TLDR;
This YouTube video features a presentation on cyber security and cyber attacks in Indonesia, particularly in relation to the implementation of the PDP Law. The presentation covers the background of cyber security, the causes of cyber crime, a review of cyber security incidents in 2023, challenges in the cyber world, and strategies for enhancing cyber security. It also discusses the sources and types of cyber threats, security domains, and control measures for information systems.
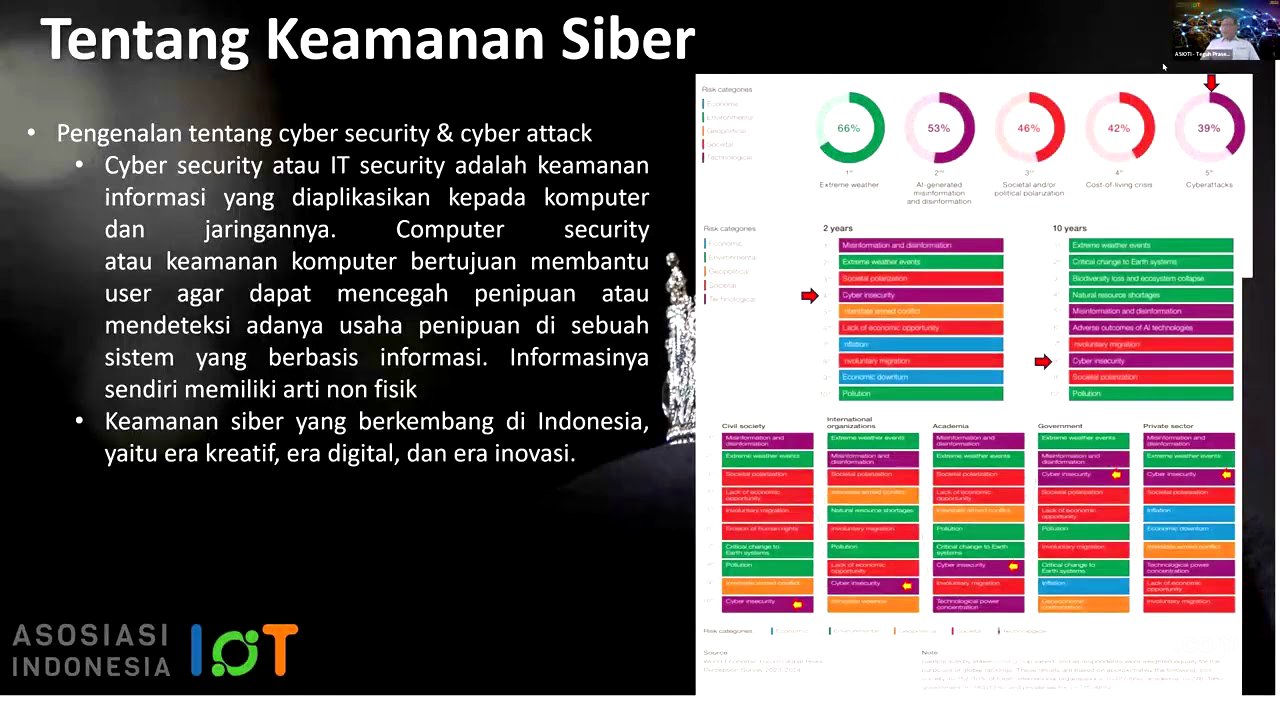
- Cyber security is a major concern, ranking high in global risk assessments.
- Cyber crime is increasing due to various factors, including the growing number of internet users and the availability of hacking tools.
- Law enforcement against cyber crime is lacking, and a comprehensive cyber security law is needed.
- A multi-stakeholder approach is essential for ensuring cyber security, involving government, private sector, academia, and the public.
Introduction to Cyber Security and PDP Law [0:00]
The presenter begins by introducing the topic of cyber security and its close relationship with the implementation of the PDP (Personal Data Protection) Law in Indonesia. Cyber security is defined as information security applied to computers, IT devices, and networks. The goal is to prevent fraud and detect fraudulent attempts within information-based systems. The development of cyber security is extensive, especially in the current era of digital innovation.
Global Risks and Cyber Attacks [1:57]
Globally, cyber attacks are a significant risk, accounting for 39% of overall risks, behind extreme weather (66%) and AI misuse (53%). Misinformation spread through AI is a growing concern. Cyber insecurity is a major concern for governments and the private sector, ranking among the top three security risks. The presenter hopes that increased attention to preventive and corrective measures will reduce this ranking in the future.
Causes of Cyber Crime [8:56]
Several factors contribute to cyber crime, including the increasing number of computer and internet users (over 210 million in Indonesia). The misuse of software originally intended for system audits, the availability of free hacking tools, and inadequate law enforcement are also significant factors. Additionally, the widespread use of the internet by companies and the vulnerabilities in business applications increase the risk of cyber attacks.
Cyber Security Incidents in 2023 [13:44]
The presentation reviews various cyber security incidents that occurred in 2023. These include fraud disguised as wedding invitations in APK format, the rise of online gambling infiltrating state-owned sites, leaks of BPJS data, fraud using charity schemes, disruptions to Islamic banking systems, and data leaks from government ministries. The presenter notes that legal action against perpetrators is often lacking, and preventive measures are insufficient.
