TLDR;
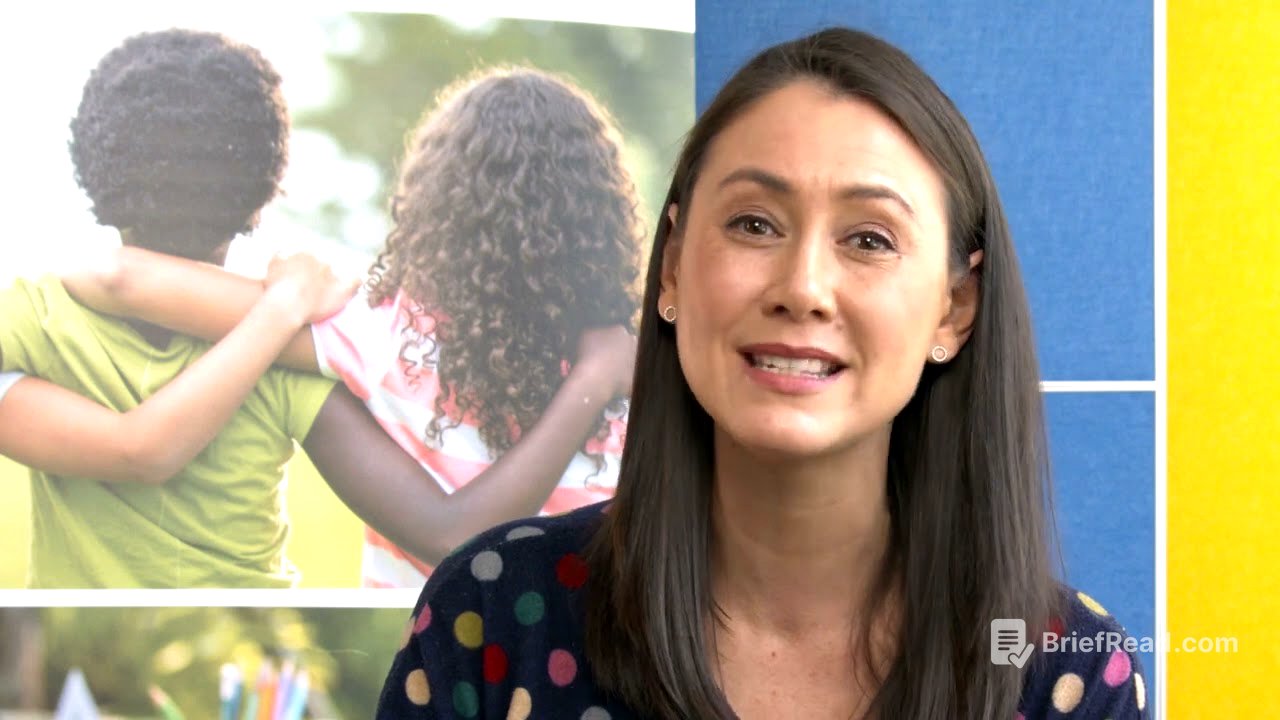
This video provides an overview of Victoria's Child Safe Standards, emphasizing their importance in creating a safe environment for children within organizations. It highlights the 11 updated standards that came into effect on July 1, 2022, and what organizations need to do to comply with them. The video also includes insights from the Commission's Youth Council on what safety in organizations looks and feels like to them.
- Importance of implementing Child Safe Standards to prevent child abuse in organizational settings.
- Overview of the 11 Child Safe Standards and their alignment with the National Principles for Child Safe Organizations.
- Key terms and definitions related to child safety, including abuse and the definition of a child or young person.
Introduction to Child Safe Standards [0:07]
Liana Buchanan, the Principal Commissioner for Children and Young People, introduces a video about Victoria's Child Safe Standards. The video will cover child safety in organizations, the 11 Child Safe Standards, and compliance requirements. It will also feature insights from the Commission's Youth Council on organizational safety. Viewers are encouraged to consult the Commission's website for detailed guides and to seek support if needed due to the sensitive nature of the topic.
Importance of Implementing Child Safe Standards [1:48]
Implementing Child Safe Standards is crucial to prevent child abuse in organizations. Past inquiries have revealed widespread harm to children in organizational settings lacking adequate safeguards. The Royal Commission into Institutional Responses to Child Sexual Abuse heard from over 8,000 survivors. While most people working with children have good intentions, it's easy to become complacent and not address potential risks. Implementing these standards fosters a culture that values child safety, clarifies appropriate behavior, and empowers children to report concerns.
