TLDR;
This video explains how the internet works, starting from a home network and expanding to the global level. It covers the components of a home internet setup, the role of Internet Service Providers (ISPs), and how data travels across the internet. The video also discusses internet exchange points, data centers, and the importance of fiber optic cables in providing fast internet connectivity.
- Home internet setup involves a modem and router for wired and wireless connections.
- ISPs connect homes to the broader internet through various technologies.
- Internet exchange points and data centers improve connectivity and reduce latency.
- Fiber optic cables form the backbone of the internet, enabling high-speed data transmission.
Home Internet Setup [0:22]
The explanation begins with a typical home internet setup. Users subscribe to a broadband service, which may be delivered via cable TV infrastructure. A modem is used to connect to the ISP, and a router provides both wired and wireless connectivity within the home. The router assigns IP addresses to devices on the home network, allowing them to communicate with each other and the internet. Fiber junction boxes are used by ISPs to manage connections.
Role of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) [2:13]
ISPs connect homes to the broader internet using various technologies. The traffic from a user's machine is routed through the ISP to its destination on the internet. When a user requests a webpage, the request is sent as a packet of information, which travels through different stations to reach the web server. The server then sends the requested page back to the user through a similar path.
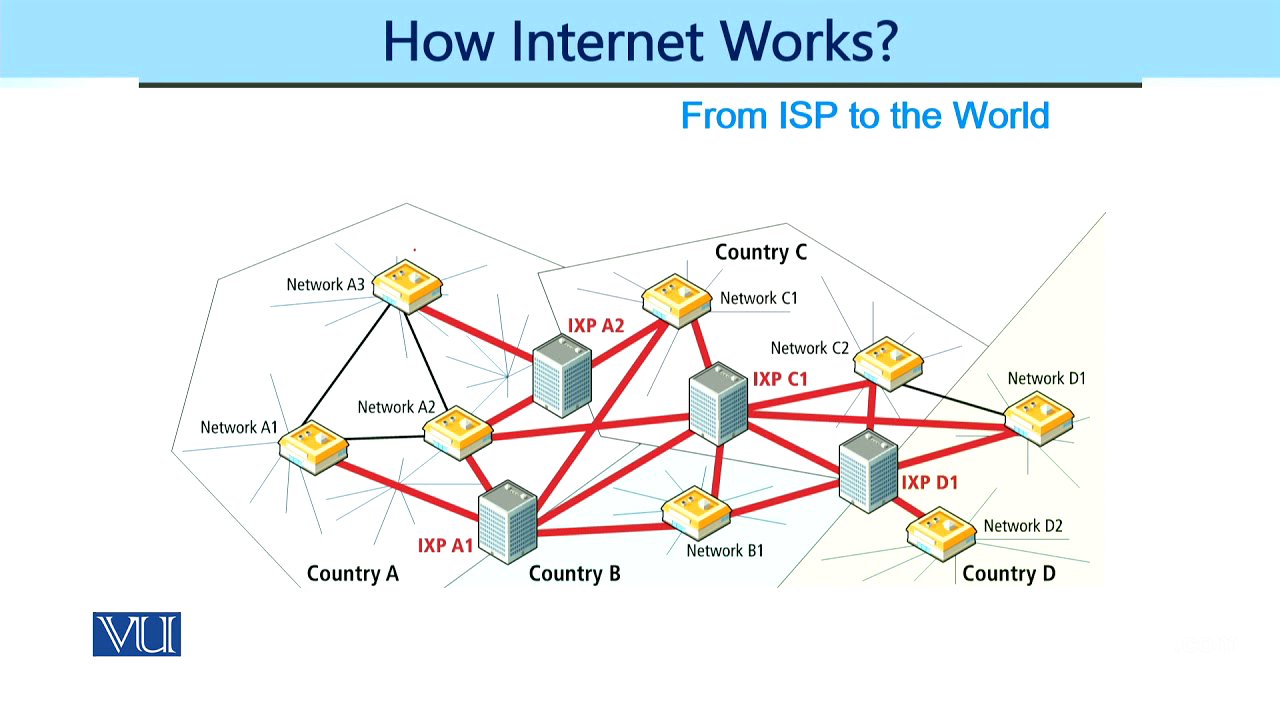
Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) [4:09]
Internet exchange points (IXPs) facilitate the exchange of internet traffic between different networks. These points allow networks to connect directly to each other, reducing the need to route traffic through distant locations. Direct connections or connections through IXPs improve network efficiency and reduce latency. Data centers are often located in close geographical proximity to internet access points to provide faster connectivity and high bandwidth.
Global Internet Connectivity [6:38]
The video highlights the global infrastructure that supports the internet, focusing on fiber optic cables. These cables form the backbone of the internet, providing fast and reliable data transmission across continents. The presenter shows a visual representation of how different countries are connected through these cables, emphasizing their crucial role in enabling global internet connectivity. Internet access points are connected through this high speed internet work.