TLDR;
This video introduces the fundamental concepts of the Entity-Relationship (ER) model, focusing on entities and attributes. It explains different types of attributes, including composite, simple, single-valued, multi-valued, derived, stored, and complex attributes. The video also covers null values, entity types, entity sets, key attributes, and value sets, providing a comprehensive overview of the basic terminologies used in ER modeling.
- Entities are real-world objects with independent existence.
- Attributes are properties that describe entities.
- Different attribute types help in accurately modeling data.
Introduction to ER Model [0:06]
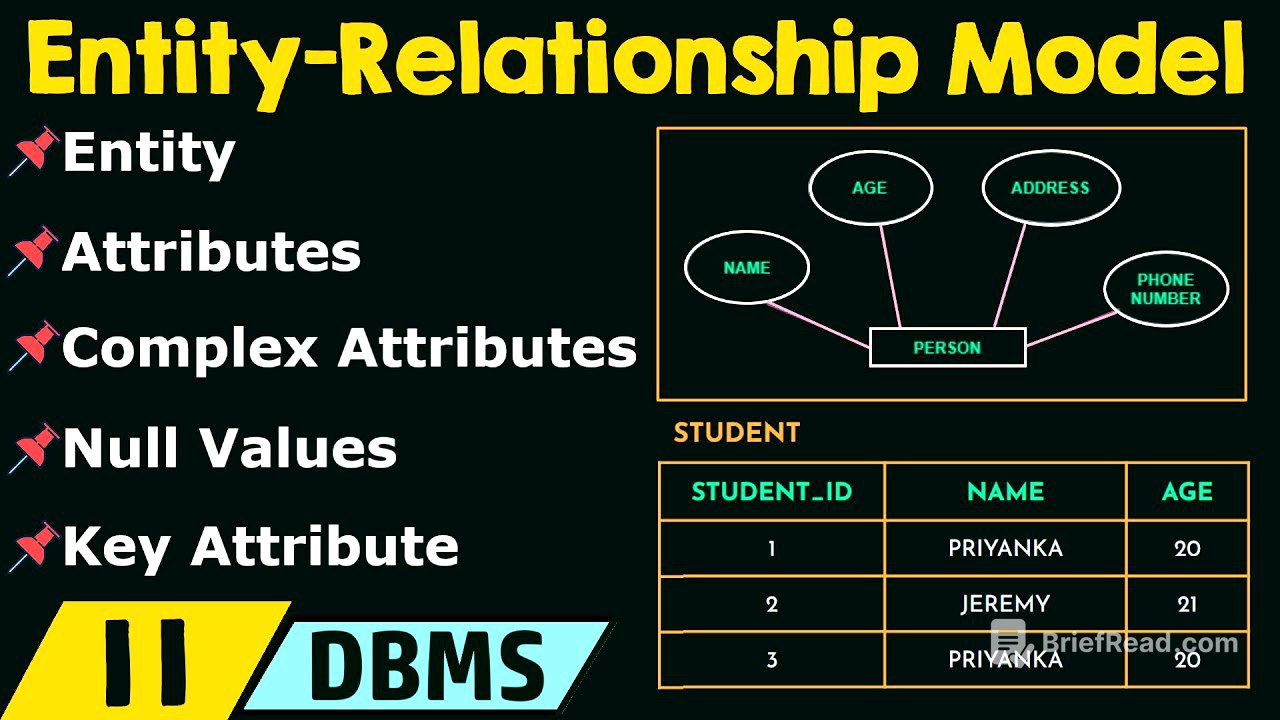
The Entity-Relationship (ER) model describes data using entities, attributes, and relationships. This video focuses on entities and attributes, with relationships to be covered later. An entity is a real-world object with an independent existence, possessing its own identity and being easily identifiable. Entities can be physical, like a house, person, or employee, or conceptual, like a course or job.
Types of Attributes [1:15]
Attributes are properties that describe entities. There are several types of attributes in the ER model: Composite attributes can be divided into further parts, such as a name being divided into first name, middle name, and last name. Simple attributes cannot be divided further, like weight, salary, or age. Single-valued attributes have a single value for an entity, such as age. Multi-valued attributes can have a set of values for an entity, such as college degrees or languages known. Derived attributes can be derived from other attributes, like age derived from date of birth. Stored attributes are those from which the value of other attributes are derived, such as date of birth.
Complex Attributes [4:07]
A complex attribute combines multi-valued and composite components. Multi-valued attributes are represented within curly brackets, while composite attributes are represented within round brackets or parentheses. An example is college degrees {degree1 (major, university), degree2 (major, university)}, where college degrees is multi-valued, and each degree has composite attributes like major and university.
Null Values [4:54]
A null value indicates something that is not applicable or unknown. Null values can mean "not applicable," such as a college degree attribute for someone without a degree, or "unknown," such as when a phone number is not known. The "unknown" category can be further classified into cases where the value exists but is missing (e.g., age of Joshua) or when it is not known if the value exists or not (e.g., whether Jeremy has a phone number).
Entity Type and Entity Set [6:27]
An entity type is a collection of entities that share the same attributes, such as "student." An entity set is a collection of entities of a particular entity type at a specific point in time, such as students whose age is between 19 and 23.
Key Attribute and Value Set [7:17]
A key attribute is an attribute that uniquely identifies each entity, such as a student's role number. The value set of attributes is the set of values that can be assigned to a particular attribute. For example, if the allowed age range for an employee is between 22 and 60, the value set for the age attribute is a set of integer numbers between 22 and 60.