Overview of the Child Safe Standards [4:42]
Victoria introduced mandatory Child Safe Standards in 2016 following the Betrayal of Trust inquiry, and in 2017, the Royal Commission recommended similar schemes nationwide. The 11 updated Standards, effective July 1, 2022, align with the National Principles for Child Safe Organizations. These standards include promoting cultural safety for Aboriginal children and empowering children. Organizations must comply with all aspects of the Standards, with legal consequences for non-compliance. The Commission for Children and Young People helps organizations understand and implement the Standards, with enforcement powers for non-compliance.
Understanding Key Terms [6:15]
Key terms to understand include "abuse," which encompasses sexual abuse, grooming, physical abuse, emotional or psychological harm, and neglect. A "child or young person" refers to someone under 18. The term "Aboriginal" includes Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Most organizations providing services or facilities to children must comply with the Child Safe Standards, ranging from small volunteer groups to national organizations and government departments.
Child Safe Standard 1: Cultural Safety for Aboriginal Children [9:18]
Meena Singh, the Commissioner for Aboriginal Children and Young People, provides an overview of Standard 1, which requires organizations to establish a culturally safe environment where the identities and experiences of Aboriginal children are valued and respected. This involves ensuring Aboriginal children feel safe and proud of their culture, and taking specific steps to create a supportive environment. Organizations should view cultural safety as a long-term journey requiring dedication and engagement with Aboriginal culture and community.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 1 [11:54]
To comply with Standard 1, organizations must meet five minimum requirements:
- Encourage and actively support a child's ability to express their culture and enjoy their cultural rights.
- Embed strategies to acknowledge and appreciate the strengths of Aboriginal culture and understand its importance to the wellbeing and safety of Aboriginal children.
- Adopt measures to ensure racism within the organization is identified, confronted, and not tolerated, with appropriate consequences for any instances of racism.
- Actively support and facilitate participation and inclusion within the organization by Aboriginal children, young people, and their families.
- Ensure all policies, procedures, systems, and processes create a culturally safe and inclusive environment that meets the needs of Aboriginal children, young people, and their families.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 1 [17:45]
Members of the Youth Council share their perspectives on what indicates an organization acknowledges and respects Aboriginal culture, such as displaying Aboriginal flags and having Aboriginal staff in various roles. They also discuss how to identify an organization's commitment to stamping out racism, including having policies in place and addressing incidents immediately and respectfully. The challenge for organizations is to understand the diversity of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people and continue the dialogue with indigenous peoples.
Child Safe Standard 2: Organizational Leadership, Governance, and Culture [19:04]
To meet the requirements of Child Safe Standard 2, organizations must embed child safety and wellbeing in organizational leadership, governance, and culture. This standard sets the foundation for an organization's child safety system, requiring leaders who champion child safety, governance arrangements and policies that support child safety, and a culture that embeds child safety considerations into every part of the organization.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 2 [19:40]
To comply with Standard 2, organizations must meet six minimum requirements:
- Make a public commitment to child safety.
- Champion and model a child-safe culture at all levels of the organization.
- Implement governance arrangements that facilitate the Child Safety and Wellbeing Policy at all levels.
- Establish a Code of Conduct that provides guidelines for staff and volunteers on expected behavioral standards and responsibilities.
- Implement risk management strategies that focus on preventing, identifying, and mitigating risks to children and young people.
- Ensure staff and volunteers understand their obligations regarding information sharing and record keeping.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 2 [26:25]
Youth Council members discuss how an organization can demonstrate that they take child safety seriously by adopting a whole organizational approach, ensuring every employee and stakeholder is aware of the processes and practices in place. They also share their expectations for leaders, including making sure that everything the organization does revolves around children and young people, and regularly engaging with them through formal and informal conversations. The challenge for organizations is to regularly review their practices and policies surrounding child safety, ensuring genuine engagement with young people.
Child Safe Standard 3: Empowering Children and Young People [28:31]
Under Child Safe Standard 3, organizations must ensure that children and young people are empowered, have information about their rights, participate in decisions affecting them, and are taken seriously. This involves creating a culture where children feel confident to report problems, building their skills and knowledge, informing them about their rights, and listening to their views.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 3 [30:02]
To comply with Standard 3, organizations must meet six minimum requirements:
- Inform children and young people about all of their rights, including the right to safety.
- Recognize the importance of friendships and encourage support from peers to help children and young people feel safe and be less isolated.
- Offer access to sexual abuse prevention programs and relevant related information in an age-appropriate way.
- Ensure staff and volunteers are attuned to the signs of harm and facilitate child-friendly ways for children and young people to express their views, participate in decision-making, and raise their concerns.
- Implement strategies to develop a culture that facilitates participation and is responsive to the input of children and young people.
