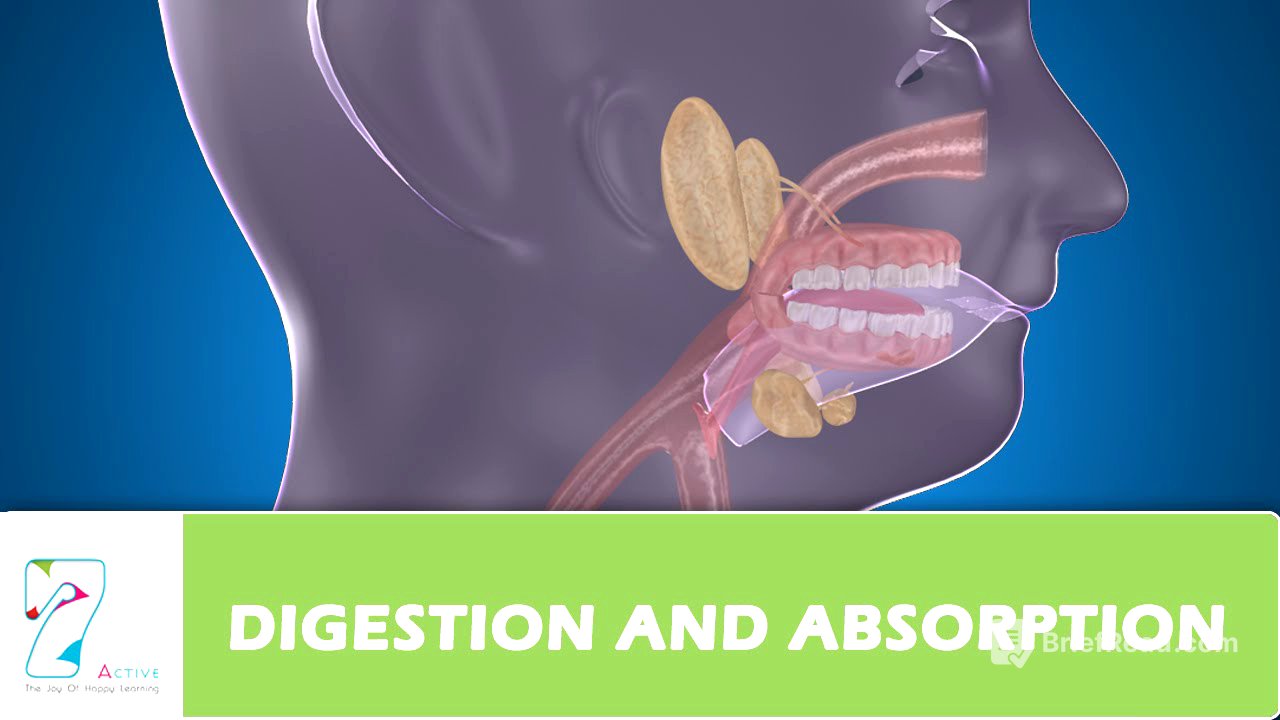
Elementary Canal [1:54]
The elementary canal begins with the mouth and ends with the anus. It is a muscular, coiled, tubular structure, varying in length from eight to nine meters. The mouth cavity contains teeth and the tongue. The various organs, starting from the mouth, are the esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum), and large intestine (cecum, colon, and rectum).
Digestive Glands [2:36]
There are three main digestive glands: salivary glands, the pancreas, and the liver. These glands produce enzymes that aid in the chemical breakdown of food.