Challenges in the Cyber World [25:12]
One of the main challenges in the cyber world is recognizing true identities due to the anonymity and layers of masks that can be used to hide personal information. To address this, the presenter emphasizes the need for preventive and corrective measures involving all stakeholders to ensure cyber security in Indonesia.
Stakeholders in Cyber Security [26:57]
The stakeholders include the executive and legislative branches of government, owners and operators of critical infrastructure, the judiciary, law enforcement agencies, the intelligence community, technology vendors, academics, citizens, civil society, and global partners. Collaboration among these stakeholders is essential for ensuring cyber security.
Goals and Policies for Cyber Security [29:01]
The goals of cyber security efforts include prioritizing security considerations, guaranteeing community safety, establishing an integrated policy framework, defining governance structures, encouraging cyber security cooperation, and regulating compliance. The presenter notes that the cyber security law has not yet been passed in the DPR (People's Representative Council), making it a shared task to enact this legislation.
Cyber Security Framework Flow Diagram [32:24]
The presentation outlines a cyber security framework flow diagram, starting with national cyber security legislation. This framework involves creating a national security framework, integrating it with stakeholders, ensuring compliance by law enforcement and critical infrastructure owners, and conducting audits to check effectiveness. The framework is designed for continuous improvement and adaptation.
Stages of Implementing a Cyber Security Framework [35:44]
The stages include determining a national cyber security strategy, forming a working group, integrating the framework, establishing a communication framework, implementing the framework, and reporting periodic compliance. Incident management should include prevention, detection, reaction, and determination.
Principles of Response to Cyber Security Incidents [42:15]
The principles of response include prevention, detection, reaction, and determination. Prevention involves securing logical and physical conditions. Detection includes checking log files and alarms. Reaction involves taking action to close leaks and improve security. Determination involves proactive measures to defeat intrusions.
Cyber Security Strategy Model [44:42]
The cyber security strategy model involves determining the objectives of national cyber security, considering threats, risks, and national interests, and adopting international conventions. It also includes legal, technical, and organizational improvements, capacity building, and collaboration.
Sources and Types of Cyber Threats [47:11]
Typical sources of cyber threats include organized crime groups, hacker activists, extremist organizations, journalists, internal employees, competitors, and foreign intelligence agencies. Cyber violations include illegal access, data espionage, illegal interception, data disruption, system disruption, fraud, illegal content, copyright violations, and identity-related crimes.
Cyber Security in Asia Pacific [52:12]
Cyber security spending in the Asia Pacific region is growing rapidly, with an average annual market growth of 15%. The Indonesian market is expected to grow by 23% per year until mid-2025, reaching over $1 billion USD in 2024. This growth is driven by needs in various sectors, including finance, telecommunications, health, e-commerce, and government.
Industry and Domains of Cyber Security [54:46]
Improving cyber security in industry has a return on investment of over 52% within two years. Key factors for success include developing HR, providing clear investment targets, focusing on solving main problems, implementing change management strategies, and securing support from top executives. The 10 domains of cyber security include access control, telecommunications and network security, practical management, application system development, encryption, information system architecture, operation, business continuity planning, legal requirements, and physical placement.
Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Security Controls [1:00:34]
Threats can be natural, human, or environmental. Vulnerabilities are defects or weaknesses in a system. Security controls include administrative controls, controls over system development and maintenance, operational controls, and physical protection of data centers.
Administrative Controls and Employee Recruitment [1:08:25]
Administrative controls involve implementing a clear control framework, formal procedures, and careful employee recruitment. Employee supervision and task separation are also crucial.
System Development and Operational Controls [1:12:34]
Controlling system development and maintenance requires involving information system auditors from the beginning and equipping applications with audit trails. Operational controls include restricting data access, controlling personnel, equipment, archive storage, and virus control.
Preventive, Detective, and Corrective Controls [1:15:59]
The presentation provides examples of preventive, detective, and corrective controls for virus protection. Preventive measures include avoiding untrusted sources and checking new programs with antivirus software. Detective measures include routinely running antivirus programs and comparing file sizes and dates. Corrective actions include ensuring backups and removing infected programs.
Physical Protection and Hardware Controls [1:18:29]
Physical protection involves upgrading data centers and maintaining environmental factors. Hardware controls involve implementing fault-tolerant systems with backups for power, CPU, and memory.
Access Control and Information Access [1:21:30]
Restricting access to the system involves unique usernames and passwords, ID cards, PINs, and biometrics. Firewalls are used to prevent access from outside the intranet. Information must be encrypted using cryptography techniques such as DES and PKI.
Recovery and Disaster Recovery Planning [1:24:49]
Recovery involves emergency plans, backup plans, recovery plans, and testing. Disaster recovery planning and insurance are also essential.
Conclusion: Cyber Security and Industry 4.0 [1:26:06]
The presentation concludes that information system security must be seen from various aspects according to the security domain. The demand for cyber security is high for the adoption of Industry 4.0, requiring strong support and incentives from regulators. Developing a cyber security chain ecosystem and encouraging digital transformation are also crucial.