- Provide opportunities for children and young people to participate and are responsive to their contributions, thereby strengthening confidence and engagement.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 3 [36:29]
Youth Council members discuss the impact of not being involved in decisions that affect them, emphasizing the importance of considering every demographic that an issue affects. They suggest making participation regular, creating a discussion-based environment, and involving multiple young people to provide a sense of comfort and familiarity. Organizations should also inform children and young people about what has been done with their opinions and how it has contributed to the work that they do.
Child Safe Standard 4: Involving Families and Communities [38:19]
For Child Safe Standard 4, organizations must ensure families and communities are informed and involved in promoting child safety and wellbeing. This involves supporting families and communities to play a part in the organization's approach to child safety, making them aware of what makes organizations child safe, and informing them what to do if they are concerned about a child's safety or wellbeing.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 4 [39:22]
To comply with Standard 4, organizations must meet four minimum requirements:
- Ensure families participate in decisions affecting their child.
- Engage and openly communicate with families and the community about its child-safe approach, and ensure relevant information is accessible.
- Ensure families and communities have a say in the development and review of the organization's policies and practices.
- Inform families, carers, and the community about the organization's operations and governance.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 4 [42:15]
Youth Council members emphasize the importance of involving families and communities in organizations, as families help young people access services and provide a sense of familiarity and safety. They suggest informing families about what the organization does, providing accessible information, and creating opportunities for dialogue and questions.
Child Safe Standard 5: Equity and Diverse Needs [43:59]
Under Child Safe Standard 5, organizations must ensure that equity is upheld and diverse needs are respected in policy and practice. This involves understanding that each child has unique abilities, skills, and life experiences, and that differences in backgrounds, characteristics, personality, and beliefs shape how a child experiences the world and what they need.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 5 [45:57]
To comply with Standard 5, organizations must meet four minimum requirements:
- Ensure the organization, including staff and volunteers, understands children and young people's diverse circumstances and provides support and response to those who are vulnerable.
- Ensure children and young people have access to information, support, and complaints processes in ways that are culturally safe, accessible, and easy to understand.
- Pay particular attention to the needs of children and young people with disability, children and young people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds, those who are unable to live at home, and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and intersex children and young people.
- Pay particular attention to the needs of Aboriginal children and young people and provides and promotes a culturally safe environment for them.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 5 [49:21]
Youth Council members discuss what a safe place to be yourself feels like, emphasizing the importance of not being judged and being able to relax and do what needs to be done without pressure. They also provide examples of when an organization responded well to support diverse children, such as using closed captions on Zoom calls and including pronouns.
Child Safe Standard 6: Suitable Staff and Volunteers [50:29]
Under Child Safe Standard 6, organizations must ensure that people working with children and young people are suitable and supported to put child safety and wellbeing values into practice. This involves having policies and procedures to make sure staff and volunteers are suitable to work with children, strong recruitment practices, and comprehensive induction and ongoing support and supervision.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 6 [51:27]
To comply with Standard 6, organizations must meet four minimum requirements:
- Ensure recruitment, including advertising, referee checks, and staff and volunteers pre-employment screening, emphasizes child safety and wellbeing.
- Ensure relevant staff and volunteers have current working with children checks or equivalent background checks.
- Ensure all staff and volunteers receive an appropriate induction and are aware of their responsibilities to children and young people, including record keeping, information sharing, and reporting obligations.
- Ensure ongoing supervision and people management is focused on child safety and wellbeing.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 6 [55:10]
Youth Council members discuss the ideal qualities of a staff member or volunteer who works with children, including patience, kindness, and respect. They also share ideas about how children's feedback can be obtained about staff, such as having conversations with them and asking them questions about how they're feeling.
Child Safe Standard 7: Child-Focused Complaints and Concerns Processes [56:34]
Standard 7 requires organizations to ensure that processes for complaints and concerns are child-focused. This involves having a positive complaints culture, encouraging and welcoming reported concerns, responding promptly and thoroughly, and taking immediate action to protect children from risk.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 7 [57:49]
To comply with Standard 7, organizations must meet five minimum requirements:
- Have an accessible child-focused complaint handling policy that clearly outlines the roles and responsibilities of leadership, staff, and volunteers, approaches to dealing with different types of complaints, breaches of relevant policies, or the code of conduct, and obligations to act and report.
- Ensure effective complaint handling processes are understood by children and young people, families, staff, and volunteers, and are culturally safe.
- Ensure complaints are taken seriously and responded to promptly and thoroughly.
- Have policies and procedures in place that address reporting of complaints and concerns to relevant authorities, whether or not the law requires reporting, and cooperates with law enforcement.
