TLDR;
This video provides an overview of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), explaining its foundational theories and therapeutic processes. It highlights the interconnectedness of emotions, thoughts, and behaviors, and how CBT targets maladaptive thoughts and behaviors to improve psychological well-being. The video also touches on the importance of exploring past experiences to address core beliefs and coping mechanisms for sustained remission of symptoms.
- CBT helps identify and correct maladaptive thoughts and behaviors.
- Emotions, thoughts, and behaviors are interconnected.
- CBT targets thoughts and behaviors, addressing core beliefs and coping mechanisms.
Introduction to CBT [0:00]
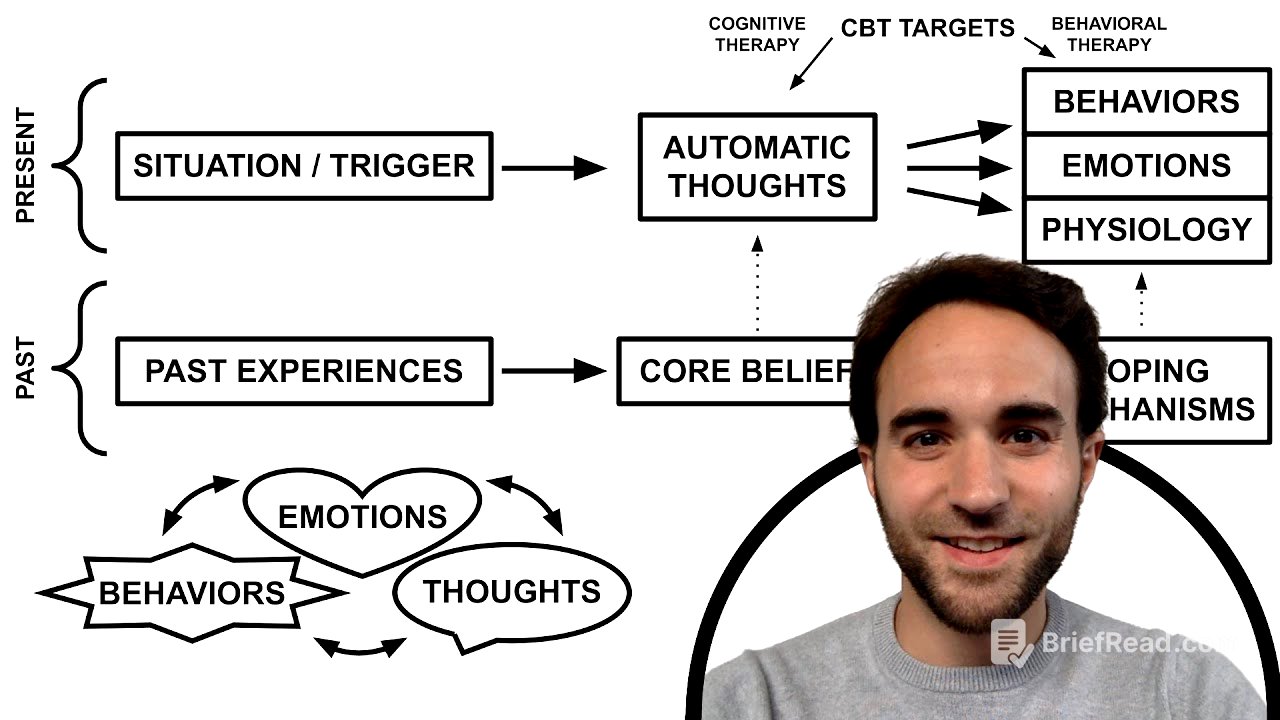
The video introduces Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) as a psychotherapy approach focused on identifying and correcting maladaptive thoughts and behaviors. It promises to explain the basics of CBT theories and therapeutic processes using simple frameworks. The core principle of CBT is that emotions influence thoughts, thoughts influence behaviors, and behaviors influence emotions, creating a cycle.
The Interplay of Emotions, Thoughts, and Behaviors [0:18]
The video explains how situations trigger automatic thoughts, which are quick, evaluative thoughts that arise spontaneously. These thoughts then lead to behaviors, emotions, and physiological changes. For example, a presentation at work can trigger thoughts of success or failure, leading to different emotional states and behaviors like socializing or isolating. While one cannot change the initial situation or directly alter emotions, CBT focuses on modifying thoughts and behaviors in response to the situation.
Cognitive vs. Behavioral Therapy [1:37]
CBT has two main routes: cognitive therapy and behavioral therapy. Cognitive therapy centers on understanding and changing thoughts, while behavioral therapy focuses on understanding and changing behaviors. Addressing thoughts and behaviors in the present can be sufficient for some patients to resolve their problems and alleviate psychological symptoms.
The Role of Past Experiences and Core Beliefs [1:56]
For many patients, exploring past experiences is crucial to address the root of their problems and ensure lasting symptom relief. Important or repeated past experiences lead to the development of core beliefs, which are enduring understandings of oneself, others, and the world. These beliefs are often resistant to change and may be unconscious, influencing a person's thoughts, behaviors, and coping mechanisms. Core beliefs influence automatic thoughts, and coping mechanisms manifest as typical behavior patterns. Modifying maladaptive thoughts or behaviors often requires understanding and modifying the underlying core beliefs and coping mechanisms.
CBT Logistics and Therapeutic Alliance [3:15]
CBT typically involves weekly, structured sessions with a therapist, focusing on a specific problem. Techniques used include record-keeping of thoughts and behaviors, problem-solving, and guiding the patient to better self-understanding. Patients often complete homework assignments between sessions. Therapy duration can range from six weeks to years, depending on the problem's depth. Forming a strong therapeutic alliance between the therapist and patient is essential for successful treatment.
![If I Were to Start Freelancing In 2025, This is What I'd Do [0 to $100K FULL GUIDE]](https://wm-img.halpindev.com/p-briefread_c-10_b-10/urlb/aHR0cDovL2ltZy55b3V0dWJlLmNvbS92aS9jcnpFcHFLQzdpOC9ocWRlZmF1bHQuanBn.jpg)







