TLDR;
The video gives a detailed look at the incredible journey of life, starting from the microscopic world of sperm and egg to the formation of a new human being. It highlights the challenges sperm face, the moment of fertilization, and the initial cell divisions that lead to the embryo implanting in the uterus.
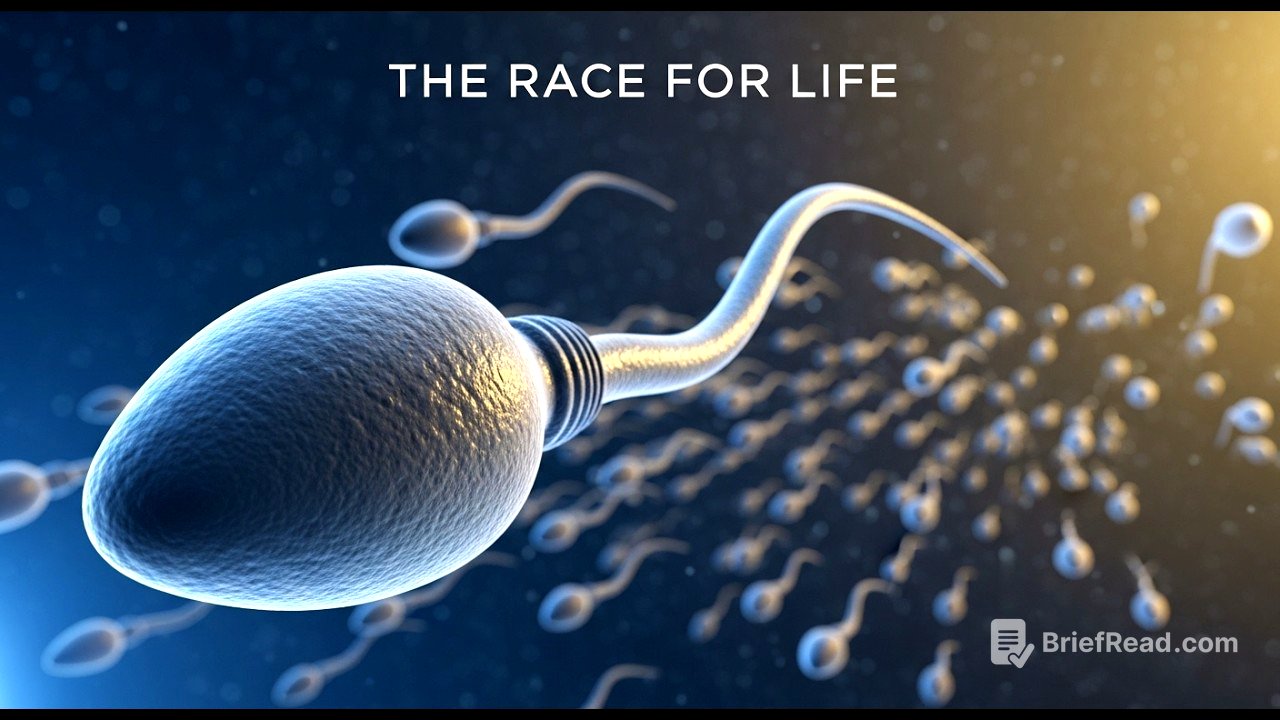
- The journey of millions of sperm to reach the egg.
- The process of fertilization and the formation of the zygote.
- The initial cell divisions and the development of the blastocyst.
- Implantation in the uterus and the beginning of pregnancy.
The Great Race Begins [0:00]
The video starts with the beginning of life, focusing on the journey of sperm cells. Millions of sperm cells start their race to find the egg, each carrying half of the genetic code. This race is not just about speed or strength, but also about endurance, precision, and a bit of luck. The journey starts with the release of over 300 million sperm, all propelled by energy and instinct.
Barriers and Challenges [2:05]
The journey through the female body is full of challenges. The sperm first encounter the cervical mucus, which acts as a filter, blocking weak or abnormal sperm. The uterus is like a battlefield where the female immune system attacks most sperm as foreign invaders. Chemical gradients guide the survivors towards the fallopian tubes, but the environment remains hostile, eliminating nearly all but a few hundred of the strongest sperm.
The Final Destination: The Egg [3:12]
After surviving many barriers, the remaining sperm reach the fallopian tube, the final stage of their journey. Fluid currents guide them towards the egg. Inside the tube, cilia help transport both sperm and egg. The sperm gather around the egg, each searching for the right spot to make contact. Only one will break through the egg's defenses.
The Moment of Fertilization [4:10]
When a sperm makes contact with the egg's outer layer, the zona pellucida, the acrosome reaction begins. Enzymes are released, dissolving a path through the egg's protective coating. Only one sperm finds the perfect match, and its membrane fuses with the egg's membrane. Electrical changes prevent other sperm from entering. The sperm's nucleus travels to the egg's core, carrying half the genetic code, marking the true beginning of new life.
The Zygote: The First Cell [5:12]
Inside the egg, the sperm's nucleus moves towards the egg's nucleus. Each carries 23 chromosomes, and they unite to form a single genetic blueprint, creating the zygote, the first cell of a new human. This cell contains every trait and potential of the future human being.
Cell Division and Early Development [6:14]
The zygote's genetic material organizes, and the chromosomes pair up. The cell prepares to copy its DNA for the first time. The zygote then divides into two identical cells, each with 46 chromosomes. These two become four, then eight, forming a cluster of cells called the morula. The embryo remains protected within the zona pellucida as it travels towards the uterus.
The Blastocyst and Implantation [8:13]
As the cells divide, a hollow sphere called the blastocyst forms. Inside, a group of cells will become the embryo, while the outer layer will form the placenta. The blastocyst drifts down the fallopian tube and, around the fifth day, emerges from the zona pellucida and attaches to the uterine lining. This implantation marks the beginning of pregnancy, and from here, all organs and systems will develop.
The Miracle of Life [9:12]
From a single fertilized cell, a new human journey begins. The embryo attaches to the uterus, where cells multiply and specialize. Every heartbeat and breath can be traced back to this moment, the union of two cells creating something new. Life emerges as complex, delicate, and miraculous.



![FREE MOVIE [Survival Suspense Horror FULL Movies by 412A TV] full length movie](https://wm-img.halpindev.com/p-briefread_c-10_b-10/urlb/aHR0cDovL2ltZy55b3V0dWJlLmNvbS92aS9La3NjUzJyZ0kyVS9ocWRlZmF1bHQuanBn.jpg)