- Ensure reporting, privacy, and employment law obligations are met.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 7 [1:03:26]
Youth Council members discuss what children and young people need to know in order to make a complaint, including knowing that they're allowed to make a complaint, who to go to, what processes are involved, and that their concerns will be taken seriously. They also share how children and young people should be responded to if they raise a complaint, emphasizing the importance of validating their concerns and rectifying the situation respectfully and promptly.
Child Safe Standard 8: Ongoing Education and Training [1:04:25]
To meet the requirements of Child Safe Standard 8, organizations must ensure that their staff and volunteers are equipped with the knowledge, skills, and awareness to keep children and young people safe through ongoing education and training. This involves providing comprehensive and continuous training to uphold child-safe values and report concerns effectively.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 8 [1:05:31]
To comply with Standard 8, organizations must meet four minimum requirements:
- Ensure staff and volunteers are trained and supported to effectively implement the organization's Child Safety and Wellbeing Policy.
- Ensure staff and volunteers receive training and information to recognize indicators of child harm, including harm caused by other children and young people.
- Ensure staff and volunteers receive training and information to respond effectively to issues of child safety and wellbeing and support colleagues who disclose harm.
- Ensure staff and volunteers receive training and information on how to build culturally safe environments for children and young people.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 8 [1:09:02]
Youth Council members discuss the information staff and volunteers need to know to help keep children safe from abuse, including policies in place and transparent escalation processes. They also share what staff and volunteers need to know to support children who disclose they are feeling unsafe, such as training in mental health first aid and referring them to the right support services.
Child Safe Standard 9: Physical and Online Safety [1:10:59]
Overall, the outcome for Standard 9 is that physical and online environments promote safety and wellbeing while minimizing the opportunity for children to be harmed. This standard focuses on the identification and management of risk as an important way for your organization to prevent child abuse and harm.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 9 [1:12:06]
To comply with Standard 9, organizations must meet four minimum requirements:
- Staff and volunteers identify and mitigate risks in the online and physical environments without compromising a child's right to privacy, access to information, social connections, and learning opportunities.
- The online environment is used in accordance with the organization's Code of Conduct and Child Safety and Wellbeing Policy and practices.
- Risk management plans consider risks posed by organizational settings, activities, and the physical environment.
- Organizations that contract facilities and services from third parties have procurement policies that ensure the safety of children and young people.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 9 [1:19:17]
Youth Council members discuss how to determine if an organization takes the safety of children seriously, including visible signs such as up-to-date child safety policies and the embedded culture of the organization. They also share ways children can have a say about what makes them feel safe or unsafe, such as asking them about the child-safe policy and acting on their feedback.
Child Safe Standard 10: Regular Review and Improvement [1:19:38]
Under Standard 10, organizations must ensure that the implementation of the Child Safe Standards is regularly reviewed and improved. This involves ongoing commitment, effort, and regularly reviewing the organization's child-safe policies, procedures, and practices.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 10 [1:20:14]
To comply with Standard 10, organizations must meet three minimum requirements:
- Regularly review, evaluate, and improve child-safe practices.
- Analyze complaints, concerns, and safety incidents to identify causes and systemic failures to inform continuous improvement.
- Report on the findings of relevant reviews to staff and volunteers, community and families, and children and young people.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 10 [1:22:57]
Youth Council members discuss how children can be involved in reviewing an organization's child-safe practices, such as including them in the actual review process and asking them what needs to be improved and what the organization is working well at.
Child Safe Standard 11: Policies and Procedures [1:23:52]
Under Standard 11, organizations must demonstrate that policies and procedures document how the organization is safe for children and young people. This involves having clear policies and procedures that help everyone know what should happen and what they should do.
Minimum Requirements for Child Safe Standard 11 [1:24:20]
To comply with Standard 11, organizations must meet five minimum requirements:
- Ensure policies and procedures address all Child Safe Standards.
- Ensure policies and procedures are documented and easy to understand.
- Ensure best practice models and stakeholder consultation inform the development of policies and procedures.
- Ensure leaders champion and model compliance with policies and procedures.
- Ensure staff and volunteers understand and implement policies and procedures.
Youth Council Insights on Child Safe Standard 11 [1:27:29]
Youth Council members discuss what makes a document easy for children and young people to understand, including using child-friendly language and avoiding super content-heavy documents. They also share how to tell whether people in organizations follow policies and procedures about child safety, such as observing how the organization is running and how quickly incidents are rectified.
Conclusion [1:28:47]
The video concludes by thanking viewers and expressing hope that the information provided has been useful in understanding the Child Safe Standards and the role organizations play in keeping children safe. The Commission and other regulators offer resources to assist in building a child-safe organization, and viewers are encouraged to check relevant websites and register for Commission updates.